Blood Types Explained - A, B, AB and O | Red Cross Blood Services Find a Blood Drive Emergency Blood Shortage The American Red Cross is experiencing an emergency blood shortage as the nation faces the lowest number of people giving blood in 20 years. The ABO system has four major blood types: A, B, AB, and O. Blood types are further categorized by the presence (positive or +) or absence (negative or -) of the Rh (D) antigen on the surface of their red blood cells, also known as the Rh factor. This produces the eight major blood types. A and B antigens are sugars.
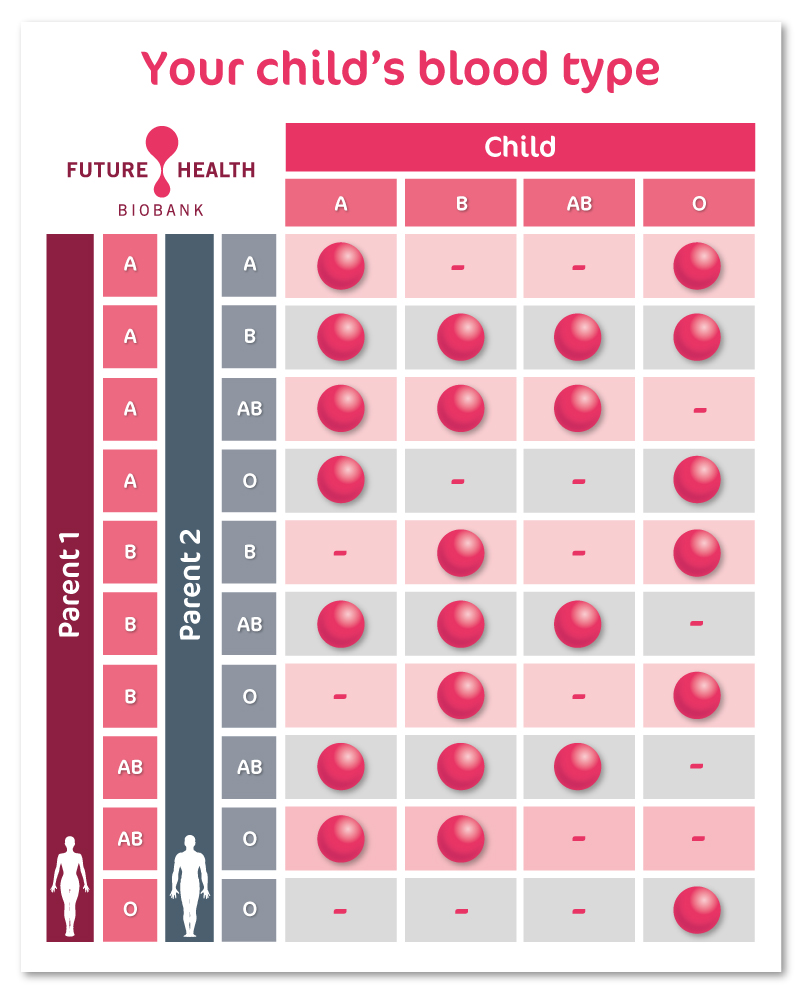
The importance of knowing your baby’s blood type Future Health Biobank
There are four main blood types: A, B, AB and O. Blood bank specialists determine your blood type based on whether you have antigen A or B on your red blood cells. They also look for a protein called the Rh factor. They classify your blood type as positive (+) if you have this protein and negative (-) if you don't. A positive A negative O positive O negative A negative blood type is rarer, with 1 in 16 people having the blood group, and able to receive only A negative and O negative transfusions. There are four ABO types: A, B, AB and O. Your blood type is also determined by Rh status: Rh+ or Rh-. That leaves us with eight possible blood types: Each of these eight types is unique. Blood types determine who you can give blood to and receive blood from. The eight common blood types: A+, A-, B+, B-, O+, O-, AB+, and AB-. In the United States, O+ is the most common blood type, found in about 37% of the population, followed by A+ in around 36% of.

National Blood Donor Month Blood type compatibilities Compound Interest
Type O blood: A high- protein diet heavy on lean meat, poultry, fish, and vegetables, and light on grains, beans, and dairy. D'Adamo also recommends various supplements to help with tummy troubles. There are eight different blood types: A positive: This is one of the most common blood types (35.7% of the U.S. population has it). Someone with this type can give blood only to people who are A. Blood types are determined by unique proteins found on the surface of the red blood cells known as antigens. Knowing your blood type is important if you need a blood transfusion, are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, or if you are going to be a transplant donor or recipient. Around 82% of people in the U.S. have Rh-positive blood. The rarest blood group type is AB negative. These are the main types. Within the eight main groups, are there also many lesser-known and.

What’s your type?
Stomach Cancer. 2 /12. A, AB, and B blood types are more at risk than type Os. Specifically, people with type A blood are more likely to get stomach cancer. Researchers think this might be because. Your blood type is determined based on specific antigens present in your blood. You can find out your blood type by asking your doctor for a test, donating blood, or taking an at-home blood test.
If your blood is A positive (A+), it means that your blood contains type-A antigens with the presence of a protein called the rhesus (Rh) factor. Antigens are markers on the surface of a blood. When identifying a patient's blood type, the Rh group is designated by adding the word positive or negative to the ABO type. For example, A positive (A +) means ABO group A blood with the Rh antigen present, and AB negative (AB −) means ABO group AB blood without the Rh antigen. The following chart summarizes the distribution of the ABO and.
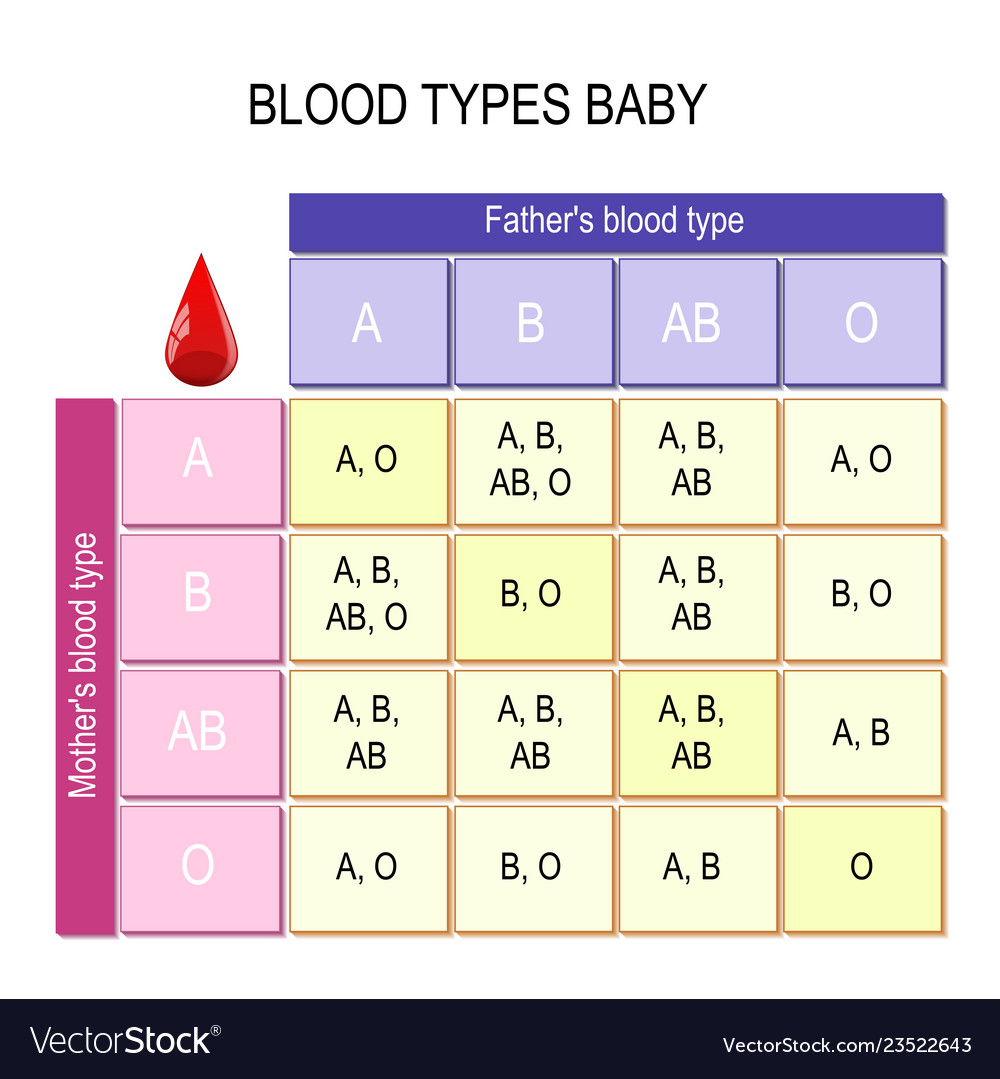
Blood Group Inheritance Chart Best Image Home
Type A Positive. 1 in 3 people are A positive, which is why it is one of the most common blood types. As you can imagine A positive blood is in high demand, because it is present in a large percentage of the population. Patients undergoing chemotherapy treatments also have a high demand for the platelets from those with the A positive blood type. What blood type am I? There are four main groups of blood: A, B, AB, and 0. Each of them contains different antigens (such as carbohydrates or proteins) on the membrane of red blood cells.




