The cell then divides in two, and each new cell obtains a copy of the micronucleus and the macronucleus. Ciliate undergoing the last processes of binary fission. Typically, the cell is divided transversally, with the anterior half of the ciliate (the proter) forming one new organism, and the posterior half (the opisthe) forming another. However. The ciliated simple columnar epithelium bears cilia (finger-like projections of the plasma membrane) on the apical surfaces of cells, with goblet cells usually scattered throughout the epithelium. Up to 300 cilia may be present on each cell, beating in a synchronized manner with adjacent cells to propel materials over the surface of the epithelium.

Protista cillia flagella Cell theory, Nuclear membrane, Plasma membrane
Ciliated Epithelium Cell - Concept. A section of epithelium is made up of columnar or cuboidal cells with hairlike appendages that can beat rapidly (see cilium). In structures like the trachea, bronchial tubes, and nasal cavities, the ciliated epithelium is responsible for transporting particles or fluid over the epithelial surface. Ciliated epithelial cells are simple columnar epithelial cells. These cells possess cilia, which extend into the internal cavity of the structure they line. Each cell contains between 200 and 300. The cilium (plural: cilia) is a microtubule-based organelle that projects from the cellular membrane of many cells.Cilia can be divided into two types: motile and non-motile. Motile cilia sway in a wave-like motion in order to generate fluid movement. These types of cilia are found on the surface of cells such as the epithelial cells of upper respiratory and reproductive tract. Ciliated cells are located, with a small portion of cytoplasm, on the basement membrane and reach through the basal cells to the epithelial surface. The oval nucleus is present in the middle third of these cells. In the cytoplasm, which has a loose structure, scattered ribosomes are found, sometimes in groups.

Cilia in the CNS The Quiet Organelle Claims Center Stage Neuron
5.6: Flagella and Cilia. Flagella (singular = flagellum) are long, hair-like structures that extend from the plasma membrane and are used to move an entire cell, (for example, sperm, Euglena ). When present, the cell has just one flagellum or a few flagella. Prokaryotes sometimes have flagella, but they are structurally very different from. This structure is known as an axoneme, and the arrangement as '9+2', an arrangement ubiquitous in motile cilia. The microtubules are held together by cross-linking proteins. Between the nine outer pairs are motor proteins called dynein.. These ciliated epithelial cells remove mucus, bacteria, and other debris from the lungs. Another. In general, the primary cilium is a sensory organelle that responds to mechanical and chemical stimuli in the environment, communicates that external signal to the cell's interior. However, many. Cells co-expressing gene markers of ciliated cells, including FOXJ1, and goblet cell genes such as MUC5AC, were termed 'mucous ciliated cells' and are postulated to represent a novel.
/ciliated_epithelial_cells-5a7cb8926edd650036eb92da.jpg)
Cilia and Flagella Function
Ciliated epithelial cells. In this clip the structure and function of a ciliated epithelial cell is described. Cilia are tiny hair like structures on the surface of the cell. The hairs sweep hair. Columnar ciliated cells are found throughout the. E. & Mukherjee, A. B. Uteroglobin: structure, molecular biology, and new perspectives on its function as a phospholipase A2 inhibitor..
ciliate, any member of the protozoan phylum Ciliophora, of which there are some 8,000 species; ciliates are generally considered the most evolved and complex of protozoans. Ciliates are single-celled organisms that, at some stage in their life cycle, possess cilia, short hairlike organelles used for locomotion and food gathering.. The cilia are usually arranged in rows, known as kineties, on. The first pages illustrate introductory concepts for those new to microscopy as well as definitions of commonly used histology terms. The drawings of histology images were originally designed to complement the histology component of the first year Medical course run prior to 2004. They are sketches from selected slides used in class from the.
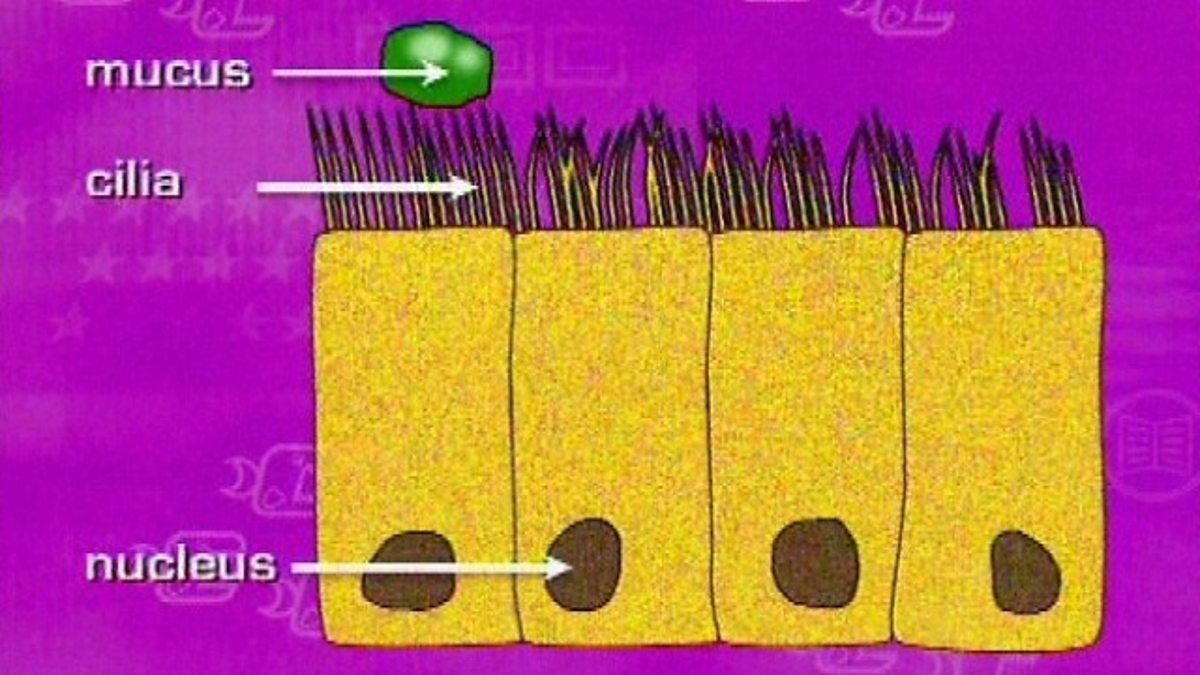
BBC Two Key Stage Three Bitesize Revision, 28/03/2001, Ciliated Epithelial Cells
Other articles where ciliated epithelium is discussed: adenoids:.of the adenoids consists of ciliated epithelial cells covered by a thin film of mucus. The cilia, which are microscopic hairlike projections from the surface cells, move constantly in a wavelike manner and propel the blanket of mucus down to the pharynx proper. From that point the mucus is caught… The term 'cilia' is a Latin term meaning eyelash indicating the tiny eyelash-like appearance of the structure. Cilia are most prominent in protozoans of the phylum Ciliophora which are characterized by the presence of cilia. Ciliated cells are found in different tissues in complex animals like vertebrates, where they have distinct functions.


/ciliated_epithelial_cells-5a7cb8926edd650036eb92da.jpg)

