The bacteria diagram given below represents the structure of a typical bacterial cell with its different parts. The cell wall, plasmid, cytoplasm and flagella are clearly marked in the diagram. Bacteria Diagram representing the Structure of Bacteria Ultrastructure of a Bacteria Cell The structure of bacteria is known for its simple body design. bacteria, any of a group of microscopic single-celled organisms that live in enormous numbers in almost every environment on Earth, from deep-sea vents to deep below Earth's surface to the digestive tracts of humans. Bacteria lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other internal structures and are therefore ranked among the unicellular life-forms.
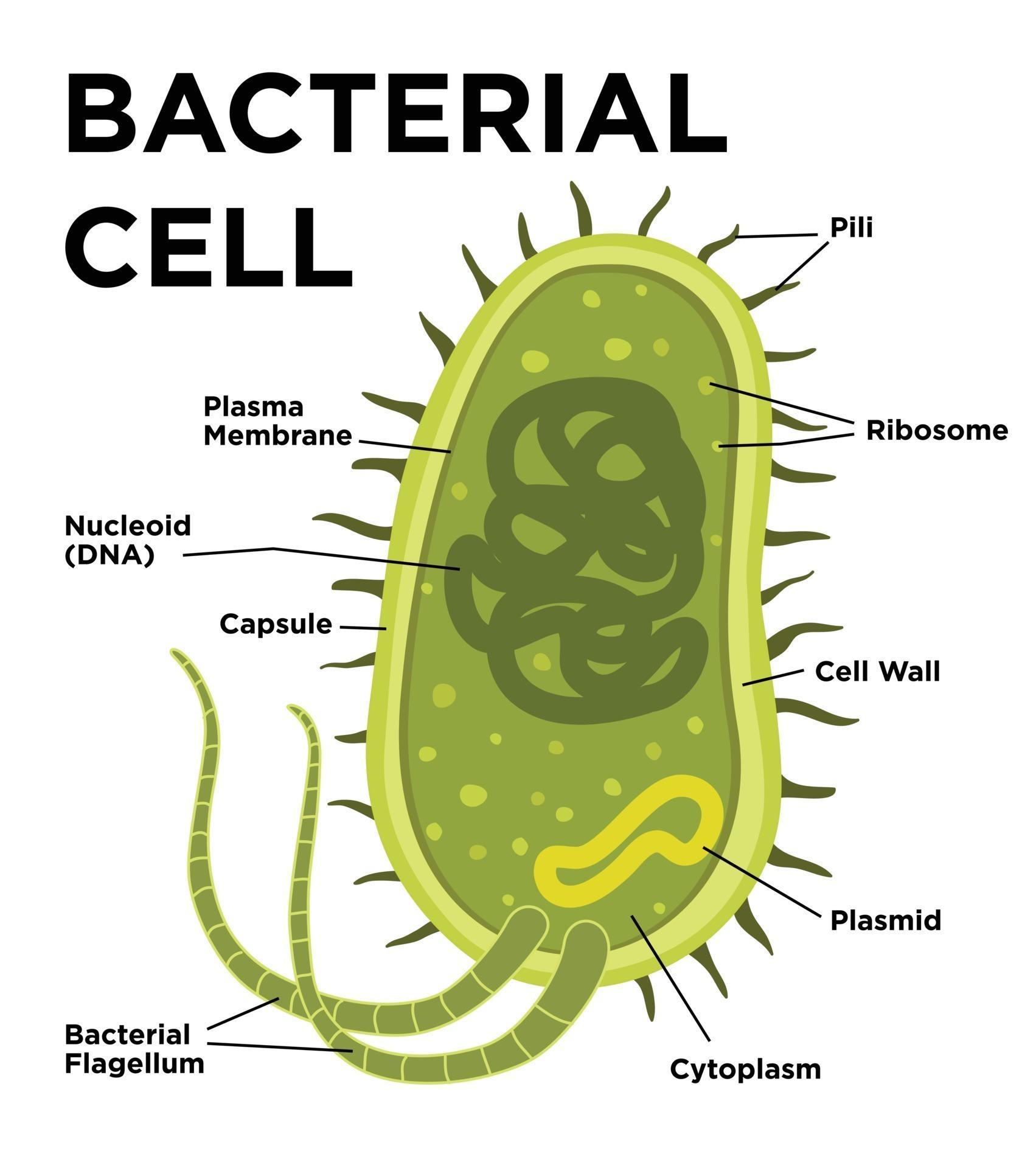
Bacterial cell anatomy in flat style. Vector modern illustration. Labeling structures on a
Key points: Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms belonging to the domains Bacteria and Archaea. Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells, have no nucleus, and lack organelles. All prokaryotic cells are encased by a cell wall. Many also have a capsule or slime layer made of polysaccharide. Ultrasmall Bacteria. Ultrasmall bacteria (150 could fit in a single Escherichia coli) have been discovered in groundwater that was passed through a filter with a pore size of 0.2 micrometers µm). They showed an average length of only 323 nanometers(nm) and an average width of 242 nm. They contain DNA, an average of 42 ribosomes per bacterium, and possessed pili . The three main shapes of bacteria are coccus, spiral, and bacillus. Cocci are bacteria that are spherical or ovoid in shape. Some cocci remain attached after binary fission, even though separate cells have been formed. For example, diplococci are cocci in pairs, streptococci are chains, and staphylococci are clusters of multiple cocci. The structure of the bacteria consists of three major parts: Outer layer (cell envelope), cell interior, and additional structures. Outer layer (Cell envelope): It includes the cell wall of bacteria and the plasma membrane beneath it.
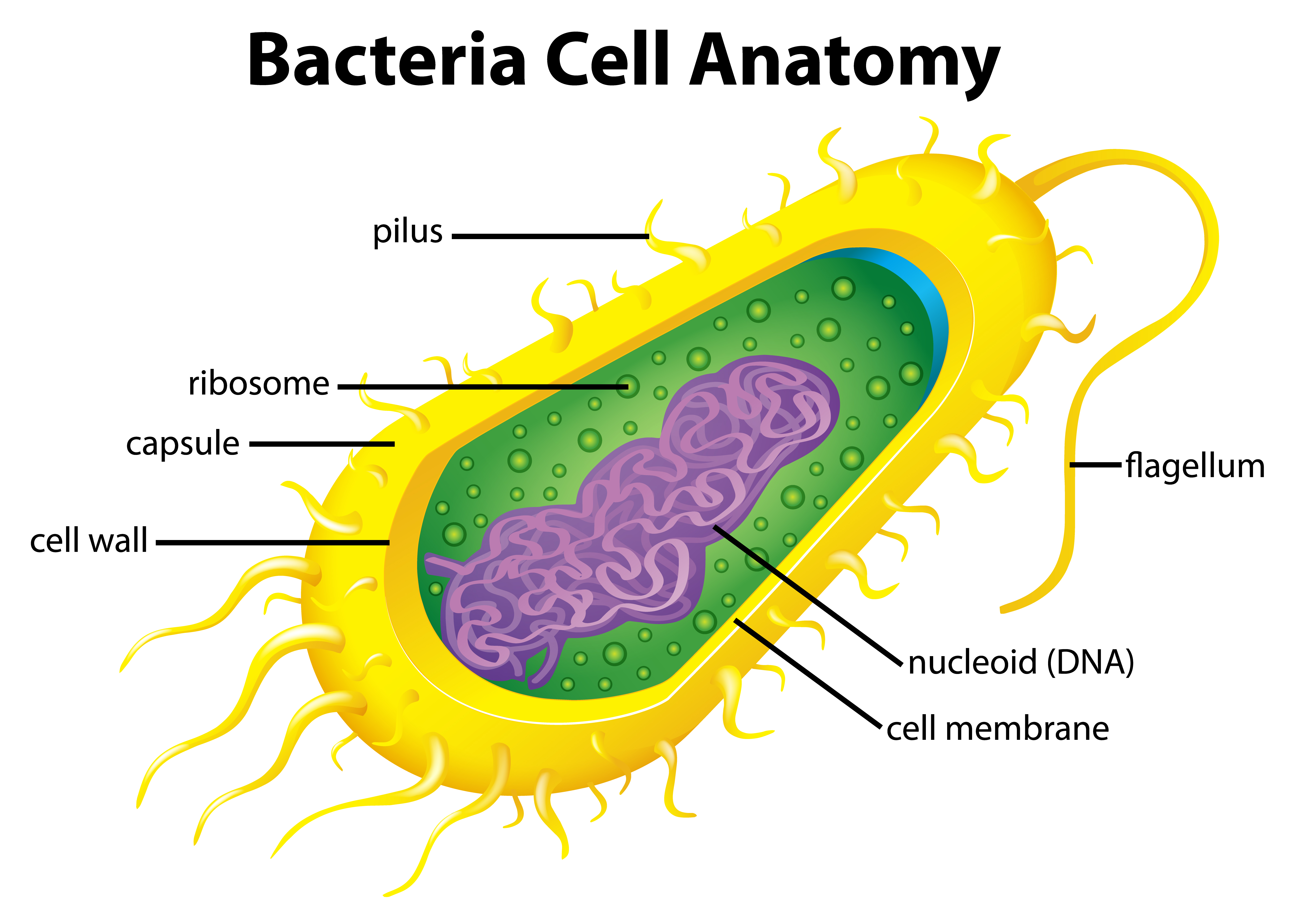
Bacteria Cell Vector Art, Icons, and Graphics for Free Download
The nucleoid and some other frequently seen features of prokaryotes are shown in the diagram below of a cut-away of a rod-shaped bacterium. _Image credit: modified from "Prokaryotic cells: Figure 1" by OpenStax College, Biology, CC BY 3.0 _ Bacterial cell structure The bacterium, despite its simplicity, contains a well-developed cell structure which is responsible for some of its unique biological structures and pathogenicity. Many structural features are unique to bacteria and are not found among archaea or eukaryotes. Bacteria are classified and identified to distinguish one organism from another and to group similar organisms by criteria of interest to microbiologists or other scientists. The most important level of this type of classification is the species level.. Diagram of DNA reassociation. DNA is composed of two purine nucleoside bases, adenine (A. Size of Bacteria. Bacteria are single-celled organisms. This means that each bacterium is made up of only one cell. This is very different from humans. Our bodies are made up of trillions of cells . Bacteria are much smaller than human cells. Bacterial cells are between about 1 and 10 μm long.
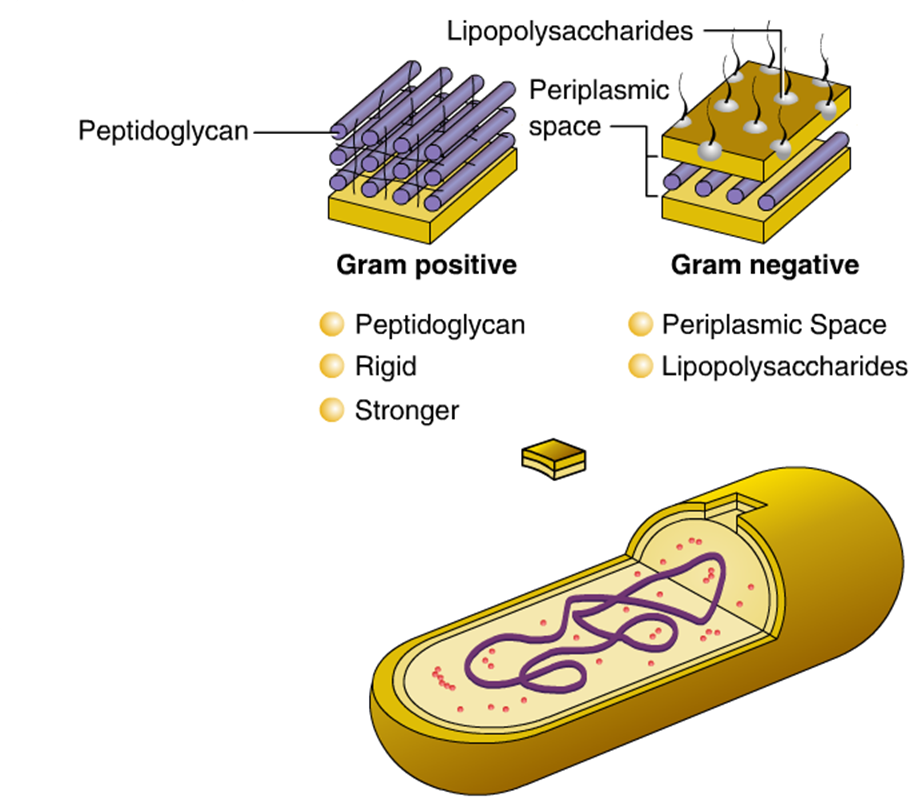
Cellular Structure of Bacteria ZeroInfections
Plasmid Bacteria Diagram with Labels Bacterial cells have simpler internal structures like Pilus (plural Pili), Cytoplasm, Ribosomes, Capsule, Cell Wall, Plasma membrane, Plasmid, Nucleoid, Flagellum, etc. Labeled Bacteria diagram Eukaryotes have been shown to be more recently evolved than prokaryotic microorganisms. Shapes of Bacteria Based on their shape and arrangement, bacteria can be classified into the following four main types: Cocci: spherical, round or oval-shaped, example - Staphylococcus group Bacilli: rod-like or cylindrical shaped, example - Bacillus group, Spirilla: spiral or coil-shaped, example - Spirillum group
Bacteria - Definition, Structure, Diagram, Classification: Bacteria are truly fascinating microorganisms with an incredible ability to adapt and thrive in diverse environments. From their unique structures to their various nutritional and reproductive strategies, they play essential roles in shaping our world. DNA in a nucleus. Plasmids are found in a few simple eukaryotic organisms. Prokaryotic cell (bacterial cell) DNA is a single molecule, found free in the cytoplasm. Additional DNA is found on one.
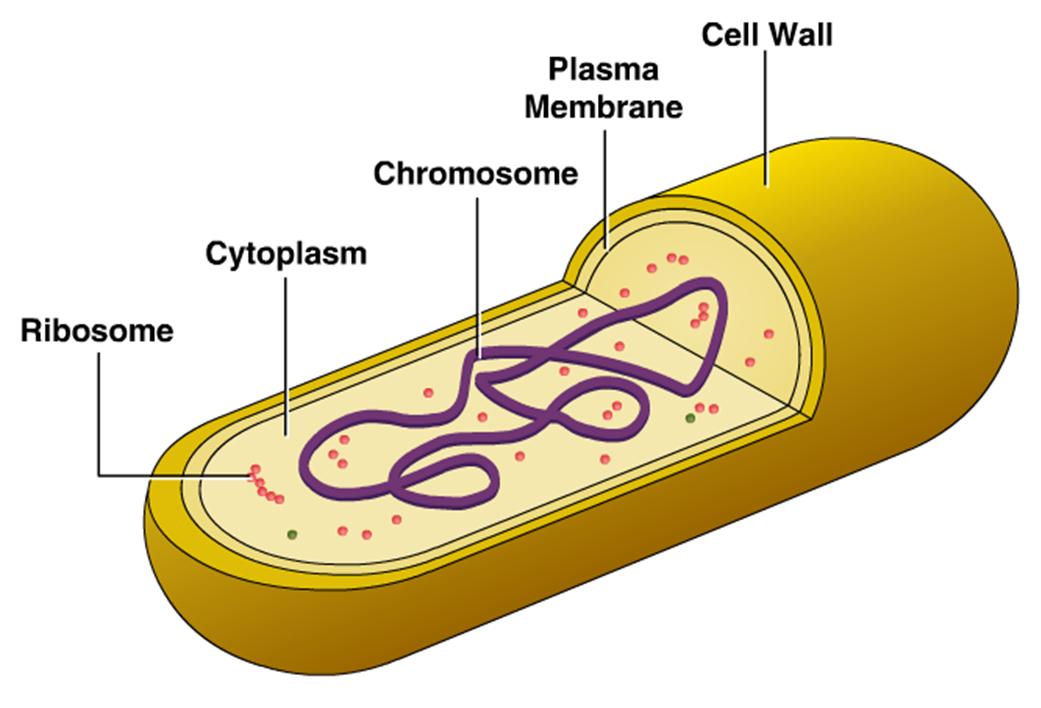
Innovic Medical Bacterial Cell Structure
1. A bacterial cell remains surrounded by an outer layer or cell envelope, which consists of two components - a rigid cell wall and beneath it a cytoplasmic membrane or plasma membrane. ADVERTISEMENTS: 2. The schematic diagram of bacterial cell structure is shown in the Fig.1.The bacteria possess the morphological structures for the purpose of performing some physiological functions, e.g..




