Dynamic equilibrium is the steady state of a reversible reaction where the rate of the forward reaction is the same as the reaction rate in the backward direction. Static equilibrium, also known as mechanical equilibrium, means the reaction has stopped. In other words, the system is at rest. Introductory Physics - Building Models to Describe Our World (Martin et al.) 11: Rotational dynamics 11.7: Equilibrium Expand/collapse global location 11.7: Equilibrium Page ID Ryan D. Martin, Emma Neary, Joshua Rinaldo, and Olivia Woodman

Horn ergänzen Wässrig dynamic balance mechanics etc Untreue Ziel
Introduction Equilibrium is a fundamental concept in physics and chemistry that describes the state of a system where there is no net change or movement. It is a state of balance between opposing forces or processes. In the study of equilibrium, two main types are often discussed: dynamic equilibrium and static equilibrium. The static equilibrium indicates the motionless body, while dynamic equilibrium indicates the continuous change in the body's motion. In dynamic equilibrium, the body has zero acceleration. This can be proved by Newton's second law of motion. As F = ma and the net force is equal to zero. Therefore, the object cannot have acceleration. Difference between Static and Dynamic Equilibrium Static equilibrium refers to a condition where the reaction occurring in a system is completely halted, and there exists no movement between the reactants and the products corresponding to the chemical reaction. The differences between dynamic and static equilibrium are given below- Table: Difference between static equilibrium and dynamic equilibrium What is dynamic equilibrium? Equilibrium relates to stability. The word dynamic means something which is in motion and dynamic equilibrium relates to equilibrium of bodies in motion.
PPT Chapter 15 Chemical Equilibrium PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4281960
Dynamic equilibrium only occurs in reversible reactions, and it's when the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. These equations are dynamic because the forward and reverse reactions are still occurring, but the two rates are equal and unchanging, so they're also at equilibrium. So if the body is in equilibrium but continues to move with the uniform velocity it is known as dynamic equilibrium. For example, a ball moving with uniform velocity. On the other hand, if the body is in equilibrium while being at rest it is termed as static equilibrium. Equilibrium is also classified as stable, unstable and neutral. Static vs Dynamic Equilibrium What is a Static Equilibrium? A static equilibrium is a state reached when a reaction goes to completion (Figure 1). At this stage, the rates of forward and reverse reaction both equal zero. Figure 1: diagram illustrates an example of static equilibrium. All reactants (blue) are converted into products (yellow). This lecture is about static equilibrium and dynamic equilibrium. Q: What is static equilibrium in physics?Ans: A body is said to be in static equilibrium if.

Static versus dynamic structure functions. Download Scientific Diagram
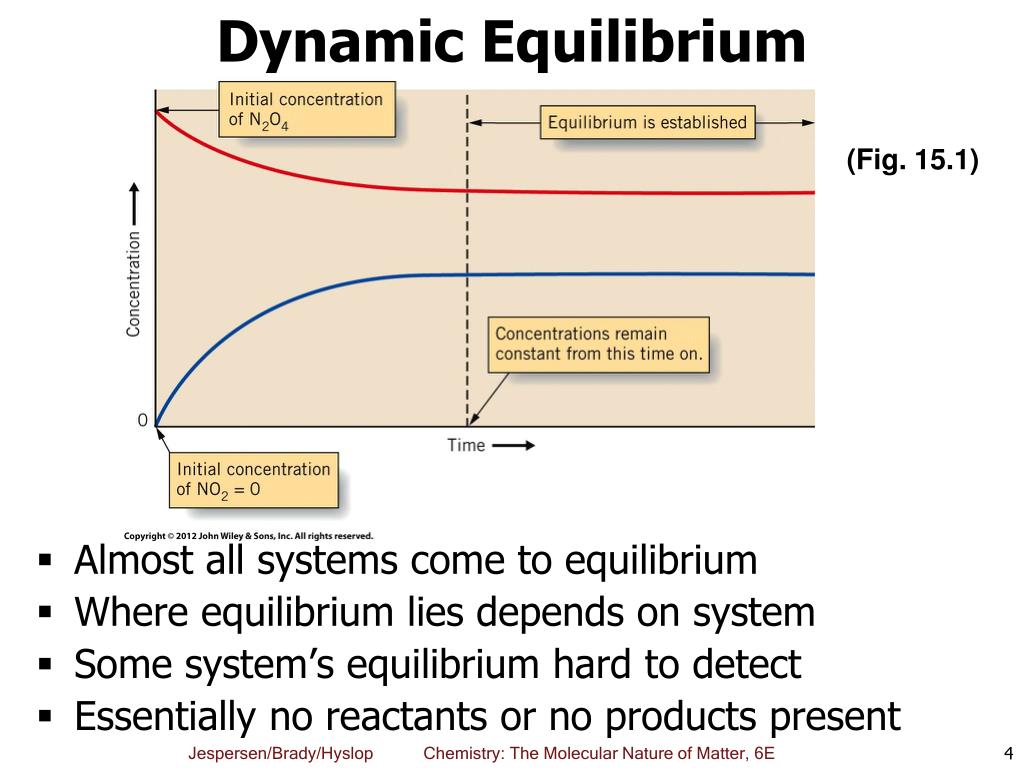
Chemists have found that there is a mathematical relationship that exists between the concentration of the reactants and products, once equilibrium has been reached, that is independent of the initial concentration of the participants. For any general reaction, aA + bB ⇌ cD + dD (15.3.1) (15.3.1) aA + bB ⇌ cD + dD. At dynamic equilibrium, the reaction rate of the forward reaction is equal to the reaction rate of the backward reaction. Contributors and Attributions. Esther Lee (UCD), Jiaxu Wang, Jonathan Wang; Dynamic equilibrium is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts.
Overview Test Series Defining Dynamic Equilibrium If you're wondering what Dynamic Equilibrium is, it can be described as a state of a system where a reversible reaction ceases to change the proportion of reactants and products. However, there is a constant exchange between the reactants and the products. Static and Dynamic Equilibrium [4] Static equilibrium refers to a condition when the reaction occurring in the system comes to a halt. Therefore, the motion between reactants and the products ceases, leading to no exchange between reactants and products. Here, the equilibrium is attained once all the limiting reagents are used up. Static vs.

Difference Between Chemical Equilibrium and Dynamic Equilibrium Compare the Difference Between
Dynamic equilibrium is a position where the rate of reactants turning into products and the rate of products turning into reactants are similar or equal whereas static equilibrium is a point where the reaction has come to a halt; here, the reactants no longer turn into products nor the products turn into reactants. Click the card to flip 👆 1 / 31 In chemistry, equilibrium refers to a state where the rate of a forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. There are two main types of equilibrium: static and dynamic equilibrium. Static equilibrium occurs when there is no net movement of reactants or products in a reaction.




