¡Precios increíbles y alta calidad aquí en Temu. Envío gratuito en todos los pedidos. ¡Solo hoy, disfruta de todas las categorías hasta un 90% de descuento en tu compra. Learn More About Dino Light & Find An Authorized Dino-Lite Reseller Today!

Flashcard of iron with atomic mass Royalty Free Vector Image
Characteristics Allotropes Molar volume vs. pressure for α iron at room temperature At least four allotropes of iron (differing atom arrangements in the solid) are known, conventionally denoted α, γ, δ, and ε . The first three forms are observed at ordinary pressures. Element Iron (Fe), Group 8, Atomic Number 26, d-block, Mass 55.845. Sources, facts, uses, scarcity (SRI), podcasts, alchemical symbols, videos and images.. The mass of an atom relative to that of carbon-12. This is approximately the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.. These atoms that have been lost from the. Fig. 1. Melting temperature TM, and density, ρ, versus atomic number Z of the elements of the first transition period. Iron is found between these two groups of elements. It crystallizes in both the fcc (912° < Tγ < 1394°C) and the bcc lattices (1394° > Tα < 1538°C) and again at Tα <912°C. ferroalloy alpha iron beta iron gamma iron oolitic iron deposit On the Web: The Matthau Company - A Giant of an Actor (Jan. 05, 2024) See all related content → iron (Fe), chemical element, metal of Group 8 (VIIIb) of the periodic table, the most-used and cheapest metal. Occurrence, uses, and properties

Iron, atomic structure Stock Image C023/2516 Science Photo Library
Periodic Table element Summary Iron Iron is a chemical element with symbol Fe and atomic number 26. Classified as a transition metal, Iron is a solid at room temperature. 26 Fe Iron View All Properties H He Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Structure, properties, spectra, suppliers and links for: Iron, 7439-89-6, 8048-10-0, 33485-98-2, 70892-58-9. Jump to main content Jump to site nav. Home;. An elemental iron in which the atom has an oxidation state of zero. ChEBI CHEBI:18248, CHEBI:82664: An iron group element atom that has atomic number 26. ChEBI CHEBI:18248,. Iron is also the fourth most common element in Earth's crust by weight and much of Earth's core is thought to be composed of iron.. Atomic weight (average mass of the atom): 55.845; Density: 7.. atomic chemical properties chemical property chemistry d block d-block diagram electron configuration electron shell electronic electrons element elemental elements fe group 8 illustration
Symbol and electron diagram for Iron illustration Stock Vector Image & Art Alamy
This iron atom has 26 protons and 56 − 26 = 30 neutrons. Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\) How many protons are in \(\ce{_{11}^{23} Na}\). The Bohr model of the atom was the first complete physical model of the atom. It described the overall structure of the atom and how atoms bond to each other. Bohr's planetary atomi model was not perfect and. In the body-centered cubic structure, each atom forms a total of 14 bonds to neighboring atoms, although six of these bonds are somewhat weaker than the other eight.. Below 910C, iron metal packs in a body-centered cubic structure, in which the holes are too small to hold carbon atoms.
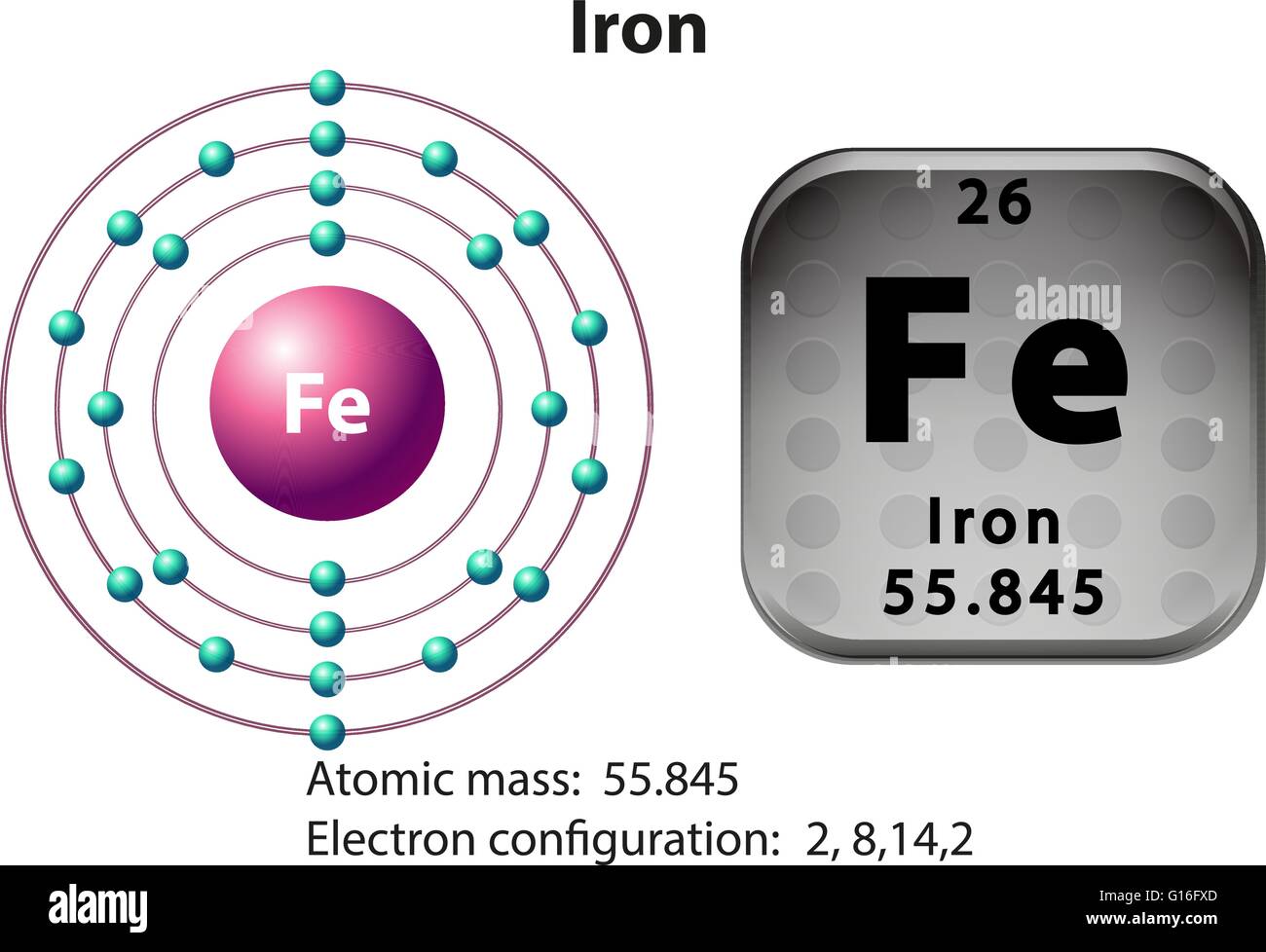
A neutral iron atom contains 26 protons and 30 neutrons plus 26 electrons in four different shells around the nucleus. As with other transition metals, a variable number of electrons from iron's two outermost shells are available to combine with other elements. Iron has two different crystal structures at atmospheric pressure: the body centered cubic (bcc) and the face centered cubic (fcc). In the ground state the bcc α-phase is stable, and at the temperature T=1184 K (A 3 point), α-Fe transforms into fcc α-Fe, which is stable up to 1665 K (A 4 point). Above this temperature, iron transforms back.

Iron, atomic structure Stock Image C013/1539 Science Photo Library
Crystal structure: cubic, body centered: Physical properties; State of matter. A typical iron atom has 56 times the mass of a typical hydrogen atom. Iron is the most abundant metal, and is believed to be the tenth most abundant element, in the universe. This activity checks on the misconceptions that: The structure of iron is an example of a giant molecule. The atoms of iron are held together by ionic bonds. Iron conducts electricity because iron atoms move through the solid. Iron expands when heated because the atoms get bigger. Iron metal is silver because iron atoms are silver.




