Artwork: The basic concept of a catalytic converter: sitting between your car's engine and tailpipe, it takes in dirty air and removes a significant amount of pollution from it using chemical catalysts. Sponsored links Contents Why engines make pollution What is a catalytic converter? What happens inside the converter? A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device which converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction.
Catalytic Converter Vector Illustration on Behance
7.1: Catalytic Converters. A catalytic converter is a device used to reduce the emissions from an internal combustion engine (used in most modern day automobiles and vehicles). Not enough oxygen is available to oxidize the carbon fuel in these engines completely into carbon dioxide and water; thus toxic by-products are produced. Catalytic converters are designed to reduce all three: Carbon monoxide (CO) is a poisonous gas that is colorless and odorless. Hydrocarbons or volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are a major component of smog produced mostly from evaporated, unburned .fuel. A catalytic converter is a vehicle emissions control device that is used to convert toxic byproducts of combustion (occurring in the exhaust of an internal combustion engine) to less toxic. Catalytic converters take advantage of all five factors that affect the speed of chemical reactions to ensure that exhaust emissions are as safe as possible.. A diagram is shown of two possible interactions of an enzyme and a substrate. In a, which is labeled "Lock-and-key," two diagrams are shown. The first shows a green wedge-like.

Catalytic Converter Schematic Diagram Circuit Diagram
In this video, you'll learn how a catalytic converter (cat) works.Also check out our video on how a diesel particulate filter (DPF) works 👉 https://bit.ly/3. This diagram from MagnaFlow shows the overall construction and reactions for a catalytic converter. When Catalytic Converters Go Bad. Damage to a cat can occur through physical damage, such as smashing the case on a speed bump, or chemical, such as allowing a contaminant to cause "catalyst poisoning", which coats the honeycomb, keeping it from doing it's job. Reaction Diagrams for Catalyzed Reactions The two reaction diagrams here represent the same reaction: one without a catalyst and one with a catalyst. Estimate the activation energy for each process, and identify which one involves a catalyst. Solution The metals in catalytic converters are catalysts. Catalysts are compounds that trigger a chemical reaction without being affected themselves. Catalytic converters have a honeycomb structure because it provides a lot of surface area for a lot of reactions. Catalytic converters use elements like Platinum (Pt), Palladium (Pd), and Rhodium (Rh) as.
Manigandan Blog Catalytic converter
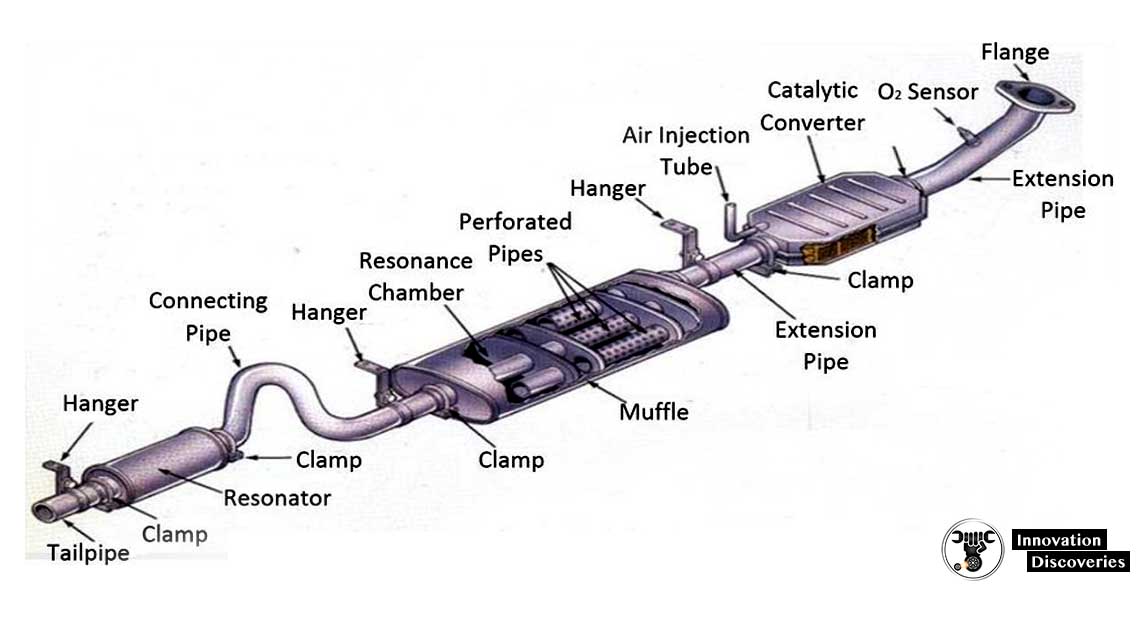
Where is the Catalytic Converter Located? - In The Garage with CarParts.com If you're new to auto repair, you might be wondering where the catalytic converter is located. Find out in this article plus tips on how to access it. Exhaust System Parts 101: The Basics (Diagram Included) - In The Garage with CarParts.com Learn about your car's exhaust system, so you can talk to your mechanic more confidently if parts need to be repaired in the future. Read on.
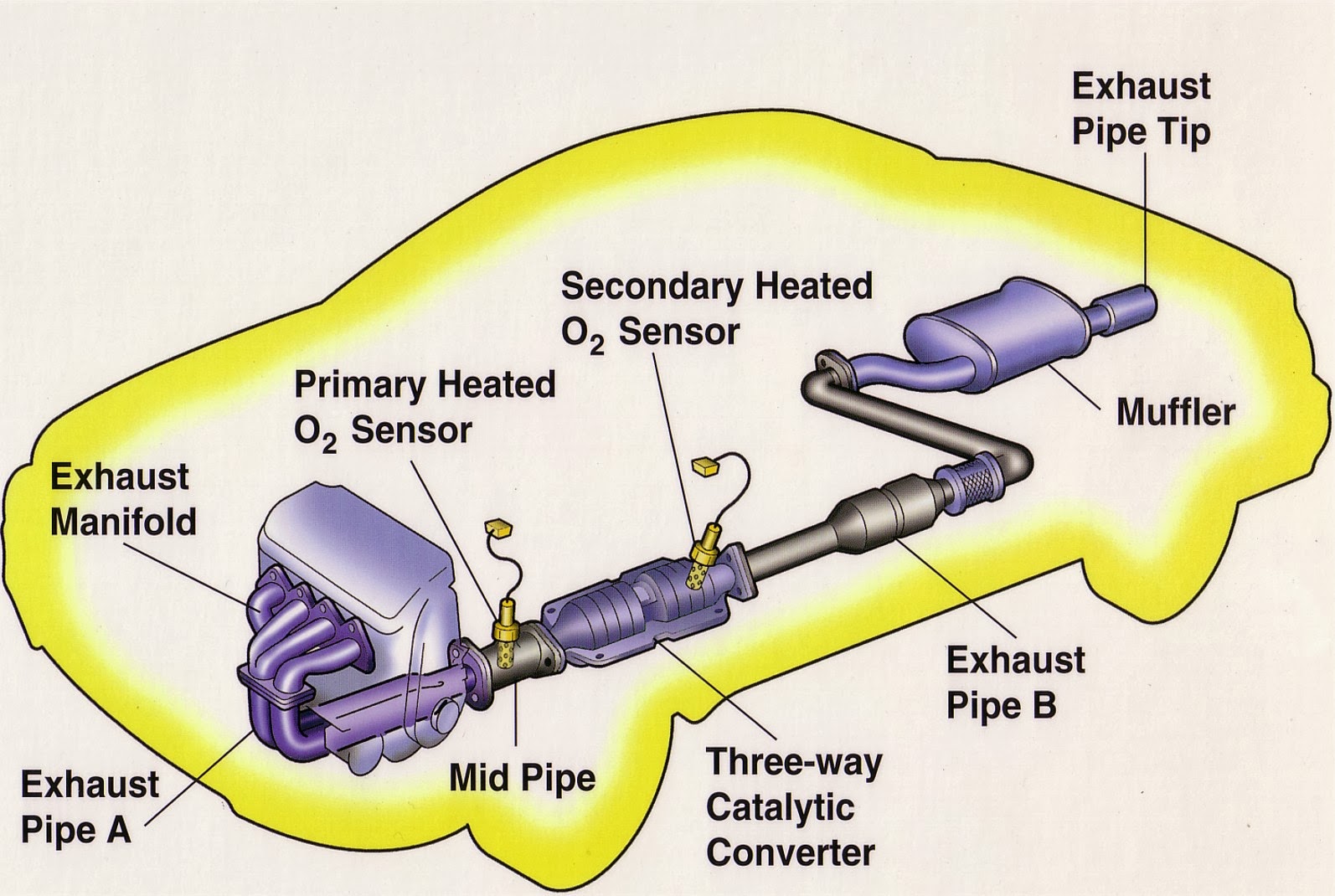
Exhaust pipes, manifold, catalytic converter, and muffler. News Features New Cars Used Cars Shopping Tools. Exhaust System Diagram. The activation energy is the difference between the energy of the starting reagents and the transition state—a maximum on the reaction coordinate diagram. The reagents are at 6 kJ and the transition state is at 20 kJ, so the activation energy can be calculated as follows: Ea = 20kJ − 6kJ = 14kJ (4.6.1) (4.6.1) E a = 20 k J − 6 k J = 14 k J.
Catalytic Converter
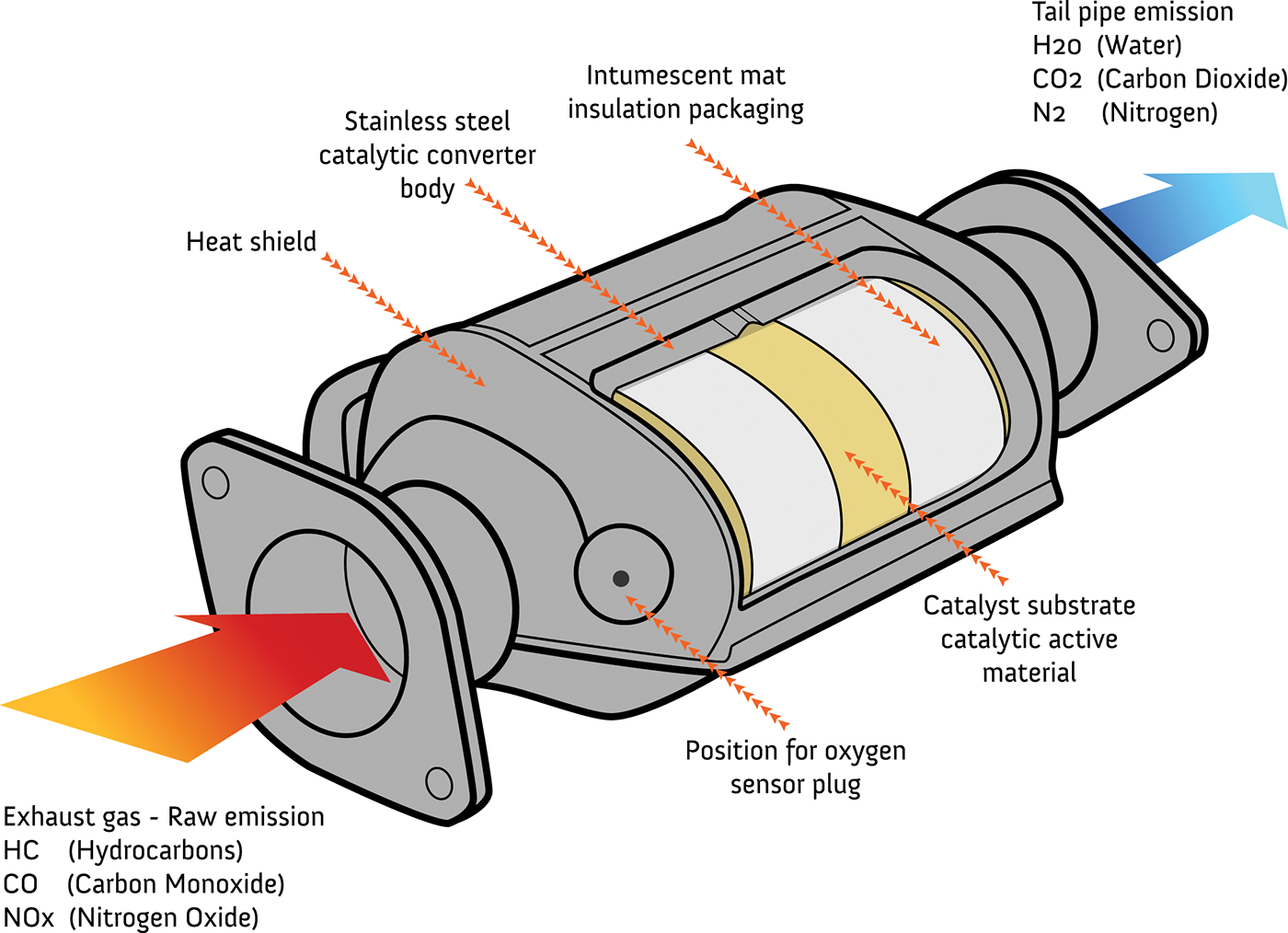
Here is a diagram of how a catalytic converter works: The catalyst is filled with hot exhaust gas. Exhaust gas interacts with the catalyst after passing through the honeycomb substrate. Chemical reactions that transform the toxic emissions in exhaust gas into less toxic emissions are accelerated by the catalyst. Catalytic converters use metallic catalysts to promote the desired reactions at lower temperatures than would otherwise be needed. Typical values are shown in Figure 8.21.The catalyst types could be a base metal (e.g., copper, Cu, or chromium, Cr) but are more usually noble metal (platinum, Pt, palladium, Pd, rhodium, Rh). The transition metal oxides of copper, cobalt, iron chromate, and.




