3 min read Retinal imaging takes a digital picture of the back of your eye. It shows the retina (where light and images hit), the optic disc (a spot on the retina that holds the optic nerve,. Eye Anatomy: The Back of the Eye Dr. Russel Lazarus, October 11, 2020 Did you know that the back of the eye is responsible for transferring visual information from the eye to the brain? In order to see clearly, light is focused onto the back of your eye where it is transformed into electrical impulses.
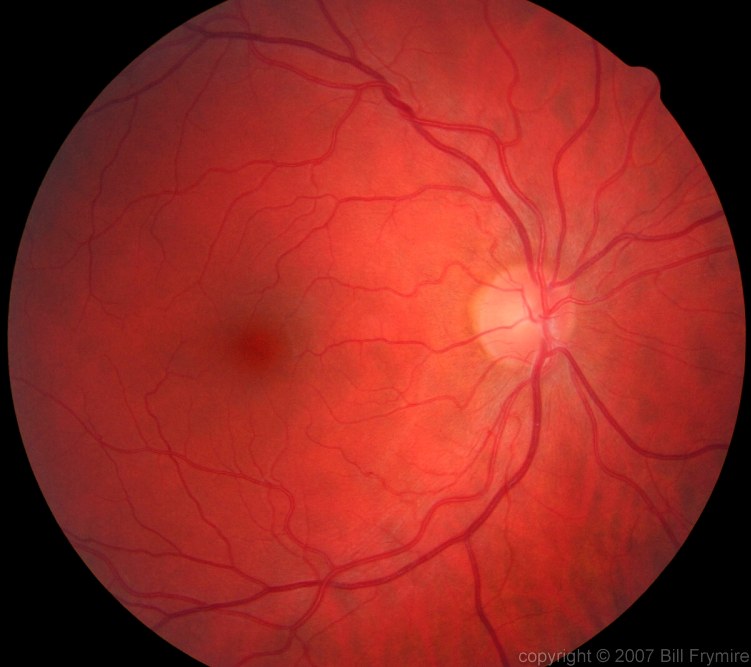
Looking at the back of a retina Image of the Week Bill FrymireBill Frymire
Optical coherence tomography, or OCT, is an imaging method used to generate a picture of the back of your eye, called your retina. The noninvasive method produces an image by measuring the amount of a dim red light that reflects off of your retina and optic nerve. Cornea. The clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye. Iris. The colored part of the eye. The iris is partly responsible for regulating the amount of light permitted to enter the eye. Lens (also called crystalline lens). The transparent structure inside the eye that focuses light rays onto the retina. Lower eyelid. Search from Back Of The Eye stock photos, pictures and royalty-free images from iStock. Find high-quality stock photos that you won't find anywhere else. Light projects through your pupil and lens to the back of the eye. The inside lining of the eye is covered by special light-sensing cells that are collectively called the retina. It converts.

Eye Anatomy
The iris (colored part) of the eye functions like the diaphragm of a camera, controlling the amount of light reaching the retina by automatically adjusting the size of the pupil (aperture). The eye's crystalline lens is located directly behind the pupil and further focuses light rays. With OCT, a machine scans the back of your eye. This provides very detailed pictures of the retina and macula. Your ophthalmologist studies these pictures to check for problems. Mayo Clinic Overview Parts of the eye Enlarge image Retinal diseases vary widely, but most of them cause visual symptoms. Retinal diseases can affect any part of your retina, a thin layer of tissue on the inside back wall of your eye. Retinal detachment describes an emergency situation in which a thin layer of tissue (the retina) at the back of the eye pulls away from its normal position. Retinal detachment separates the retinal cells from the layer of blood vessels that provides oxygen and nourishment to the eye. The longer retinal detachment goes untreated, the greater.

Human eye Wikiwand
Muscles in the iris dilate (widen) or constrict (narrow) the pupil to control the amount of light reaching the back of the eye. Directly behind the pupil sits the lens. The lens focuses light toward the back of the eye. The lens changes shape to help the eye focus on objects up close. Overview What is a retinal hemorrhage? A retinal hemorrhage is the medical term for bleeding in your retina. Hemorrhages are any type of bleeding from a damaged blood vessel. Retinal hemorrhages can be caused by traumas (like getting hit in the head) and health conditions that affect your eyes or blood vessels.
Our eye doctors at GHEye excel in prescription of glasses, contact lenses and the diagnosis of a variety of eye diseases. Call our optometrists at (571) 445-3692 to schedule your appointment today for a retinal photo or a standard eye exam. Our eye doctors, Dr. Ally Stoeger and Dr. Jennifer Sun provide the highest quality optometry services and. Symptoms. Eye melanoma may not cause signs and symptoms. When they do occur, signs and symptoms of eye melanoma can include: A sensation of flashes or specks of dust in your vision (floaters) A growing dark spot on the iris. A change in the shape of the dark circle (pupil) at the center of your eye. Poor or blurry vision in one eye.

20+ Anatomy Of An Eye Pics anatomysystems
Then they will take pictures of your eye using optical coherence tomography (OCT). With OCT, a machine scans the back of your eye. This provides very detailed pictures of the retina and macula. Your ophthalmologist studies these pictures to check for problems. Macular Hole Treatment. Surgery called vitrectomy is the best way to treat a macular. The retina is a thin layer of light-sensitive tissue that lines the back of the eye. Located near the optic nerve, it receives light and sends pictures to the brain of what the eye sees. As we age, the vitreous gel, a clear jelly-like substance that fills most of the eye's interior, begins to break down, shrink, and pull away from the retina..




