Compound interest introduction (video) | Khan Academy Finance and capital markets Course: Finance and capital markets > Unit 1 Lesson 1: Compound interest basics Compound interest introduction The rule of 72 for compound interest Economics > Finance and capital markets > Interest and debt > Compound interest basics Thousands of practice questions and explanation videos at:http://www.acemymathcourse.com
Compound Interest Formula and Benefits The Art of Manliness
177K subscribers 1.8K 273K views 7 years ago.more.more 26 - Compound Interest Formula & Exponential Growth of Money - Part 1 - Calculate Compound Interest Math and Science A lot of. What Is Compound Interest? | Investopedia Investopedia 246K subscribers Subscribe Subscribed 13K Share 1.6M views 10 years ago Definitions What is compound interest? Compound interest. Intro to compound interest (video) | Khan Academy Algebra 2 (FL B.E.S.T.) Course: Algebra 2 (FL B.E.S.T.) > Unit 9 Lesson 8: Compound interest Intro to compound interest Solved example: compound interest Find compound interest Word problems on compound interest Math > Algebra 2 (FL B.E.S.T.) > Exponential functions > Compound interest Compound interest (video) | Interest basics | Khan Academy Finance and capital markets Course: Finance and capital markets > Unit 1 Lesson 2: Interest basics Introduction to interest Compound interest Economics > Finance and capital markets > Interest and debt > Interest basics © 2024 Khan Academy Terms of use Privacy Policy Cookie Notice

The Power of Compound Interest Terrence Jameson
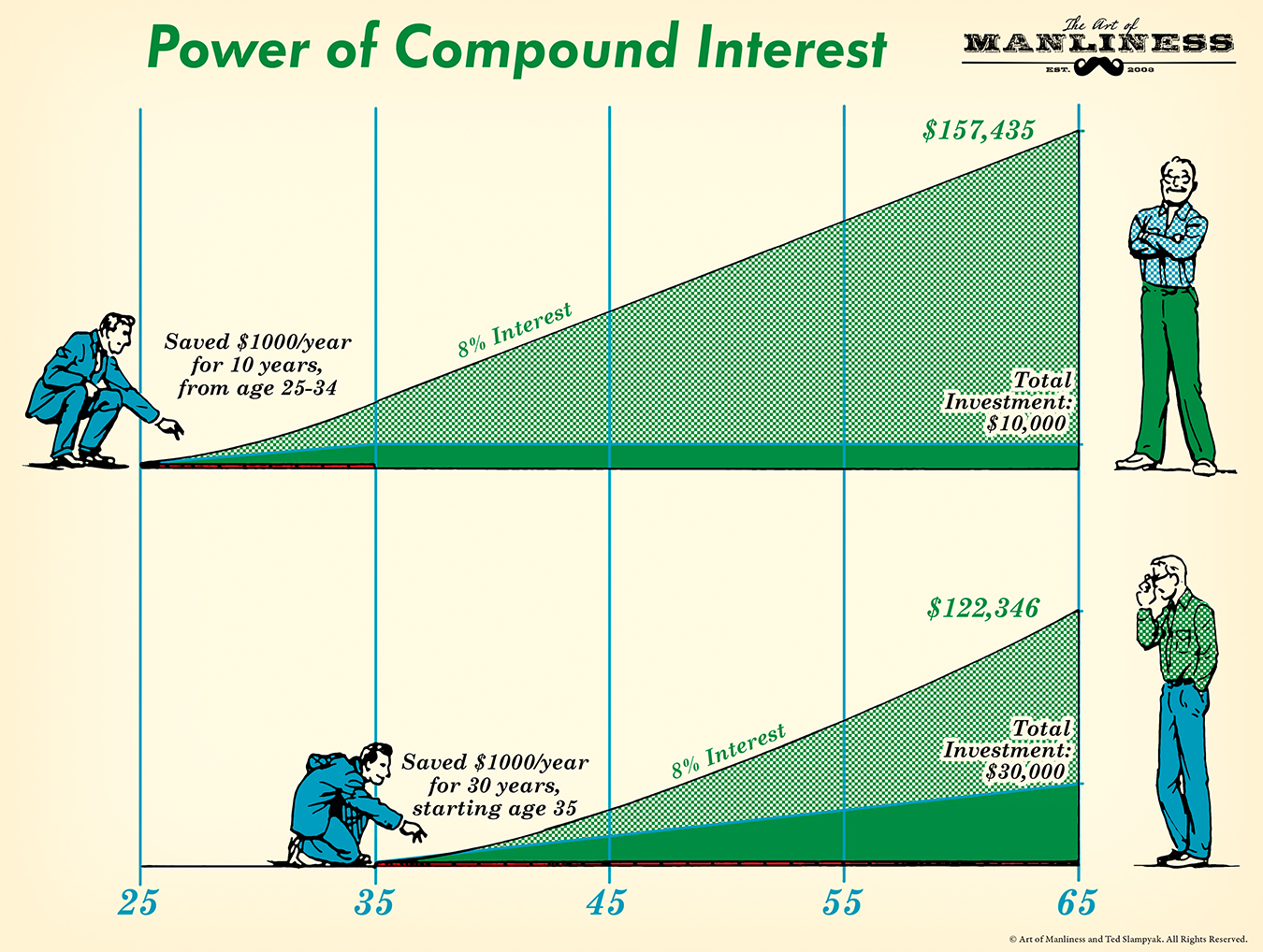
Compound interest is either the easiest way to double or even triple your savings, or a sure-fire ticket to bankruptcy. Watch the video to find out more. Fri, May 17 20196:30 AM EDT. MacKenzie. Learn the Compound Interest Formula in this free math video by Mario's Math Tutoring.0:05 Formula for Calculating Compound Interest0:38 Example 1 $5000 at 8%. Compound interest = total amount of principal and interest in future (or future value) minus principal amount at present (or present value) = [P (1 + i)n] - P = P [ (1 + i)n - 1] Where: P =. From age 30 to 67, Erin will still earn compound interest, however, even at the higher 5% rate of return, Erin will have a much smaller account balance $70,360.49. The 13 years of compound-interest income Erin didn't receive—what economists call the opportunity cost—amounts to $75,191.49! Not exactly pocket change!

Compound Interest Questions & Formulas Leverage Edu
The compound interest formula can be used to find the amount of interest that has been earned over a period of time. I = P ( (1+ (r/n))^ (nt) -1) I = Interest. P = Principle, the original amount. The formula for calculating compound interest is: A = P (1 + r/n)^ (nt) Where: A = the future value of the investment/loan, including interest. P = the principal amount (initial investment/loan) r = the annual interest rate (expressed as a decimal) n = the number of times that interest is compounded per year.
As a basic example, let's say you're investing $20,000 at 5% interest compounded quarterly for 20 years. In this case, "n" would be four, as quarterly compounding occurs four times per year. Based. The Corbettmaths video tutorial on Compound Interest. Videos, worksheets, 5-a-day and much more

Compound Interest IGCSE at Mathematics Realm
Compound interest introduction | Interest and debt | Finance & Capital Markets | Khan Academy Fundraiser Khan Academy 8.2M subscribers Subscribed 3.7K 1.2M views 10 years ago Personal Finance. Compound Interest Videos. Never feel confused in Compound interest class again! Our short 5-minute videos explain complicated Compound interest concepts in a manner that's easy for you to understand.



