A teeth chart is a simple drawing or illustration of your teeth with names, numbers, and types of teeth. There are separate teeth number charts for adults as well as babies. This diagram helps us learn the names of each tooth, the corresponding number, and their location. Learn about the types of teeth in a fast and efficient way using our interactive tooth identification quizzes and labeled diagrams. This leaves up to eight adult teeth in each quadrant and separates the opposing pairs within the same alveolar bone as well as their counterparts in the opposing jaw. Each quadrant contains: a medial incisor

Mouth Teeth Diagram with Label Health Images Reference
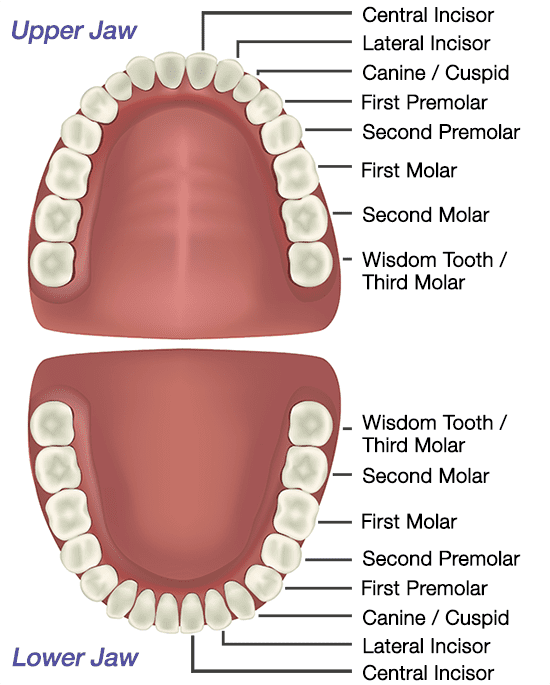
Canines Canines are the sharp, pointed teeth that sit next to the incisors and look like fangs. Dentists also call them cuspids or eyeteeth. Canines are the longest of all the teeth, and people. Diagram of the Tooth Numbering System (viewed as if looking into the mouth) Buccal (Facial) Surface Occlusal Surface Incisal Surface Right Left Maxillary Arch (Upper Jaw) Mandibular Arch (Lower Jaw) Adult Dentition = Permanent teeth 1-32 Child Dentition =Primary teeth A-T Wisdom Teeth =1, 16, 17, and 32 Central Incisor Lateral Incisor Cuspid. A View of the Mouth Inside the Tooth 3D MODEL Tooth eruption There is a broad range of normal times for teeth to push through the gum tissue (erupt) into the mouth. For primary teeth, the central incisors are the first teeth to erupt, occurring at about 6 months of age. Canine teeth help you tear into foods like meat and crunchy vegetables. Sometimes, people call canines "eye teeth" because of their position directly under your eyes. Premolars. Also called bicuspids, premolars sit between your canines and your molars (the teeth in the back of your mouth). Premolar teeth have features of both canines and.

The Anatomy Of A Tooth In Four Parts Arc Dental
Mouth. A molar tooth is located in the posterior (back) section of the mouth. It is found in most mammals that use their posterior teeth to grind food. Twelve molars are usually present in an. The teeth are multifunctional appendages that essential in basic human functions, like eating and speech. Teeth are composed of multiple unique tissues with varying density and hardness that allows them to tolerate the significant forces and wear of mastication. They are attached to the maxilla (upper jaw) and the mandible (lower jaw) of the mouth. Humans have four different types of teeth. The mandible and maxilla - like most bones in the human body - have a core of less dense cancellous bone, wrapped in an outer layer of more dense alveolar bone. The part of the mandible and maxilla that are in the mouth are covered by the gums. And the teeth rest in bony sockets within the mandible and maxilla and are surrounded by the gums. In this section, you will examine the anatomy and functions of the three main organs of the upper alimentary canal—the mouth, pharynx, and esophagus—as well as three associated accessory organs—the tongue, salivary glands, and teeth. The Mouth The cheeks, tongue, and palate frame the mouth, which is also called the oral cavity (or buccal cavity).
The Anatomy of Your Teeth Detailed information
What's my mouth's function? Your mouth supports many daily functions, including: Breathing. Talking. Chewing. Tasting. Swallowing. Eating. Drinking. Mouth function in digestive system Your mouth is where digestion begins. When you chew food, your salivary glands make saliva (spit). Saliva helps break down starches in the foods you eat. The mouth (oral cavity) consists of several components, including the teeth, gingiva (gums), tongue, palate, cheeks, lips and floor of the mouth. With the exception of the teeth, the mouth is lined by mucous membranes. The Teeth. The teeth are held within the jaw bones and serve several important functions beyond allowing you to chew.
The mouth is the entrance to both the digestive and the respiratory systems. The inside of the mouth is lined with mucous membranes. When healthy, the lining of the mouth (oral mucosa) ranges in color from reddish pink to gradations of brown or black. The oral mucosa tends to be darker in dark-skinned individuals because their melanocytes. It's made up of several parts: Root canal. The root canal is a passageway that contains pulp. Cementum. Also called cement, this bone-like material covers the tooth's root. It's connected to the.

Human Teeth Structure With Labels Ilustración de stock Getty Images
Roof The roof of the mouth proper consists of the hard and soft palates. The hard palate is found anteriorly. It is a bony plate that separates the nasal cavity from the oral cavity. It is covered superiorly by respiratory mucosa (ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium) and inferiorly by oral mucosa (stratified squamous epithelium). tooth tongue salivary gland palate lips mouth, in human anatomy, orifice through which food and air enter the body. The mouth opens to the outside at the lips and empties into the throat at the rear; its boundaries are defined by the lips, cheeks, hard and soft palates, and glottis.




