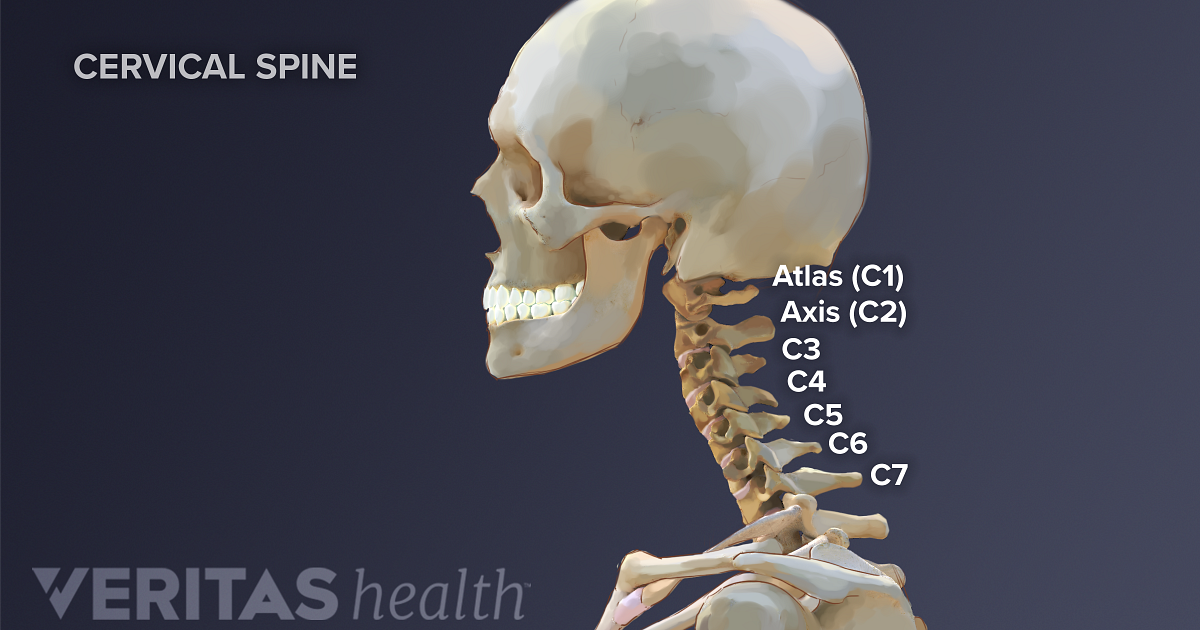
Cervical Spine The neck is part of a long flexible column, known as the spinal column or backbone, which extends through most of the body. The cervical spine (neck region) consists of seven bones ( C1-C7 vertebrae ), which are separated from one another by intervertebral discs. Your seven cervical vertebrae (C1 to C7) are connected at the back of the bone by a type of joint (called facet joints), which allow for the forward, backward and twisting motions of your neck. Your cervical spine is also surrounded by muscles, nerves, tendons and ligaments.

La chirurgie de la colonne vertébrale C4C5 et C5C6 et du col de l
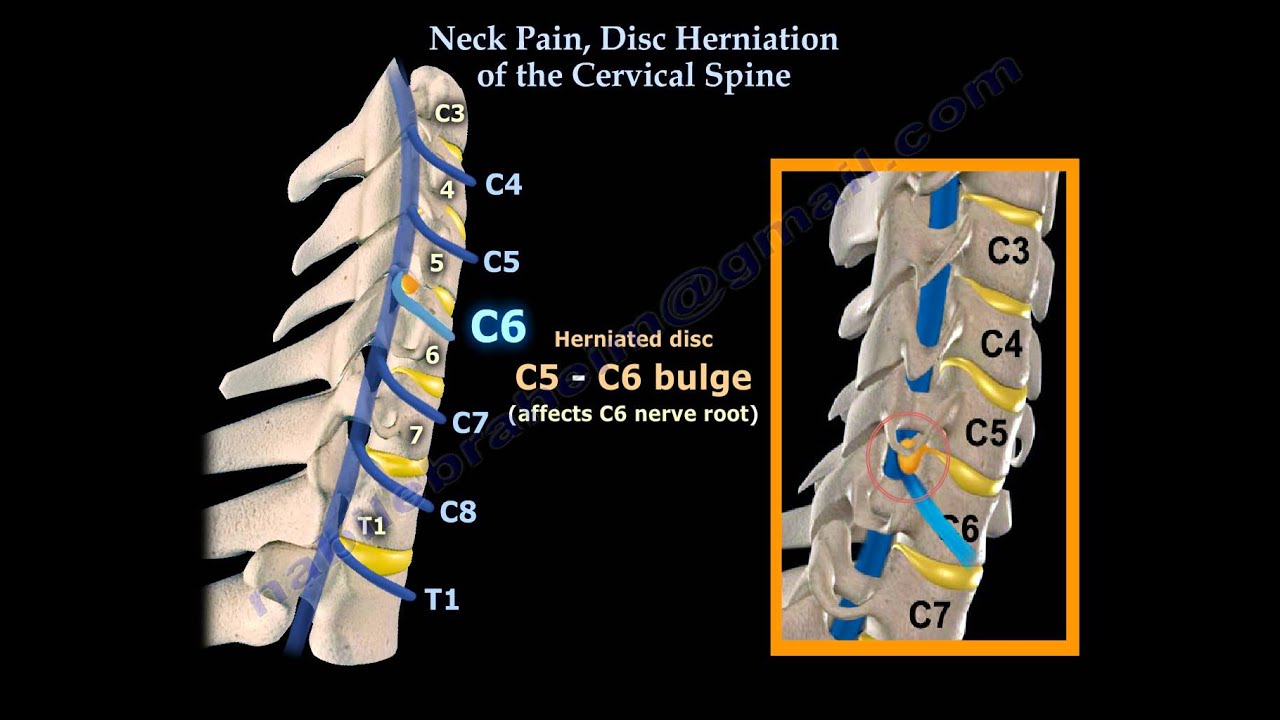
The degenerative disc disease of the cervical spine usually involves the most mobile segment that is the C5-C6 followed by C6-C7 and C4-C5 disc levels. The degeneration causes decreased water content of the disc or desiccation which leads to tears in the outer ring or the annulus fibrosus. Cervical osteophytes are bone spurs that grow on any of the seven vertebrae in the cervical spine (neck), ranging from the base of the skull, C1 vertebra, to the base of the neck, C7 vertebra. Show Transcript The term "bone spurs" might elicit images of radiating spikes, but bone spurs (osteophytes) are actually rounded and scalloped. Publish Date: Apr 26, 2021 The C3, C4, and C5 vertebrae form the midsection of the cervical spine, near the base of the neck. A cervical vertebrae injury is the most severe of all spinal cord injuries because the higher up in the spine an injury occurs, the more damage that is caused to the central nervous system. C3, C4, C5, and C6 cervical vertebrae share characteristics with most of the vertebrae throughout the spine. Cervical vertebrae C3 through C6 are known as typical vertebrae because they share the same basic characteristics with most of the vertebrae throughout the rest of the spine. Typical vertebrae have: Vertebral body.
slip disc cervical spondylosis Max Short
A pinched nerve or nerve root inflammation may also cause numbness and/or weakness to radiate down into the shoulder, arm, hand, and/or fingers. Radicular pain may also accompany radiculopathy in some instances. See Cervical Radiculopathy from a Herniated Cervical Disc Symptoms worsen with specific head positions or activities. Overview Cervical spondylosis is a general term for age-related wear and tear affecting the spinal disks in your neck. As the disks dehydrate and shrink, signs of osteoarthritis develop, including bony projections along the edges of bones (bone spurs). Cervical spondylosis is very common and worsens with age. Anterolisthesis of C3 on C4 and C4 on C5. Vertebral body heights are maintained. Multilevel degenerative changes characterized by disc space loss, uncovertebral joint degeneration, and facet arthropathy, most pronounced at C6-C7. The prevertebral soft tissues are within normal limits. Cervical nerves are spinal nerves that arise from the cervical region of the spinal cord. These nerves conduct motor and sensory information via efferent and afferent fibers, respectively, to and from the central nervous system. While classified as peripheral nerves, the motor cell body resides in the anterior horn of the spinal cord.
All About the C2C5 Spinal Motion Segments
There is a severe narrowing of the diameter of the spinal canal at C4-C5 and less prominent at C5-C6. Getty Images What Causes Cervical Spinal Stenosis? A common cause of cervical spinal. Degenerative disc disease of the cervical spine typically develops in the aging population equally in terms of patient sex. Patients most commonly present with pain. Pain, or in combination with other neurological symptoms, may require surgical intervention.
Cervical Annular Tears (C1-C7) Thoracic Annular Tears (T1-T12) Lumbar Annular Tears (L1-L5) Types of Annular Tears. Peripheral Tears - An injury such as a fall or car accident is the most common cause of this type of annular tear. These tears begin on the outside layer of the discs that surround the disc. Description. Mobi‑C is a prosthetic device for cervical intervertebral disc replacement (C3/C4, C4/C5, C5/C6, C6/C7) intended to restore disc height and retain movement in the cervical spine. It can be used for either the replacement of 1 (1‑level) or 2 (2‑level) cervical discs; 2‑level replacement requires 2 Mobi‑C devices.

C3C4 Posterior Cervical Laminectomies, C67 Laminotomy and Spin Stock
The occurrence rate of bulge or herniation at C3-C4, C4-C5, C5-C6, and C6-C7 increased with aging before age 50 years and decreased with aging after age 50 years, especially after 60 years. Moreover, the incidence of hyperosteogeny and spinal stenosis increased with aging before age 60 years and decreased with aging after age 60 years, although. Cervical discs have three purposes: cushioning the force applied to the spine to protect the vertebrae from damaging each other. acting as connective tissue to keep the cervical discs in place. acting as a cartilaginous joint to allow us to have a range of motion between bones to turn or bend the spine.




