How to Look Inside Your Dog's Mouth Nanaimo Veterinary Hospital 9 subscribers Subscribe Subscribed 40 Share 26K views 10 years ago Veterinarian Dr. Brett Hayward provides instructions and a. 25/04/2023 04/02/2022 by Sonnet Poddar The dog mouth anatomy includes the lip, oral cavity, and associated structures. But, the term mouth includes only the opening between the lips into the vestibule of the oral cavity.

A Dog's Mouth Ever wonder what the inside view of a dog's … Flickr
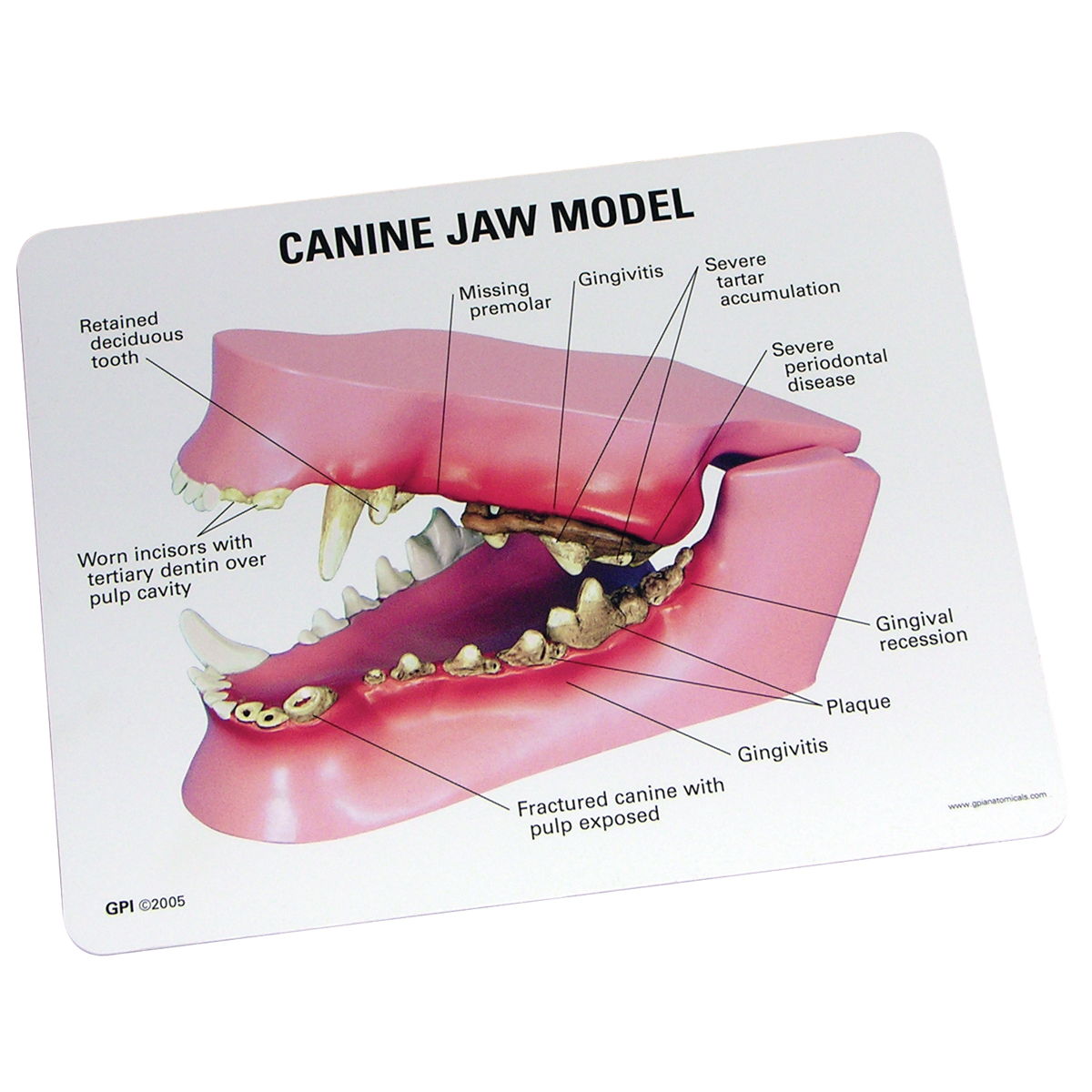
Canine stomatitis involves inflammation of the mucous membranes of the mouth. Signs include severe gum inflammation, receding gums in several sites, and large sores on the mouth surface near the surfaces of large teeth. You may notice a mass inside your dog's mouth that may be adjacent to a tooth, attached to the gum, inside of the lip, in the back of the throat, or even underneath the tongue. At times, the mass may become ulcerated (skin becomes inflamed and raw) or infected. Other signs include: Foul breath. Bleeding from the mouth or bloody saliva. Drooling Oct 13, 2023 Summary: In this blog, we learn all about the dog mouth anatomy. We'll discover what healthy dog gums should look like, the dog teeth anatomy, and how to keep your dog's mouth clean… Dog Mouth Anatomy Like our human mouths, the dog mouth contains a tongue, teeth, and gums, and the mouth is surrounded by cheeks and lips. One of the most common mouth-related conditions that veterinarians generally see in dogs is injury from foreign objects (like sticks, pieces of mulch or rawhide) embedded in a dog's mouth, says Dr. Amy Stone, Clinical Assistant Professor at the University of Florida's College of Veterinary Medicine in Gainsville, Fla.
dog jaw anatomy
What's That Bump in My Dog's Mouth? Humans are not the only ones to get lumps and bumps on their bodies. Canines also frequently develop odd-looking masses and growths. According to the Pet Cancer Center, oral cancer is the fourth most common cancer overall in dogs. Have your vet examine your dog's mouth at least once per year, and always bring your dog to the vet if you suspect anything is wrong, such as pain, swelling, a bad odor, blood, discharge, or if you see a mass or growth in or around your dog's mouth. Certain breeds may have malocclusion, the most common being an overbite or underbite. The mouth is located in the lower, front part of the face and is considered the entire area between the upper and lower jaws. The mouth includes the space just outside the teeth and gums, and just inside the lips and cheeks. The main part of the mouth, or oral cavity proper, is bound on the top by the hard palate and the soft palate. Causes of Inflammation of the Mouth in Dogs. If your dog is experiencing inflammation in his mouth, it might be caused by a dental issue. Other causes of inflammation in a dog's mouth include: Bacterial infection. Viruses. Diabetes. Thyroid or immune disorder. Cancer. Toxicosis.

Bad breath Thick, tacky saliva Dry cracked tongue Plaque & calculus accumulation Ulceration or
Visible mass in the mouth. Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck (occasionally) Swollen or deformed areas on the face. Causes. In most cases, there is no identifiable cause for cancer of the mouth in dogs. Diagnosis. As part of a thorough physical examination, your veterinarian will look inside your dog's mouth for tumors or other abnormalities. Canines are the long and pointed teeth found towards the front of your dog's mouth, behind the incisors on the dog dental chart. These teeth are used for tearing food such as meat apart. They are also used to lock on to an item a dog may have in its mouth, such as a bone or chew toy. Dogs grow four canine teeth, two on both the bottom and.
Some of the most common mouth problems in dogs include gingivitis, oral trauma, an embedded foreign body, tumors, and oral warts (papillomatosis) Daily teeth brushing and regular at-home and veterinary oral exams are the best way to keep on top of any changes or problems developing in your pet's mouth. There are a number of things that can go. Yes, mouth cancer in dogs is painful. Dogs with oral tumors show obvious signs of oral pain - reluctance to eat, yelping when chewing, trouble swallowing, excess drooling. In general. dogs are good at hiding pain. However, the healthy appetite combined with inability to eat is a telltale sign.

mouth (dog) Dog anatomy, Vet medicine, Animal medicine
The symptoms of dog warts can vary depending on where the warts are located. They can range from small, raised bumps on the dog's skin to large cauliflower-like lesions with sizes up to 3cm. With oral papillomatosis, large clusters of dog warts are found in and around the oral cavity. Oral papillomatosis can cause discomfort, hypersalivation. What Are Mouth Ulcers in Dogs? Oral ulcers are disruptions or breaks in the surface of the skin or mucous membrane of the mouth. An ulcer is a more severe version of erosion and excoriation, which are also types of epithelial defects. Dogs can have a mouth ulcer that affects the skin of the lips outside the mouth or the mucosa inside the oral.




