Garden classification of hip fractures Last revised by Joshua Yap on 28 Feb 2023 Edit article Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data The Garden classification of subcapital femoral neck fractures is the most widely used. It is simple and predicts the development of osteonecrosis 1,2. 65 Cases 55 Evidence 430 Video/Pods 29 Techniques 4 Images Summary Femoral neck fractures are common injuries to the proximal femur associated with increased risk of avascular necrosis, and high levels of patient morbidity and mortality. Diagnosis is generally made radiographically with orthogonal radiographs of the hip.

Garden classification of hip fractures Radiology Reference Article Hip
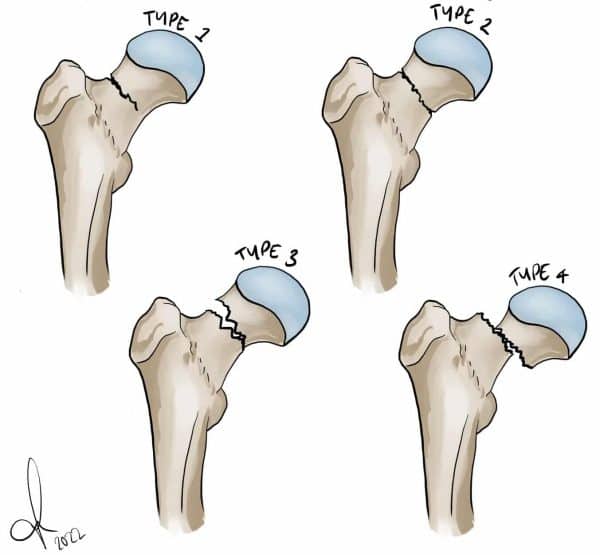
The Garden classification incorporates displacement, fracture completeness, and relationship of bony trabeculae in the femoral head and neck. Gardens' originally reviewed 80 patients with femoral neck fractures, which he classified in Types I to IV, and he followed these patients for at least 12 months postoperatively. The Garden classification is the most commonly used to classify intracapsular femoral neck fractures [1]. It is simple and predicts the development of Avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Garden splits into four categories depending on the severity of the fracture and the degree of displacement. Classification of Hip Fractures Neck of femur (NOF) fractures, or femoral neck fractures, are common injuries sustained by older patients who are more likely to have both unsteadiness of gait and reduced bone mineral density, predisposing to fracture. Elderly osteoporotic women are at greatest risk. Epidemiology The Garden classification is a system of categorizing intracapsular hip fractures of the femoral neck. This fracture often disrupt the blood supply to the femoral head .
Neck of Femur Fracture Subcapital Intertrochanteric TeachMeSurgery
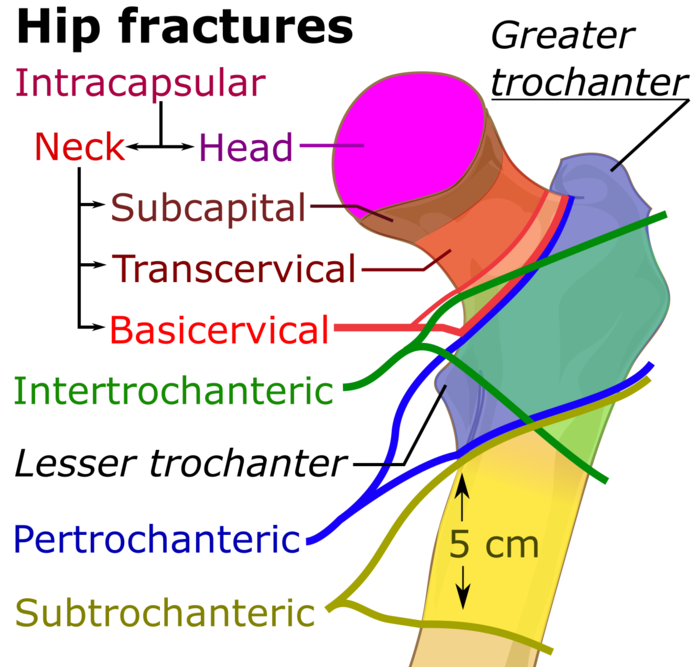
Hip fractures are an important health-care concern in the elderly population. Currently, hip fractures affect 18% of women and 6% of men globally. 1 Epidemiological studies have demonstrated that the incidence of hip fractures had increased from 1986 to 1995 but then steadily declined until 2012. Garden classification is the most commonly used classification system for femoral neck fractures. It was devised in 1961 by a British orthopaedic surgeon, who divided them into four stages according to displacement of fragments. It is considered superior to Pauwels classification. Classifications, online calculators, and tables in radiology Examples of Fracture-Specific Descriptive Classifications. Garden - guides management/surgical plan. Neer - assists describing fracture for communication. Schatzker - can predict associated injuries and prognosis. Lauge-Hansen - provides insight into mechanism. Sanders - an example of CT-based classification. HHS Vulnerability Disclosure Hip fractures are one of the most frequent fractures presenting to the emergency department and orthopedic trauma teams. The terms hip fracture and neck of femur fracture are used synonymously. Both terms describe a fracture of the proximal femur between the femoral head and 5 cm distal to the lesser trochanter.

Hip fractures in young adults Orthopaedics and Trauma
Garden classification of hip fractures (diagram) Case contributed by Frank Gaillard Diagnosis not applicable Share Add to Citation, DOI, disclosures and case data Diagram Garden classification images. 1 article features images from this case 12 public playlists include this case Related Radiopaedia articles Garden classification of hip fractures In the classification of Garden, Garden I hip fractures are expressed as the non-displaced FNFs, accounting for 15 to 20 percent of all the FNFs. The injury mechanism is the excessive external rotation leading to retroversion and valgus of femoral head.
Hip fractures is classified into intracapsular and extracapsular fractures. Intracapsular fractures (femoral neck fractures): Occurs within the hip capsule; accounts for 45% of all acute hip fractures in the elderly; susceptible to malunion/avascular necrosis of the HOF because of the limited blood supply to the area. The Femoral Neck Fractures, Garden Classification is the most commonly. with leg shortening is possible. The Garden classification distinguishes nondisplaced (Garden I and II) from displaced fractures (Garden III and IV) (Figure 2, 3). Prevention of hip fracture The majority of hip fractures occur in osteoporotic persons who fall. The occurrence of a minimal trauma fracture, in the absence of another cause of.
Femoral Neck Hip Fracture Physiopedia
Description Garden's classification is based on AP radiographs of the hip ( Table 1 ). Four types of fractures are included, incomplete and valgus impacted (Type I, Fig. 1A ), complete and nondisplaced (Type II, Fig. 1B ), complete and partially displaced (Type III, Fig. 1C ), and complete and fully displaced (Type IV, Fig. 1D ). 10. Pelvis & Hip Garden Classification of Femoral Neck Fractures References: Sheehan, S. E., et al. (2015). "Proximal Femoral Fractures: What the Orthopedic Surgeon Wants to Know." Radiographics 35 (5): 1563-1584. Garden R S. Low angle fixation in fractures of the femoral neck. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 1961; 43: 647-63 Page Views: 18,287




