Example: Fractional Knapsack, Activity Selection. Divide and Conquer: The Divide and Conquer strategy involves dividing the problem into sub-problem, recursively solving them, and then recombining them for the final answer. Example: Merge sort, Quicksort. Dynamic Programming: The approach of Dynamic programming is similar to divide and conquer. Examples include the following: Search engines rely on algorithms to find and present relevant results as quickly as possible Social media platforms use algorithms to prioritize the content that we see in our feeds, taking into account factors like our past behavior, the popularity of posts, and relevance.
Our presentation on algorithm design
The nine most commonly used algorithm design techniques and the nature of algorithms they help create are: Sorting: Sorting input in an increasing or decreasing order Greedy: Selecting each part of a solution only because it is immediately beneficial Real-life examples that define the use of algorithms: Consider a clock. We know the clock is ticking but how does the manufacturer set those nuts and bolts so that it keeps on moving every 60 seconds, the min hand should move and every 60 mins, the hour hand should move? So to solve this problem, there must be an algorithm behind it. Errata. Here are the known errata in these lecture slides. Special thanks to Pierre Flener, for finding and reporting dozens of errors and suggesting numerous improvements in the presentation. Course Overview: Introduction to fundamental techniques for designing and analyzing algorithms, including asymptotic analysis; divide-and-conquer algorithms and recurrences; greedy algorithms; data structures; dynamic programming; graph algorithms; and randomized algorithms. Required textbook: Kleinberg and Tardos, Algorithm Design, 2005.
Algorithm Design Techniques in DAA StudiousGuy
which translates to: Algorism is the art by which at present we use those Indian figures, which number two times five. The poem is a few hundred lines long and summarizes the art of calculating with the new styled Indian dice ( Tali Indorum ), or Hindu numerals. [19] English evolution of the word[] You might have an algorithm for getting from home to school, for making a grilled cheese sandwich, or for finding what you're looking for in a grocery store. In computer science, an algorithm is a set of steps for a computer program to accomplish a task. Algorithms put the science in computer science. And finding good algorithms and knowing. 1. Brute Force Algorithm: It is the simplest approach for a problem. A brute force algorithm is the first approach that comes to finding when we see a problem. 2. Recursive Algorithm: A recursive algorithm is based on recursion. In this case, a problem is broken into several sub-parts and called the same function again and again. 3. Algorithm Design: Foundations, Analysis, and Internet Examples Read an Excerpt Excerpt 1: (PDF) Excerpt 2: (PDF) Excerpt 3: (PDF) Download Product Flyer Description Related Resources About the Author Permissions Table of contents Extra Features Selected type: Paperback Quantity: Print on Demand $178.95 Add to cart
What is Algorithm Definition, Types and Application EdrawMax
The reader-friendly Algorithm Design Manual provides straightforward access to combinatorial algorithms technology, stressing design over analysis. The first part, Techniques, provides accessible instruction on methods for designing and analyzing computer algorithms. The second part, Resources, is intended for browsing and reference, and. 195K views How Do Algorithms Work? Let's take a closer look at an example. A very simple example of an algorithm would be to find the largest number in an unsorted list of numbers. If you.
. The key to any problem-solving task is to guide your thought process. The most useful thing to do is keep asking 'What if we did it this way?' Exploring different ways of solving a problem can. Greedy algorithms. A greedy algorithm solves an optimization problem by making locally optimal choices at each step. Greedy algorithms typically do not compute globally optimal solutions. In some cases they do (but typically require a non-trivial argument to show why), and in others they can still produce good (but not optimal) results. Familiar examples (all of which do compute globally.

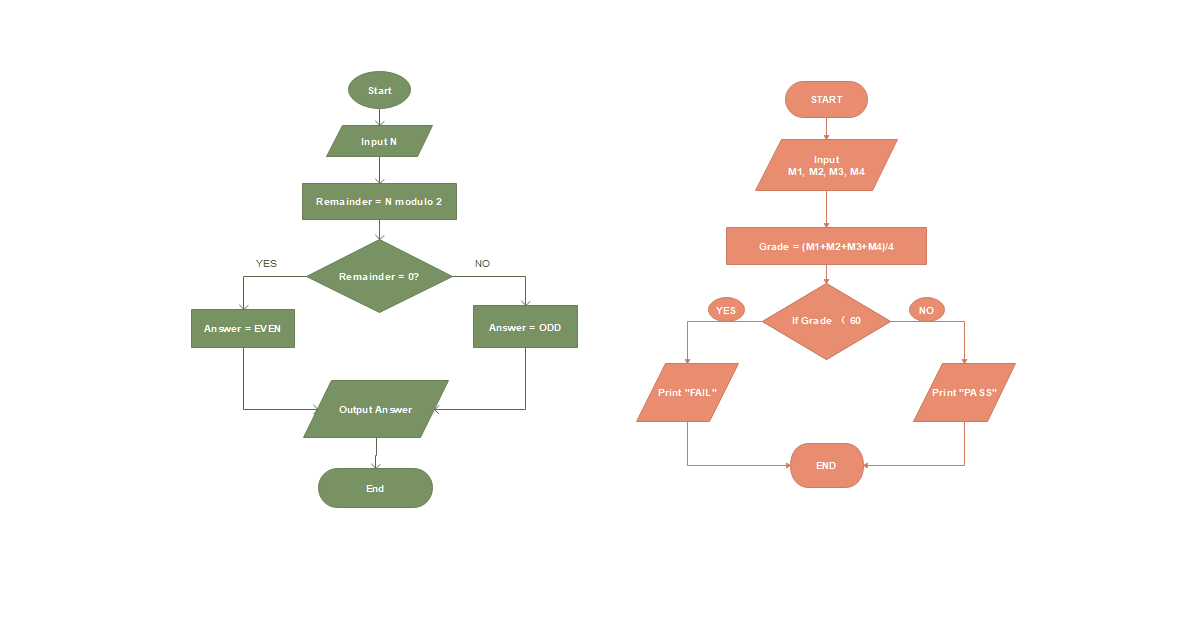
The Basic Algorithm flowchart. Download Scientific Diagram
Algorithm design : foundations, analysis, and Internet examples. Algorithm design : foundations, analysis, and Internet examples by Goodrich, Michael T. Publication date 2011 Topics Computer algorithms, Data structures (Computer science) Publisher New Delhi : Wiley-India Collection printdisabled; internetarchivebooks What is an Algorithm? In computer programming terms, an algorithm is a set of well-defined instructions to solve a particular problem. It takes a set of input (s) and produces the desired output. For example, An algorithm to add two numbers: Take two number inputs Add numbers using the + operator Display the result Qualities of a Good Algorithm




