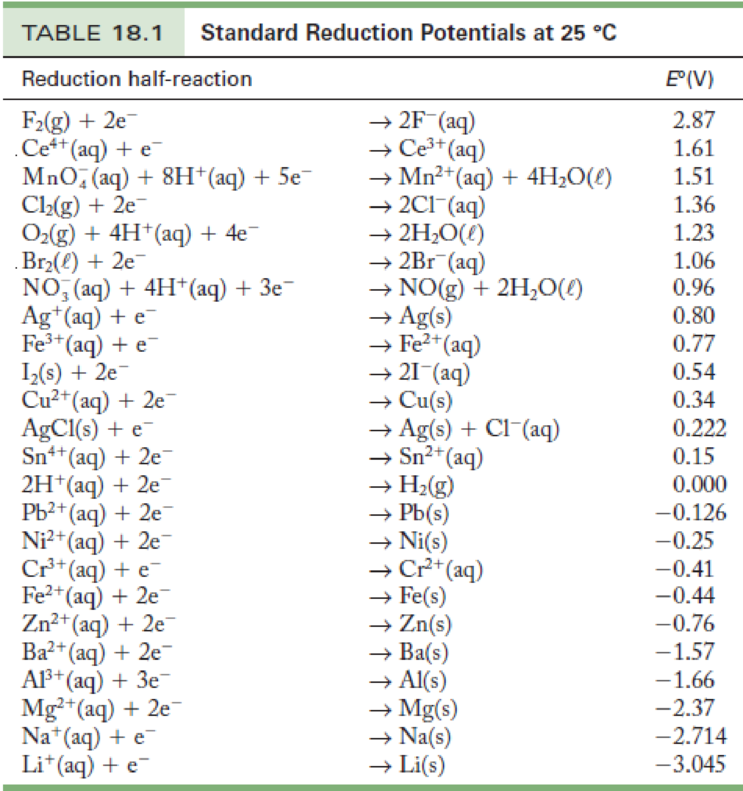
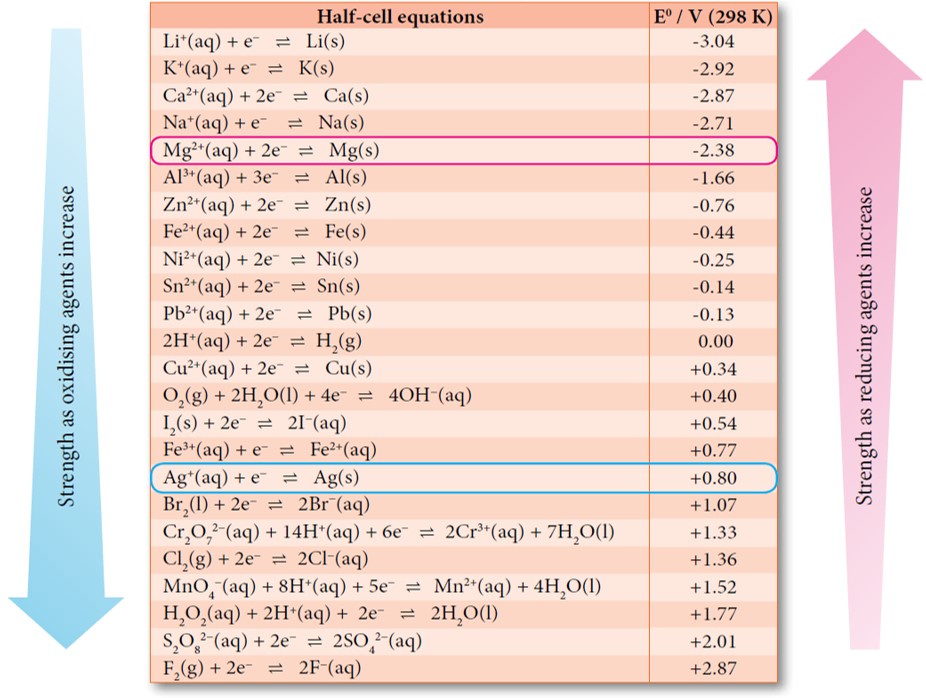
Table of standard electrode potentials Legend: ( s) - solid; ( l) - liquid; ( g) - gas; ( aq) - aqueous (default for all charged species); ( Hg) - amalgam; bold - water electrolysis equations. See also Galvanic series lists electrode potentials in saltwater Standard apparent reduction potentials in biochemistry at pH 7 The following table provides E o for selected reduction reactions. Values are from the following sources: Bard,. New York, 1985; Milazzo, G.; Caroli, S.; Sharma, V. K. Tables of Standard Electrode Potentials, Wiley: London, 1978; Swift, E. H. Standard Reduction Potential E° (volts) Li + (aq) + e-\(\rightleftharpoons\) Li(s)-3.040: Rb.
Standard Potential Table / 18 4 Standard Electrode Potential Powerpoint Presentation Free Online
Standard Electrode Potentials in Aqueous Solution at 25°C Cathode (Reduction) Half-Reaction: Standard Potential E. Standard Electrode Potentials. To measure the potential of the Cu/Cu 2 + couple, we can construct a galvanic cell analogous to the one shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\) but containing a Cu/Cu 2 + couple in the sample compartment instead of Zn/Zn 2 +.When we close the circuit this time, the measured potential for the cell is negative (−0.34 V) rather than positive. Physical & Theoretical Chemistry Thermodynamics and Chemical Equilibrium (Ellgen) 17: Electrochemistry Standard Electrode Potentials In an electrochemical cell, an electric potential is created between two dissimilar metals. This potential is a measure of the energy per unit charge which is available from the oxidation/reduction reactions to drive the reaction.

Electrochemical Series Electrochemistry, Chemistry, Chemistry notes
The electrode potential (EX) for a half-cell X is defined as the potential measured for a cell comprised of X acting as cathode and the SHE acting as anode: Ecell = EX −ESHE ESHE = 0V(defined) Ecell = EX E cell = E X − E SHE E SHE = 0 V (defined) E cell = E X In electrochemistry, electrode potential is the voltage of a galvanic cell built from a standard reference electrode and another electrode to be characterized. [1] By convention, the reference electrode is the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE). It is defined to have a potential of zero volts. Essential Laboratory Skills Guide Weighing the right way These electrode potentials are given in volts relative to the standard hydrogen electrode. The values below are standard electrode potentials taken at 298 K, 1 bar pressure and in aqueous solution, of concentration 1 molar. [1] [2] [3] [4] References Tables of Standard Electrode Potentials. Journal of The Electrochemical Society , Volume 125 , Number 6 Citation G. Milazzo et al 1978 J. Electrochem. Soc. 125 261C DOI 10.1149/1.2131790.
Standard Electrode Potential
Electrode potential Measuring potential Electrical double layer Table of standard reduction potentials Download chapter PDF Electroneutrality One of the basic phenomena in nature is the preservation of electroneutrality , the tendency to discourage and oppose any processes that lead to an excess of positive or negative charge. The standard electrode potential, \(E^{\circ}\), for a half-reaction is the potential when all species are present at unit activity or, for gases, unit fugacity.. The appendix in Chapter 35.8 provides a table of standard state reduction potentials for a wide variety of half-reactions at 298 K.
Introduction; 18.1 Periodicity; 18.2 Occurrence and Preparation of the Representative Metals; 18.3 Structure and General Properties of the Metalloids; 18.4 Structure and General Properties of the Nonmetals; 18.5 Occurrence, Preparation, and Compounds of Hydrogen; 18.6 Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Carbonates; 18.7 Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Nitrogen The standard hydrogen electrode is a half-cell used as a reference electrode and consists of:. Hydrogen gas in equilibrium with H + ions of concentration 1.00 mol dm-3 (at 100 kPa); 2H + (aq) + 2e-⇌ H 2 (g). An inert platinum electrode that is in contact with the hydrogen gas and H + ions; When the standard hydrogen electrode is connected to another half-cell, the standard electrode.

Electrode Potential and Standard Electrode Potential EMF Embibe
Standard electrode potential is a measurement of the potential for equilibrium. There is a potential difference between the electrode and the electrolyte called the potential of the electrode. When unity is the concentrations of all the species involved in a semi-cell, the electrode potential is known as the standard electrode potential. Topological index (numeric number) is a mathematical coding of the molecular graphs that predicts the physicochemical, biological, toxicological, and structural properties of the chemical compounds that are directly associated with the molecular graphs. The Zagreb connection indices are one of the TIs of the molecular graphs depending upon the connection number (degree of vertices at distance.




