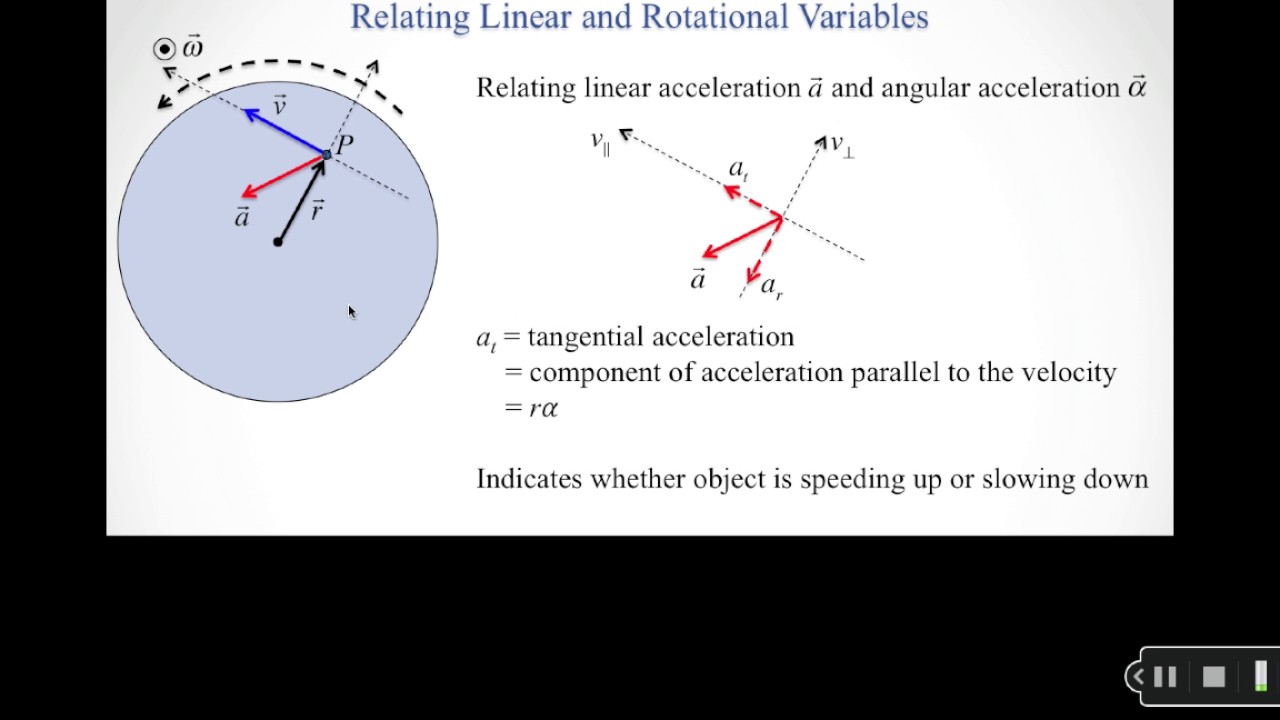
We Offer a Wide Range of Linear and Rotary Motion Components for All Industries. Learn More About Our Products or Speak to One of Our Engineers Today! It is a linear acceleration in a direction tangent to the circle at the point of interest in circular or rotational motion. Remember that tangential acceleration is parallel to the tangential velocity (either in the same direction or in the opposite direction.)
PPT Rotational Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID814209
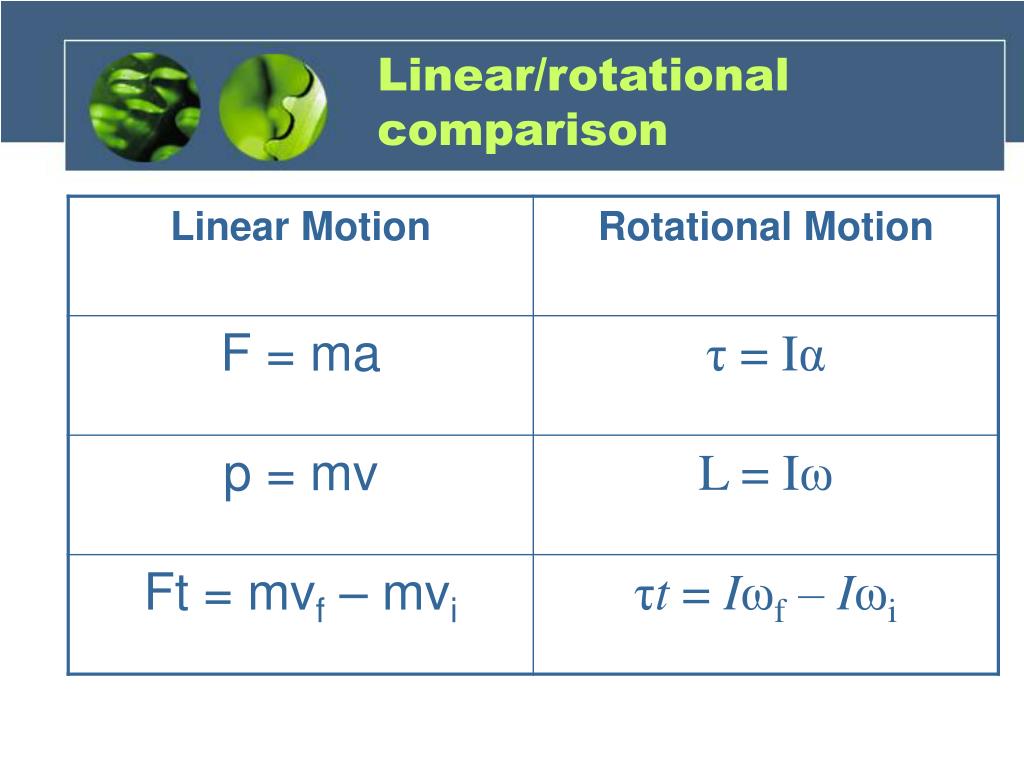
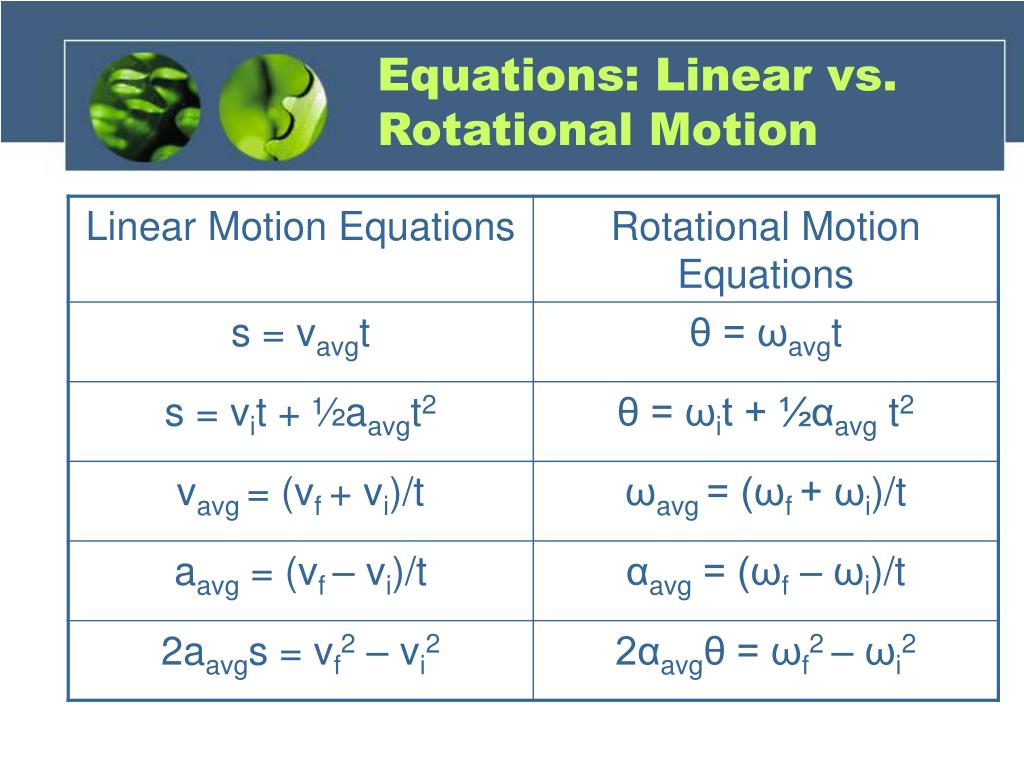
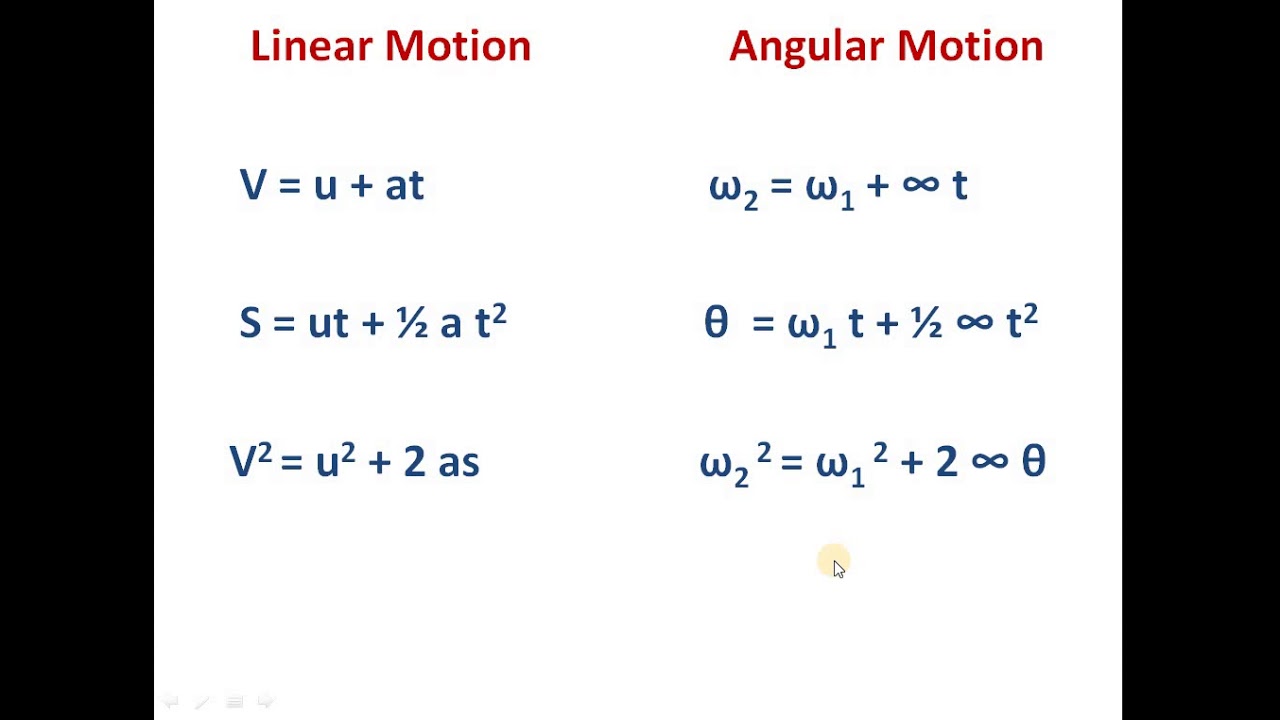
Axis of rotation. The imaginary or actual axis around which an object may rotate. Average angular acceleration ( α. . ) Measure of how angular velocity changes over time. The rotational analogue of linear acceleration. A vector quantity with counterclockwise defined as the positive direction. SI units of radians s 2. Difference between Linear Motion and Rotational Motion Linear motion is on a straight road, whereas rotational motion is along a rotational axis. Before looking at the comparison between linear motion and rotational motion, let us look into some more detailed differences between both types of motion: View more Rotary to Linear Motion 5 min read A slider-crank mechanism is a typical design which converts rotary motion into linear motion. It is achieved by connecting a slider and a crank with a rod. This mechanism is also utilized as a system that converts the reciprocating linear motion of an automobile engine into rotary motion. (Fig a) motion. The four types of motion are: linear rotary reciprocating oscillating Linear motion moves something in a straight line, eg a train moving down a track: Rotary motion is.
PPT Rotational Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID814209
Linear actuators are usually used in applications where loads need to be pushed, pulled, lifted, lowered, positioned, or rotated. Such movements are often required in the following industries: Food processing and packaging Automotive Material handling Factory automation Defense Aerospace Pharmaceutical and medicine devices Clean energy Printing Types of Linear motion along with Rotary motion and Oscillatory motion are also described. Below are some examples to have a clear understanding of uniform motion and nonuniform motion. Eg: If a car is traveling at a speed of 50 km/hour then it will cover a distance of 1 km/minute. In this sense, the motion of car acceleration is uniform. Design Essentials: How to Convert from Rotary to Linear Motion | Machine Design 3D Printing & CAD AUTOMATION & IIOT MISUMI Automation helps us examine different examples of mechanisms that. Linear motion occurs when sufficient force is applied in line with the book's center of gravity, and a combination of linear and rotary motion results from a force directed left or right of center. Similarly, an object with a fixed axis, like a door or one of the body's limbs, rotates when the force is applied off center but does not rotate.
Relating linear and rotational motion YouTube
We can apply the definition of power derived in Power to rotational motion. From Work and Kinetic Energy, the instantaneous power (or just power) is defined as the rate of doing work, P = dW dt. If we have a constant net torque, Equation 10.8.4 becomes W = τθ and the power is. P = dW dt = d dt(τθ) = τdθ dt. 1. Both the linear stroke and the rotation of the closing spindles are derived and synchronized purely mechanically from the rotary motion of the carousel using cam disks (linear stroke) and gears with a magnetic clutch (rotation). 2. A servomotor is used for the rotation and is moved up and down.
2 Hi, have you heard something about linear actuators? there are tons of ways that convert linear to rotary motion, take a look at this video, if you still have questions then we are here. - user14407 Nov 4, 2018 at 22:23 Suggested a simple device called a cam, but obviously that was not liked by a downvoter. - Solar Mike Nov 15, 2018 at 13:34 1.) The motion of object along the straight line is known as linear motion. Eg. Motion of children doing cycling, cars running on road etc. 2.) The distance travelled by object is always measured as straight line. 3.) If the starting point and ending point of motion is along a same straight path, then the magnitude of distance is equal to that.
Linear and Rotary Motion YouTube
Linear motion is defined as a change in an object's position regarding a period. We live in a constantly changing universe. The simplest particle of matter, the atom, is also constantly moving. All physical activities in the universe involve motion in some way. Motion might be quick or slow, but motion is always present. These approaches might include the selection of a smaller more power-dense product; lightweighting the rolling elements in linear and rotary bearings; and drilling extra holes (between the mounting holes) in linear rails. IKO's ML Series is an example of a standard stainless-steel linear motion guide incorporating rolling bearing elements.




