Example 1: A solvent front traveled for 0.7cm on a thin-layer chromatography paper (TLC) while a compound traveled for 0.5 cm. Calculate the Rf value. Therefore, the rf value is 0.7. Example 2: Calculate the Rf value if a compound travels 2.5 cm and the solvent front travels 6.0 cm. Therefore, the rf value is 0.42. Follow a step-by-step guide on calculating RF values in chromatography. We provide clear instructions, ensuring that even beginners can navigate the process effortlessly. Boost your confidence as you become adept at this crucial analytical skill. Tips and Tricks for Accurate RF Value Calculation Optimizing Chromatographic Conditions

Chromatograms & Calculating Rf Values Chromatography GCSE Chemistry YouTube
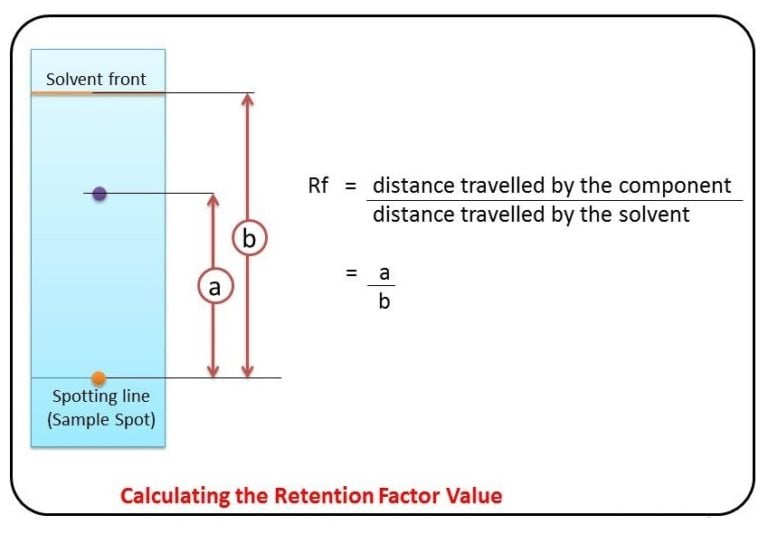
What is R F Value? The R f (retardation factor) value is the ratio of the solute's distance travelled to the solvent's distance travelled. The word comes from chromatography when it was discovered that a given component will always travel the same distance in a given solvent under the same conditions. In thin-layer chromatography, the retention factor (Rf) is used to compare and help identify compounds. The Rf value of a compound is equal to the distance traveled by the compound divided by the distance traveled by the solvent front (both measured from the origin). Chemistry RF Value Calculator Distance Traveled By Solute: Distance Traveled By Solvent: Calculate RF Value RF Value: About RF Value Calculator (Formula) The RF value calculator is a tool used in chromatography to calculate the retention factor or RF value of a compound. Calculation Methodology The crux of our journey lies in understanding how to calculate RF values. The formula involves the ratio of the distance traveled by the compound to the solvent front. This step-by-step guide ensures precision, making RF value calculation a breeze. Factors Influencing RF Values
Paper Chromatography Definition, Types, Principle, Steps, Uses
In this video you will learn all the science for this topic to get a grade 9 or A* in your science exams! In this video, you will learn this model answer to. 5 min read Chromatography and Rf Values (GCSE Chemistry) Chromatography Chromatography can separate mixtures. By using chromatography, we can separate mixtures. This will help us to identify the substances within the mixture. Chromatography has two phases. There are two phases in chromatography, called the mobile phase and the stationary phase. Formula The formula for calculating the RF Value is straightforward: RF Value = Distance Traveled by Solute (DSU) / Distance Traveled by Solvent (DSV) Distance Traveled by Solute (DSU) represents the distance the solute travels from its origin on the chromatographic medium. Rf values range from 0 to 1, with values closer to 1 indicating that the component is more attracted to the solvent than to the stationary phase. How to Calculate Rf Values. To calculate Rf values, first, measure the distance the solvent traveled from the starting line to the solvent front.

Explaining how to calculate Rf values YouTube
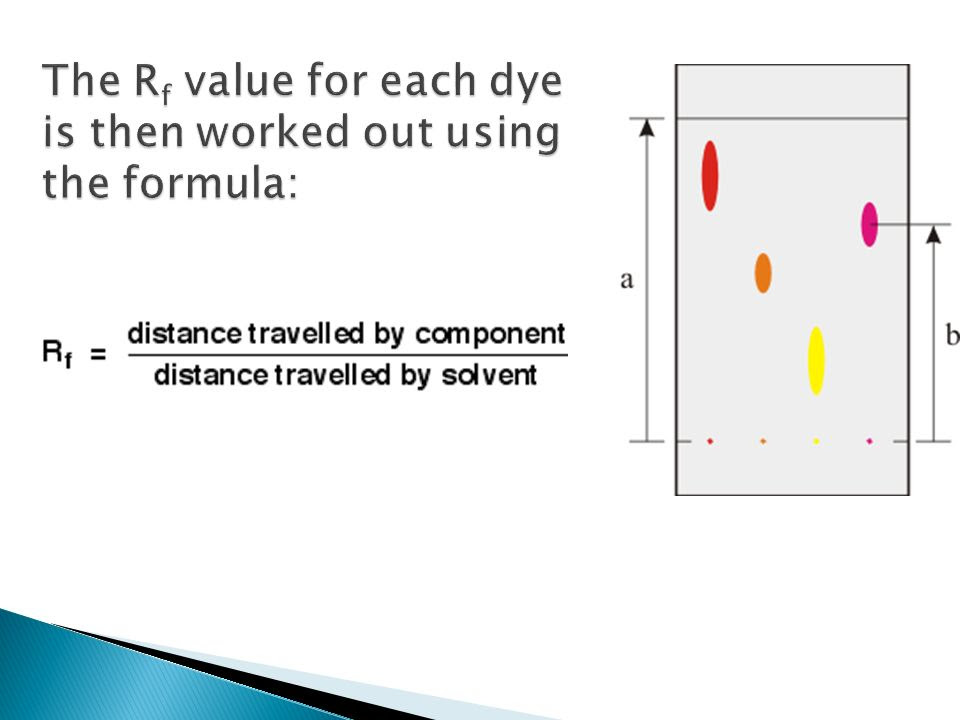
Demonstration to show hot to carry out paper chromatography to identify components in an unknown mixture. Includes explanations and how to calculate Rf value. The Rf value for a particular substance is always the same if the same solvent and stationary phase are used. The R f value of a spot is calculated using: R f =\(\frac{distance \ travelled \ by.
Retardation or retention factor (Rf) value is the ratio of distance traveled by the analyte to that of the solvent front on a chromatogram. The chromatographic techniques in which the analytes are added to the stationary phases show a difference in the movement of analytes with mobile solvents (phases). Click the "Calculate" button to obtain the Rf value. Example: Suppose the distance traveled by the substance is 4.5 cm, and the distance traveled by the solvent is 2.0 cm. After entering these values and clicking "Calculate," the Rf value would be 2.25.
How To Calculate Rf Values
Rf = Distance moved by analyte (A) / Distance moved by solvent front. To calculate the RF value, you simply divide the distance moved by the compound by the distance moved by the solvent front. The resulting value ranges from 0 to 1, with higher values indicating a greater affinity for the mobile phase. Calculating RF values allows scientists. Formula: The Rf value is calculated using the formula: =Distance Traveled by CompoundSolvent Front Distance Rf =Solvent Front DistanceDistance Traveled by Compound How to Use: Enter the distance traveled by the compound in the provided field. Enter the solvent front distance in the respective field.



