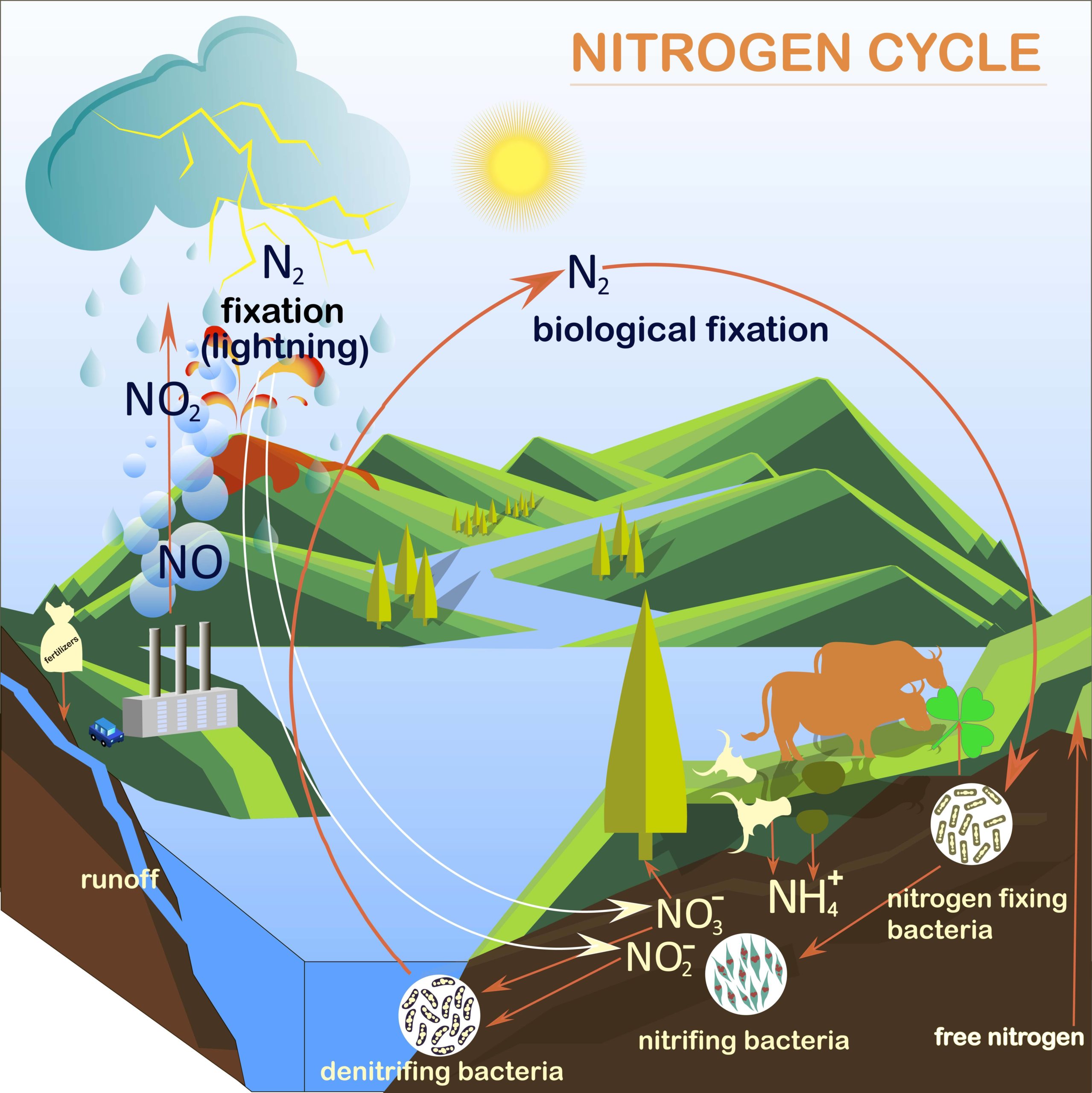
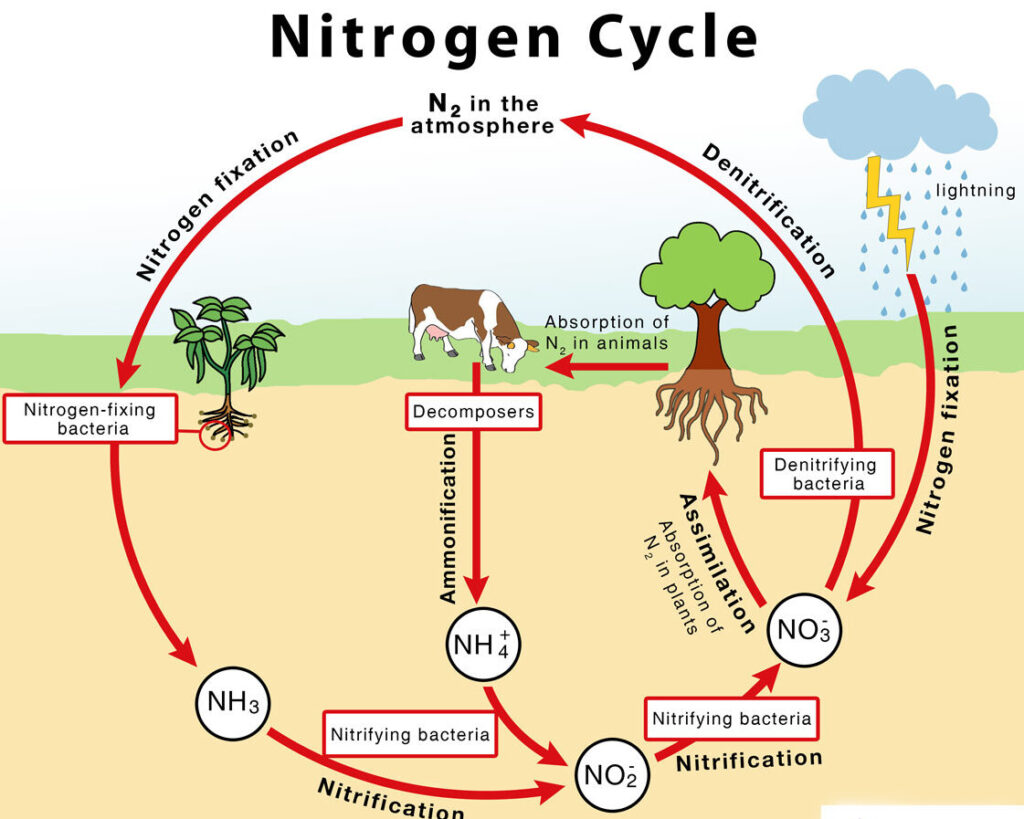
Key points Nitrogen is a key component of the bodies of living organisms. Nitrogen atoms are found in all proteins and DNA . Nitrogen exists in the atmosphere as N 2 gas. In nitrogen fixation, bacteria convert N 2 into ammonia, a form of nitrogen usable by plants. When animals eat the plants, they acquire usable nitrogen compounds. The nitrogen cycle is the cyclic movement of nitrogen in different chemical forms between living organisms and the environment. The steps of the nitrogen cycle are described below. Nitrogen fixation: During this step, atmospheric nitrogen gas is fixed, or converted into a form that can be used by plants and animals.

Nitrogen Cycle QCE Biology Revision
Nitrogen cycle | Ecology | Khan Academy Fundraiser Khan Academy 8.19M subscribers 375K views 7 years ago #YouCanLearnAnything Keep going! Check out the next lesson and practice what. © 2023 Google LLC Introduction to the nitrogen cycleWatch the next lesson: Missed the previous lesson? Watch here: Ecology on Khan Academy: Why are polar bears found only in t. The six most common elements in organic molecules—carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and sulfur—take a variety of chemical forms. They may be stored for long or short periods in the atmosphere, on land, in water, or beneath the Earth's surface, as well as in the bodies of living organisms. The Nitrogen Cycle | A-Level Biology Exam QA 4.53K subscribers Subscribe 80 1.7K views 3 years ago A-Level Biology A-Level The Nitrogen Cycle This video covers The Nitrogen Cycle in-depth and.
What is the Nitrogen Cycle? Science for Kids
We believe learners of all ages should have unlimited access to free educational content they can master at their own pace. We use intelligent software, deep data analytics and intuitive user interfaces to help students and teachers around the world. The Nitrogen Cycle | Environmental Chemistry | Chemistry | FuseSchoolNitrogen is essential to life. Plants and animals need nitrogen to make proteins, which. Hank describes the desperate need many organisms have for nutrients (specifically nitrogen and phosphorus) and how they go about getting them via the nitroge. . El nitrógeno existe en la atmósfera como N 2 gaseoso. Durante la fijación del nitrógeno, las bacterias convierten el N 2 en amoníaco, una forma de nitrógeno que puede ser utilizada por las plantas. Cuando los animales comen plantas, adquieren compuestos nitrogenados que pueden utilizar.
THE NITROGENCYCLE JSIERT
Created in Urdu by Rabiya KulsoomAbout Khan Academy: Khan Academy is a nonprofit with a mission to provide a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. Khan Academy er en nonprofit organisation med en mission om at give en gratis, verdensklasse uddannelse for alle, overalt i verden. Lær gratis om matematik, kunst, computerprogrammering, økonomi, fysik, kemi, biologi, medicin, finans, historie, og meget mere.
The steps involved in the nitrogen cycle include: Stage 1: Nitrogen Fixation. Stage 2: Mineralization. Stage 3: Nitrification. Stage 4: Immobilization. Stage 5: Denitrification. The steps of the. Азотът навлиза в живия свят чрез бактерии и други едноклетъчни прокариоти, които преобразуват атмосферния азот - N 2 — в биологично използваеми форми при процес, наречен азотно фиксиране. Някои видове азотфиксиращи бактерии са свободно-живеещи в почвата или водата, докато други са полезни симбионти, които живеят във вътрешността на растения.

How the Nitrogen Cycle Works Britannica
Prokaryotes and the Nitrogen Cycle. Nitrogen is a very important element for life because it is part of proteins and nucleic acids. It is a macronutrient, and in nature, it is recycled from organic compounds to ammonia, ammonium ions, nitrate, nitrite, and nitrogen gas by myriad processes, many of which are carried out only by prokaryotes.. . Nitrogênio existe na atmosfera como o gás N 2 . Na fixação de nitrogênio, as bactérias convertem N 2 em amônia, uma forma de nitrogênio aproveitável pelas plantas. Quando os animais comem as plantas, eles adquirem compostos de nitrogênio metabolizáveis. Nitrogênio é comumente um nutriente limitante na natureza, e na agricultura.




