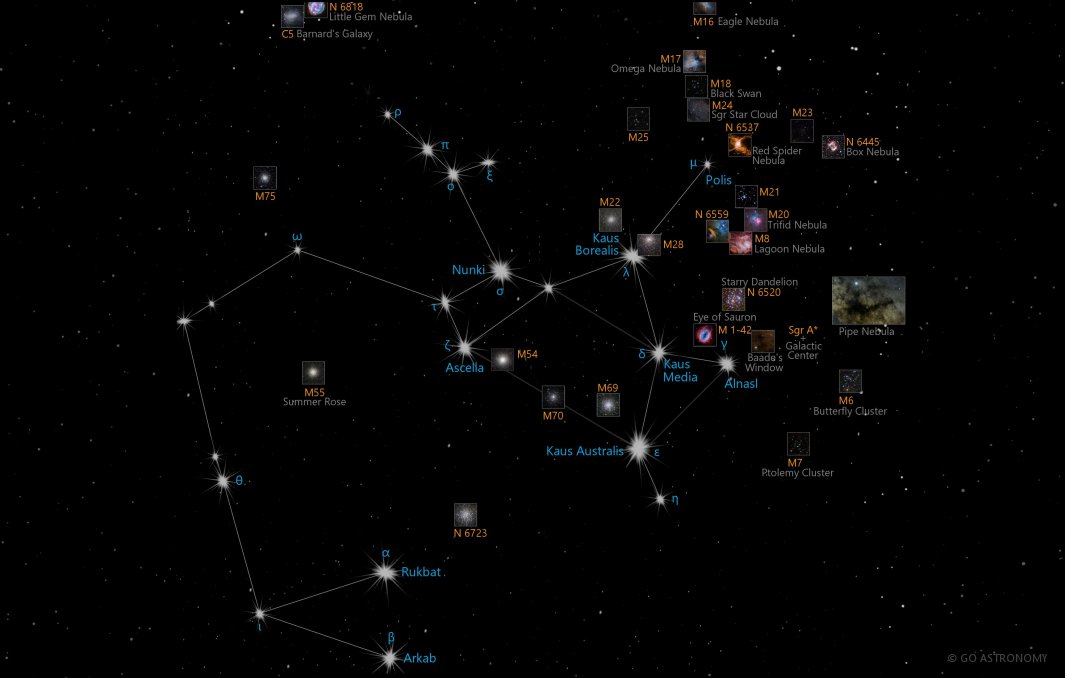
Facts, location and map Sagittarius is the 15th largest constellation in the sky. It occupies an area of 867 square degrees. It is located in the fourth quadrant of the southern hemisphere (SQ4) and can be seen at latitudes between +55° and -90°. Zodiacal Hemisphere: Southern Quadrant: SQ4 Visibility: 55° N - 90° S Best viewing month*: August Area: 867 sq. degrees Size: 15th largest Right Ascension (avg): 19h 23m Declination (avg): -26° Brightest star: Kaus Australis (1.79) Stars with planets:

Sagittarius the archer zodiac constellation map on a starry space background with the names of
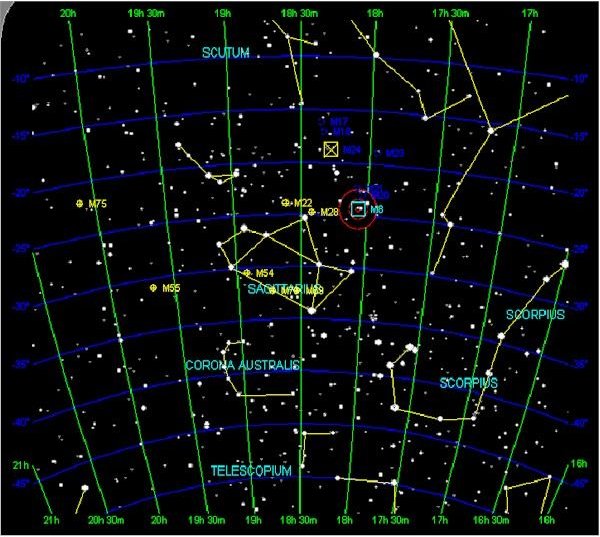
2024-01-10 Stellarium Web is a planetarium running in your web browser. It shows a realistic star map, just like what you see with the naked eye, binoculars or a telescope. Sagittarius famously points its arrow at the heart of Scorpius, represented by the reddish star Antares, as the two constellations race around the sky. Following the direct line formed by Delta Sagittarii (δ Sgr) and Gamma2 Sagittarii (γ 2 Sgr) leads nearly directly to Antares. Sagittarius is positioned along the Milky Way, with the easiest way to locate the constellation by following an imaginary line drawn through the Summer Triangle stars of Deneb (Cygnus) and Altair (Aquila), and prolonging it a similar distance until it terminates at the famous Teapot asterism in Sagittarius. Best Seen: Autumn August 20, 2022 Sagittarius the Archer has a Teapot shape and is the constellation of the zodiac that contains the center of the Milky Way. If you live far enough south, you may spot the arcing.
Sagittarius Constellation Star Map & Facts Go Astronomy
SKY MAP: The stars of Sagittarius as of 10:30 p.m. local time from mid-northern latitudes. (Image credit: Starry Night Software) On these mid-summer evenings after the sun has set, look low. Sagittarius Star Map. IUA and Sky and Telescope. The arrow is pointed at the heart of Scorpius. The neighboring constellations include Aquila, Capricornus, Indus, Microscopium, and Scutum. Moreover, Sagittarius' brightest stars also form a pattern of a teapot. Sagittarius is a large southern constellation which spans the declination range δ=12°S to δ=45°S. It appears highest in the evening sky in the months around July. This area of the sky looks directly towards the center of the Milky Way, which is marked by the radio source Sgr A. Notable stars and objects. The constellation's brightest stars — Delta, Epsilon, Zeta, Phi, Lambda, Gamma-2, Sigma and Tau Sagittarii — form a star pattern, or asterism, called the Teapot.
Interesting Facts About The Constellation Sagittarius
Sagittarius A* (pronounced "Sagittarius A-star") is the supermassive black hole at the centre of our galaxy. The Milky Way's central black hole lies at a distance of 26,673 ± 42 light years from Earth in the direction of Sagittarius constellation, near the border with Scorpius. The brightest star in the constellation Sagittarius is called Kaus Australis (or Epsilon Sagittarii). The second-brightest is Sigma Sagittarii, with a common name of Nunki. Sigma (Nunki) was one of the stars that the Voyager 2 spacecraft used for navigation as it was traveling to the outer solar system to study the gas giant planets.
From $ 29 Sagittarius Constellation Map Place your star in Sagittarius! Main Stars in The Archer (Sagittarius) The constellation Sagittarius contains several bright stars that make up its shape. Some of these main stars are known as: Kaus Australis Nunki Kaus Media Kaus Media Rukbat Arkab Ascella Sagittarius is one of 48 constellations created by the ancient astronomer Claudius Ptolemy who lived in the 2nd century Alexandria, Egypt. Sagittarius is a Latin word, and the English translation is Half-Man/Half-Horse Archer. Sagittarius's pronunciation is Sadge-e-tar-e-us.

Sagittarius Printzodiac Print Star Map Printable Art Etsy
A star finder (also known as a planisphere) is a circular map with an overlay that turns to show - through an opening in the overlay - the region of the sky that is visible for a specified time, date and location. "old/ancient star maps", as I understand it, are not about the position of stars in the universe! First, it is not about stars at all.. it is spatially in the constellation of Sagittarius. The reason for this is that the Earth's axis, which is decisive for the seasons, lurches - similar to a spinning top, but very slowly, namely one.




