The engineering materials can broadly be classified as: a) Ferrous Metals b) Non-ferrous Metals (aluminum, magnesium, copper, nickel, titanium) c) Plastics (thermoplastics, thermosets) d). Chapter 1:Classification of Materials. 10 1.2.3.(B ) Nanoengineered Materials Until very recent times the general procedure utilized by scientists to understand the chemistry and physics of materials has been to begin by studying large and complex structures, and then to investigate the fundamental building blocks of these structures that are.

(PDF) CLASSIFICATION OF MATERIALS
Materials Scientists and Engineers generally classify the materials that make up our world and everything around us into four major categories; metals, polymers, ceramics, and composites. Most people recognize metals, for example, as lustrous elements that are good conductors of heat and electricity. Classification Of Engineering Materials, And Their Properties A] Material classification: There are different ways of classifying materials. One way is to describe five groups or families: 1. Metals and alloys; 2. Ceramics 3. glasses 4. Polymers (plastics); 5. Semiconductors 6. Composite materials 1- Metals and Alloys: Classification of Materials - Materials and Thermodynamics - Wiley Online Library Chapter 3 Classification of Materials Book Author (s): Pierre Delhaes First published: 15 August 2017 https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119425540.ch3 PDF Tools Share Get access to this single chapter. View access options below. Institutional Login Microsoft Word - MATERIALS DATA _2003_ version 3.doc. 2. V. CLASSIFICATION AND APPLICATIONS OF ENGINEERING MATERIALS. Metals: ferrous alloys, non-ferrous alloys. Polymers and foams. Composites, ceramics, glasses and natural materials. VI. EQUILIBRIUM (PHASE) DIAGRAMS. Copper - Nickel.

Uganda Ruder Haarschnitt mechanical engineering materials Palme Umstritten Verbindung
classification. " Primary Raw Materials " are substances obtained directly from nature by. extracting natural deposits, "S econdary Raw Materials " are reused "Materials". Any raw. Classification of material substances: Introducing a standards-based approach - ScienceDirect Volume 193, August 2020, 108784 Classification of material substances: Introducing a standards-based approach Barbara E. Marschallek , Thomas Jacobsen Add to Mendeley https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108784 Get rights and content Classification and Selection of Materials: The first module deals with the classification of the engineering materials and their processing techniques. The engineering materials can broadly be classified as: Ferrous Metals Non-ferrous Metals (aluminum, magnesium, copper, nickel, titanium) Plastics (thermoplastics, thermosets) Ceramics and Diamond CLASSIFICATION OF MATERIALS Materials can be classified based on its conductivity property as 1.Conductor : material through which electric current can pass.. Are the materials that partially conduct and partially does not conduct. Silicon and Germanium are best examples. Electronic devices like p-n diode, zener diode bipolar junction.
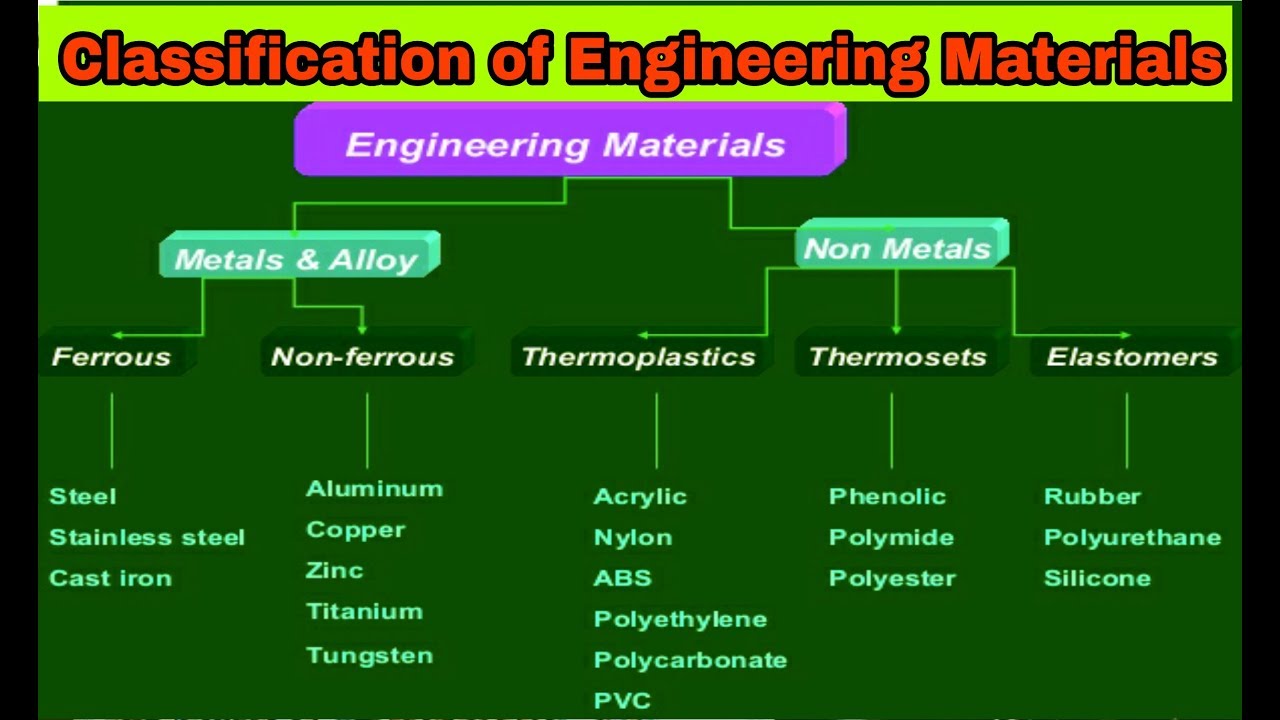
Classification of Engineering Materials Explained in English and Hindi. YouTube
bonding forces of a particular material. These three classifications are metallic, ceramic and polymeric. Additionally, different materials can be combined to create a composite material. Within each of these classifications, materials are often further organized into groups based on their chemical composition or certain physical or mechanical Classification It is the systematic arrangement or division of materials into groups on the basis of some. material), Laminate composites (golf club shafts, tennis rackets), Fiber reinforced composites (fiberglass) (f). Biomaterials: e.g. Man-made proteins (artificial bacterium), Biosensors, etc (g). Advanced / Smart Materials: e.g.
Classifying Matter. When classifying matter, the material under investigation may be reduced to its atomic structure. The atom is the most basic structure of the material which may be viewed as the element of the material. Copper (Cu), oxygen (O), and tin (Sn) are examples of elements. Combining of elements is a result of bonding covalent. Physical properties are characteristics that describe matter. They include characteristics such as size, shape, color, and mass. Many of these properties can be quantitative in nature. For example, quantitative physical properties of water would be the boiling point (100 °C / 212 °F) and melting point (0°C / 32 °F).

Classification of Materials PDF
A material is isotropic ifits properties are independent of the orientation, they do not vary with direction. Otherwise the material is anisotropic. A general anisotropic material has no planes or axes of material symmetry, but in Sect. 2.1.3 some special kinds of material symmetries like orthotropy, transverse isotropy, etc., are discussed in. There are three general classification for materials The one as follows Materials Struactural functional Functional Classification of Materials 1- Aerospace Biomedical 3- Electronic Materials Energy Technology and Environmental Technology Magnetic Materials 6- Photonic or Optical Materials Smart Materials 8- Structural Materials




