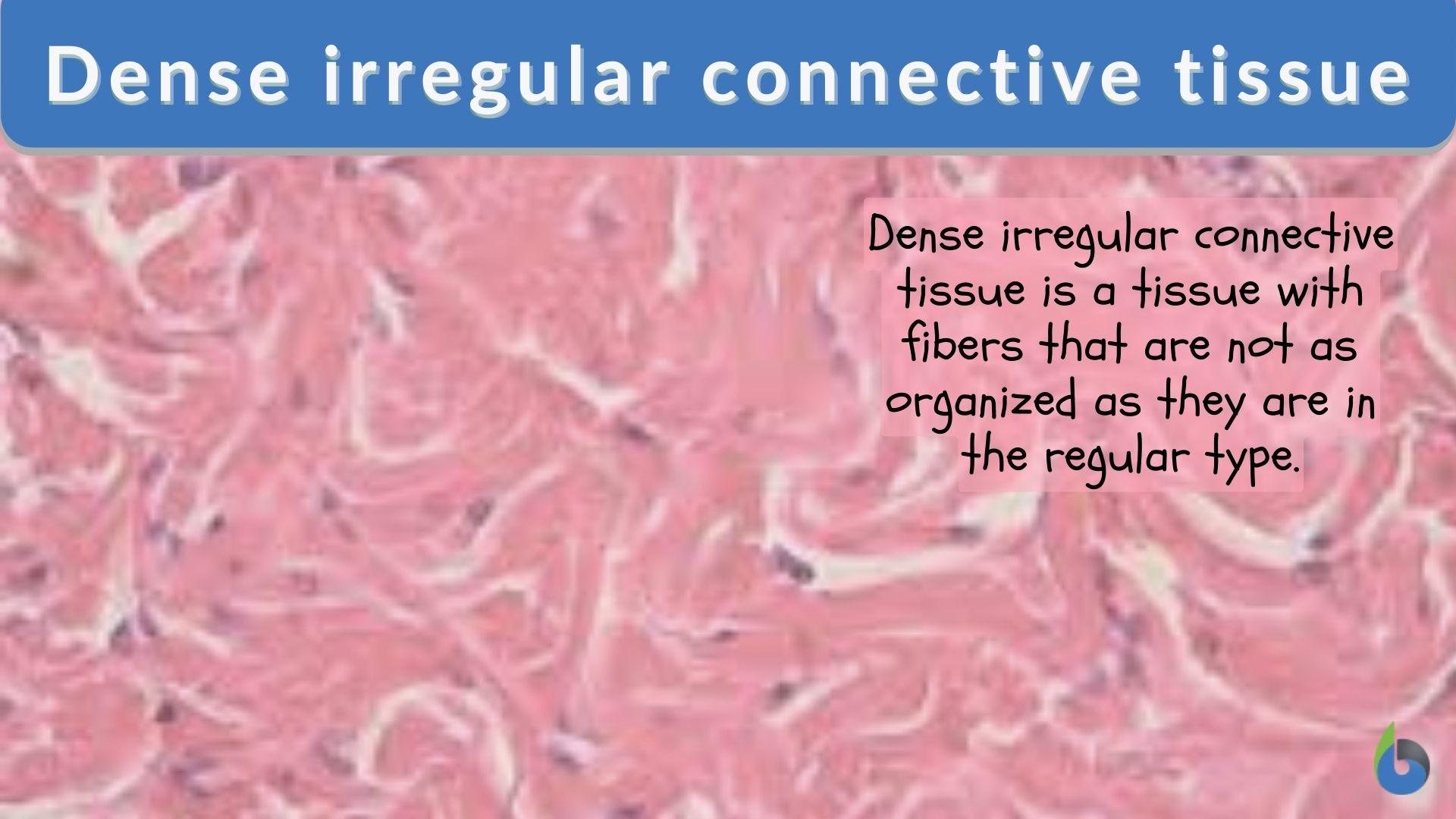
Dense irregular connective tissue is a type of dense connective tissue found widely dispersed throughout the body, particularly in areas where tension is applied from multiple different directions. In dense irregular connective tissue, the direction of fibers is random. This arrangement gives the tissue greater strength in all directions and less strength in one particular direction. In some tissues, fibers crisscross and form a mesh. In other tissues, stretching in several directions is achieved by alternating layers where fibers run in.

Connective Tissue Supports and Protects · Anatomy and Physiology
Dense connective tissue is a type of connective tissue that can be further split into dense regular connective tissue and dense irregular connective tissue. Dense regular connective tissue comprises structures such as ligaments, tendons and aponeuroses, whilst dense irregular tissue is more widely distributed throughout the body. Dense irregular connective tissue has fibers that are not arranged in parallel bundles as in dense regular connective tissue . Dense irregular connective tissue consists of mostly collagen fibers. It has less ground substance than loose connective tissue. [1] Fibroblasts are the predominant cell type, scattered sparsely across the tissue. [2] The irregular type, as the name implies, is a kind of dense connective tissue in which the extracellular fibers (especially, collagen fibers) are variably arranged in contrast to the dense regular connective tissue that has fibers arranged in a regular fashion (i.e, in parallel bundles). Dense irregular connective tissue is a type of connective tissue proper with a matrix containing densely packed interwoven collagen fibers that fill most of the extracellular space and a thick jellylike ground substance comprising the remainder of the matrix.
Dense irregular connective tissue Biology Online Dictionary
Dense regular collagenous connective tissue 1/4 Synonyms: none Connective tissue is the tissue that connects or separates, and supports all the other types of tissues in the body. Like all tissue types, it consists of cells surrounded by a compartment of fluid called the extracellular matrix (ECM). Dense connective tissue is reinforced by bundles of fibers that provide tensile strength, elasticity, and protection. In loose connective tissue, the fibers are loosely organized, leaving large spaces in between. Supportive connective tissue —bone and cartilage—provide structure and strength to the body and protect soft tissues. Figure 5.2 Layers of Skin The skin is composed of two main layers: the epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures. Dense connective tissue proper is composed of a higher density of fibers, which may be regular (with parallel fibers such as that of tendons and ligaments) or irregular (with multidirectional fibers such as that of the pericardium), or elastic (with significant embedded elastin such as that of arteries)..

Dense Irregular Connective Tissue Kit Ng, Ph.D.
In dense irregular connective tissue, the arrangement of proteins fibers is irregular and lacks the uniformity seen in dense regular . This arrangement gives the tissue greater strength in all directions and less strength in any one particular direction. In some tissues, fibers crisscross and form a mesh. Dense connective tissue helps attach muscles to bones and link bones together at joints. Specialized connective tissue encompasses a number of different tissues with specialized cells and unique ground substances. Some are solid and strong, while others are fluid and flexible. Examples include adipose, cartilage, bone, blood, and lymph.
Loose and Dense Irregular Connective Tissue. Non-specialized or general connective tissue, sometimes called connective tissue proper, is subdivided into two groups: loose and dense. The lamina propria of this fallopian tube is pale pink. Loose regular tissue has a fluid matrix and low proportions of arranged (regular) fibers. Each muscle is wrapped in a sheath of dense, irregular connective tissue called the epimysium, which allows a muscle to contract and move powerfully while maintaining its structural integrity. The epimysium also separates muscle from other tissues and organs in the area, allowing the muscle to move independently.

dense irregular connective tissue labeled Google Search Anatomy Class Help Pinterest Med
The cellular layer is adjacent to the cortical bone and is covered by an outer fibrous layer of dense irregular connective tissue (see Figure 6.3.4a). The periosteum also contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels that nourish compact bone.. Bone Matrix Osseous tissue is a connective tissue and like all connective tissues contains. A. DENSE IRREGULAR CONNECTIVE TISSUE. Slide 33 (skin, Verhoeff stain) View Virtual Slide. Slide 250-1 (vagina, H&E) View Virtual Slide. Slide 250-2 (vagina, trichrome) View Virtual Slide. The area beneath the stratified squamous epithelium shown in slide 33 is the dermis, which is composed of dense irregular connective tissue. In this section.




