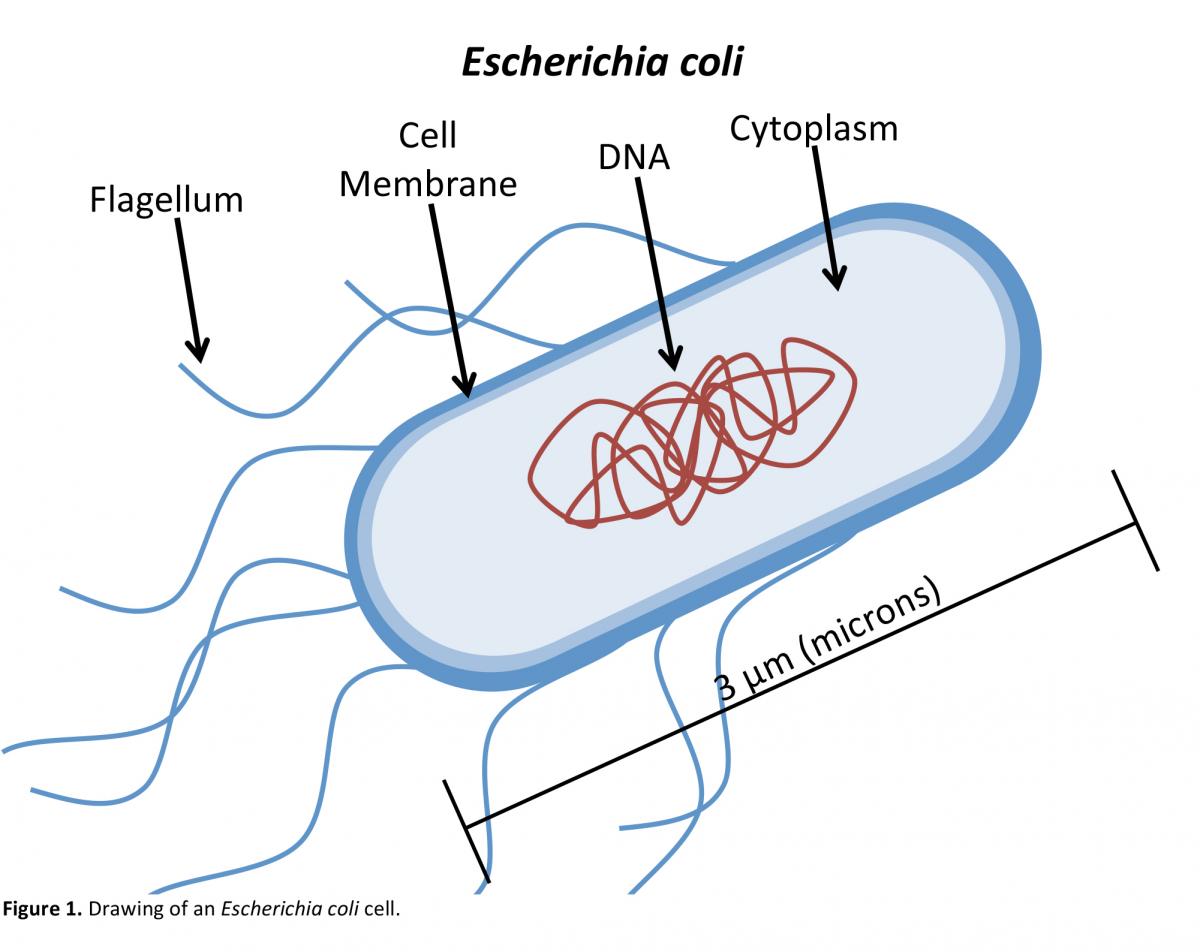
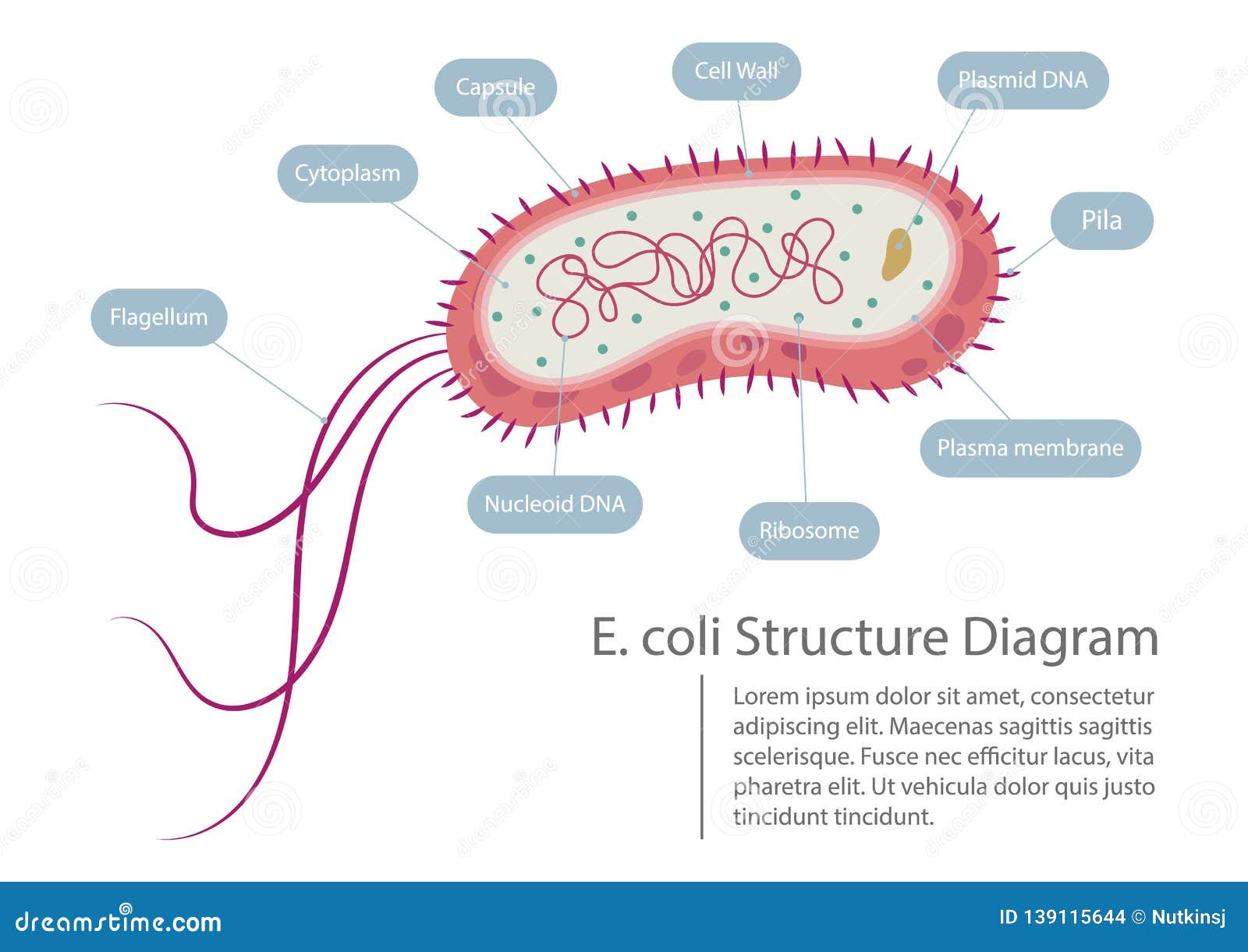
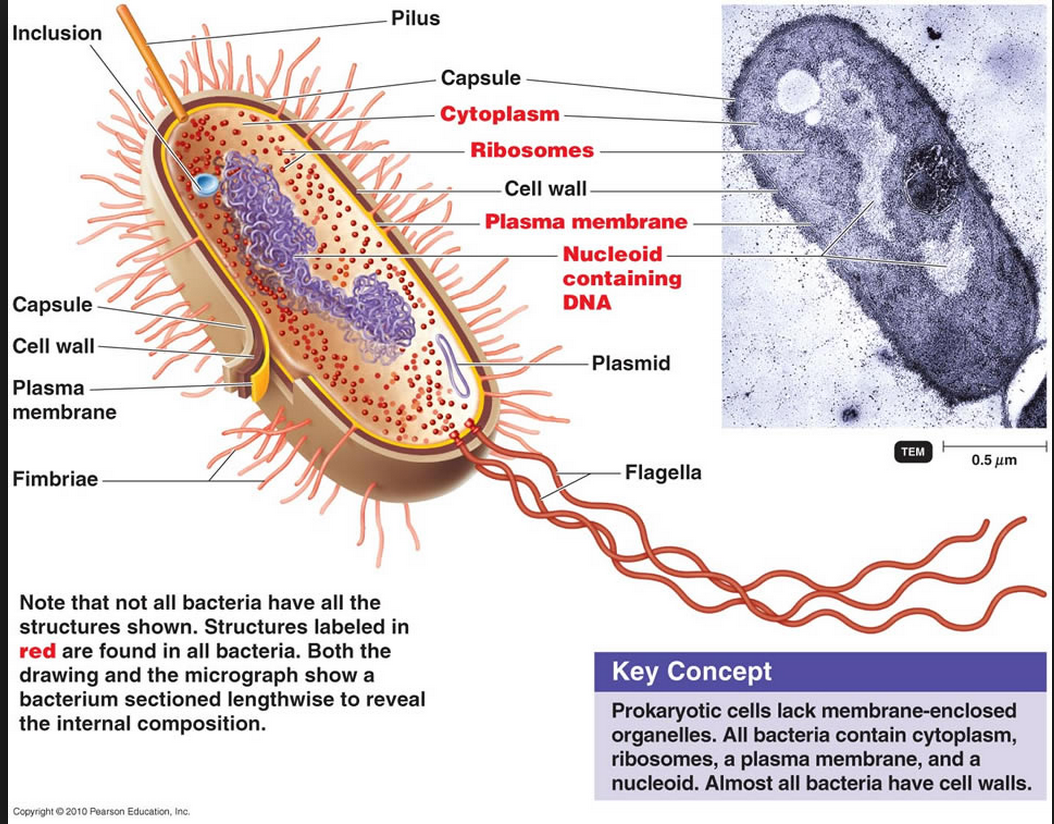
Biology and biochemistry Model of successive binary fission in E. coli Type and morphology E. coli is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobe, nonsporulating coliform bacterium. [18] Cells are typically rod-shaped, and are about 2.0 μm long and 0.25-1.0 μm in diameter, with a cell volume of 0.6-0.7 μm 3. [19] [20] [21] Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a gram negative, facultative anaerobic, coliform, rod shaped bacterium It is a part of the normal flora of the intestine of humans and many warm blooded animals; it provides benefits such as production of vitamin K2 and a stable environment where more beneficial bacteria can prosper ( Elife 2015;4:e05826 )
E Coli Drawing at GetDrawings Free download
Escherichia coli ( E. coli) is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, facultative anaerobic bacterium. This microorganism was first described by Theodor Escherich in 1885. Most E. coli strains harmlessly colonize the gastrointestinal tract of humans and animals as a normal flora. E. coli is a facultative (aerobic and anaerobic growth) gram-negative, rod shaped bacteria that can be commonly found in animal feces, lower intestines of mammals, and even on the edge of hot springs. They grow best at 37 C. E. coli is a Gram-negative organism that can not sporulate. Escherichia coli is a remarkable and diverse organism. This normally harmless commensal needs only to acquire a combination of mobile genetic elements to become a highly adapted pathogen. Home » Bacteriology E. coli (Escherichia coli)- An Overview June 23, 2022 by Sagar Aryal Edited By: Sagar Aryal Table of Contents Habitat of E. coli Morphology of E. coli Antigenic Structure H or Flagellar Antigen O or Somatic Antigen K or Capsular Antigen F or Fimbrial Antigen Cultural Characteristics of E. coli E. coli on Nutrient Agar (NA)

E. coli Symptoms; 14 Warning Signs & Symptoms of E. coli Healthella
Binary fission is a method of asexual reproduction involving the splitting of the parent organism into two separate organisms. IB Biology notes on 2.2 Prokaryotic cells However, optical microscopy studies of single E. coli have been limited by its small size, ∼1 × 3 μ m, not much larger than the optical resolution, ∼0.25 μ m. As a result, not enough quantitative dynamical information on the life cycle of single E. coli is presently available. Researchers uncovered the foundations of biology by using E. coli as a model organism. But over-reliance on this microbe can lead to knowledge blind spots with implications for antibiotic resistance. The haploid circular chromosome in E. coli consists of ~ 4.6 x 10 6 bp. If DNA is relaxed in the B form, it would have a circumference of ~1.5 millimeters (0.332 nm x 4.6 x 10 6) ( Fig 1A ). However, a large DNA molecule such as the E. coli chromosomal DNA does not remain a straight rigid molecule in a suspension.
Escherichia Coli Stock Illustrations 744 Escherichia Coli Stock Illustrations, Vectors
The trp operon, found in E. coli bacteria, is a group of genes that encode biosynthetic enzymes for the amino acid tryptophan. The trp operon is expressed (turned "on") when tryptophan levels are low and repressed (turned "off") when they are high. The trp operon is regulated by the trp repressor. E. coli, like most bacteria,. A diagram showing D N A replication. Separated double strand D N A is shown in black. The top black strand runs 3 prime to 5 prime and is attached to a leading strand that is growing from 5 prime to 3 prime due to D N A polymerase moving towards the 3 prime end of the leading strand. The 5 prime end of this.
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a bacterium that is commonly found in the gut of humans and warm-blooded animals. Most strains of E. coli are harmless. Some strains however, such as Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC), can cause severe foodborne disease. E. coli causes wound infections, usually a result of fecal contamination of external wounds or a result of wounds that cause trauma to the intestinal tract, such as surgical wounds, gunshot wounds, knife wounds, etc. E. coli is by far the most common Gram-negative bacterium causing sepsis. Septicemia is a result of bacteria getting into the.
bacteria multiplying diagram
E. coli is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic rod that is part of the normal intestinal flora and grows easily in most culture media. E. coli is classified into between 150 and 200 serotypes or serogroups based on somatic (O), capsular (K) and flagellar (H) antigens. Key Facts About Food Poisoning December 1, 2022 , Escherichia coli (abbreviated as E. coli) are bacteria found in the environment, foods, and intestines of people and animals.




