The regions of the body are labeled in boldface. A body that is lying down is described as either prone or supine. Prone describes a face-down orientation, and supine describes a face up orientation. These terms are sometimes used in describing the position of the body during specific physical examinations or surgical procedures. Regional Terms Human body diagrams [edit]. Main article at: Human body diagrams Template location:Template:Human body diagrams How to derive an image [edit] Derive directly from raster image with organs [edit]. The raster (.png format) images below have most commonly used organs already included, and text and lines can be added in almost any graphics editor.
RECURSOS CLIL BODY PARTS
Figure 1.2.1 1.2. 1 : These two people are both in anatomical position. (CC-BY, Open Stax ) When referencing a structure that is on one side of the body or the other, we use the terms "anatomical right" and "anatomical left.". Anatomical right means that the structure is on the side that a person in anatomical position would consider. Body Planes. A section is a two-dimensional surface of a three-dimensional structure that has been cut. Modern medical imaging devices enable clinicians to obtain "virtual sections" of living bodies. We call these scans. Body sections and scans can be correctly interpreted, however, only if the viewer understands the plane along which the section was made. human body, the physical substance of the human organism, composed of living cells and extracellular materials and organized into tissues, organs, and systems. Human anatomy and physiology are treated in many different articles. You can label it in a different color to indicate that it is separate from the free-body diagram. Let's apply the problem-solving strategy in drawing a free-body diagram for a sled. In Figure 5.31 (a), a sled is pulled by force P at an angle of 30 °.
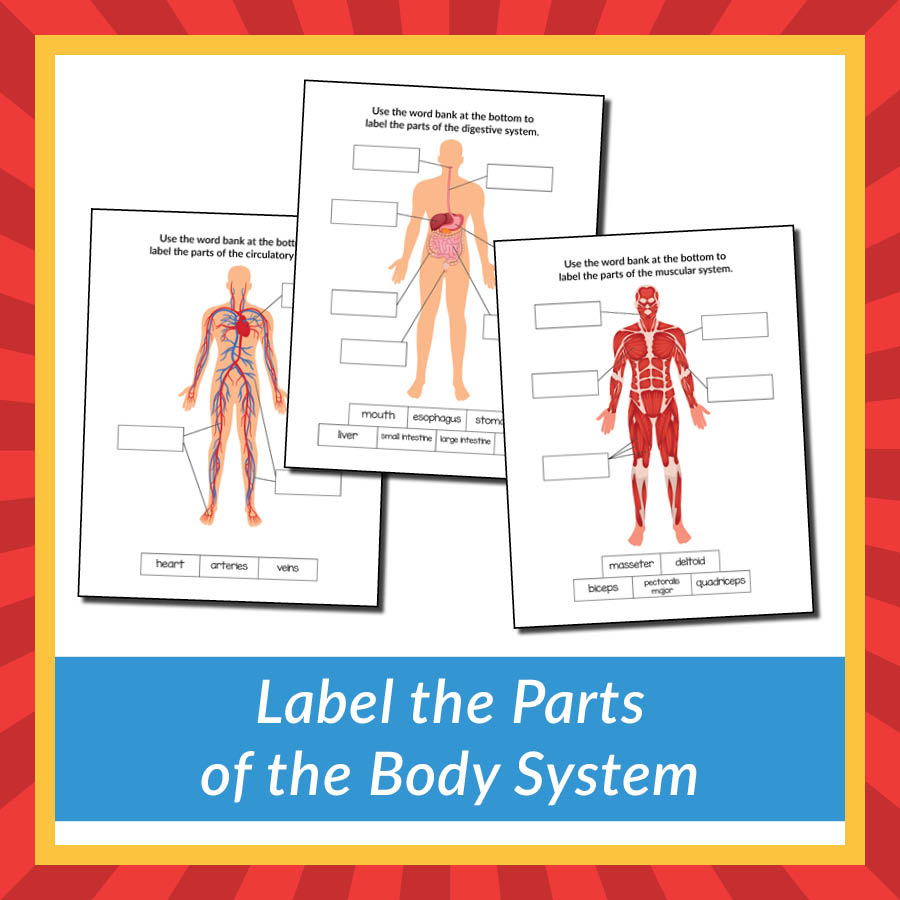
Label the Parts of the Body System Gift of Curiosity
human skeleton, the internal skeleton that serves as a framework for the body. This framework consists of many individual bones and cartilages.There also are bands of fibrous connective tissue—the ligaments and the tendons—in intimate relationship with the parts of the skeleton. This article is concerned primarily with the gross structure and the function of the skeleton of the normal. Medial: Toward the mid-line, middle, away from the side. Rostral: Toward the front. Caudal: Toward the back, toward the tail. Bilateral: Involving both sides of the body. Unilateral: Involving one side of the body. Ipsilateral: On the same side of the body. Contralateral: On opposite sides of the body. The sagittal plane (lateral or Y-Z plane) divides the body into sinister and dexter (left and right) sides. The midsagittal (median) plane is in the midline through the center of the body, and all other sagittal planes are parallel to it. The coronal plane (frontal or Y-X plane) divides the body into dorsal and ventral (back and front) portions. Muscles of the Leg and Foot Labeling Page. Muscles of the Neck, Chest and Thorax Labeling Page. Muscles of the Neck, Shoulders and Thorax (Posterior) Labeling. Muscles of the Posterior Body Labeling (HS-Adult) Muscles of the Thigh and Hip (Anterior) Labeling. Muscles of the Thigh and Hip (Posterior) Labeling. Nerve Cell (Neuron) Labeling Page.
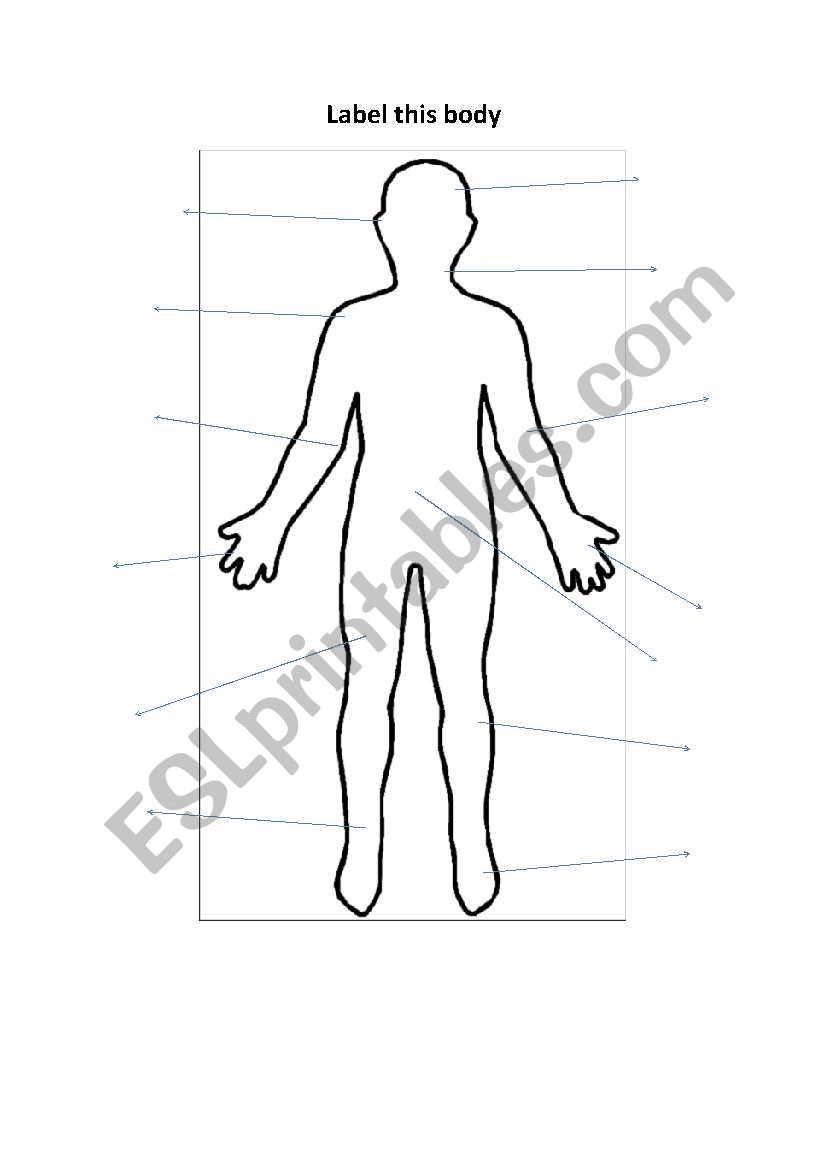
English worksheets label this body
Figure 1. Regions of the Human Body. The human body is shown in anatomical position in an (a) anterior view and a (b) posterior view. The regions of the body are labeled in boldface. A body that is lying down is described as either prone or supine. Prone describes a face-down orientation, and supine describes a face up orientation. Medical Art Library is a resource for teachers, students, health professionals or anyone interested in learning about the anatomy of the human body. We are medical artists who love anatomy. We believe that Illustrations can help you focus on key structures, see relationships, and quickly understand anatomy- in a way that words alone can't.
Figure 1.4.1 1.4. 1: Regions of the Human Body. The human body is shown in anatomical position in an (a) anterior view and a (b) posterior view. The regions of the body are labeled in boldface. A body that is lying down is described as either prone or supine. The human skeletal system consists of all of the bones, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments in the body. Altogether, the skeleton makes up about 20 percent of a person's body weight. An adult's.

Body parts English 4 Me 2
Summary. The skeletal system is made up of your bones, ligaments, and cartilage. Though its main function is to provide structural support for the body, it also stores important minerals—such as calcium—forms red blood cells, and protects your internal organs. The skeletal system can break down into two main categories—the axial skeleton. The dorsal cavity is at the posterior, or back, of the body, including both the head and the back of the trunk. The dorsal cavity is subdivided into the cranial and spinal cavities. The cranial cavity fills most of the upper part of the skull and contains the brain. The spinal cavity is a very long, narrow cavity inside the vertebral column.




