Calculating amounts in moles Key fact The amount of a given mass substance is calculated using: \ (amount=\frac {mass} {relative~atomic~or~formula~mass}\) Use Ar instead of Mr for metals. Here, Mr is the relative molar mass, also called formula weight. For normal samples from earth with typical isotope composition, the standard atomic weight or the conventional atomic weight can be used as an approximation of the relative atomic mass of the sample. Examples are: An average molar mass may be defined for mixtures of compounds. [1]

IGCSE Edexcel Chemistry Help 1.19 carry out mole calculations using relative atomic mass (Ar
A tutorial showing how to use the relative formula mass (Mr) or relative atomic mass (Ar) to calculate the mass of a substance given its moles or the number of moles in a substance. One mole of NH 3 molecules - which has a relative molecular mass (Mr) of 17 - has a mass of 17 g, and half a mole has a mass of 8.5 g. One mole of ibuprofen (C 13 H 18 O 2) has a mass of 206 g, and 0.01 moles have a mass of 2.06 g (which is still way more than is in an ibuprofen tablet). Moles allow us to compare the number of atoms or. The molar mass of a substance is the mass of one mole close mole The amount of substance that contains the same number of particles as there are atoms in 12 g of carbon-12 (contains the Avogadro's. How many atoms are there? Answer - part a The molar mass of water is 18 g/mol The number of moles is found by mass ÷ molar mass This comes to 15.7 g ÷ 18 g/mol = 0.872 mol
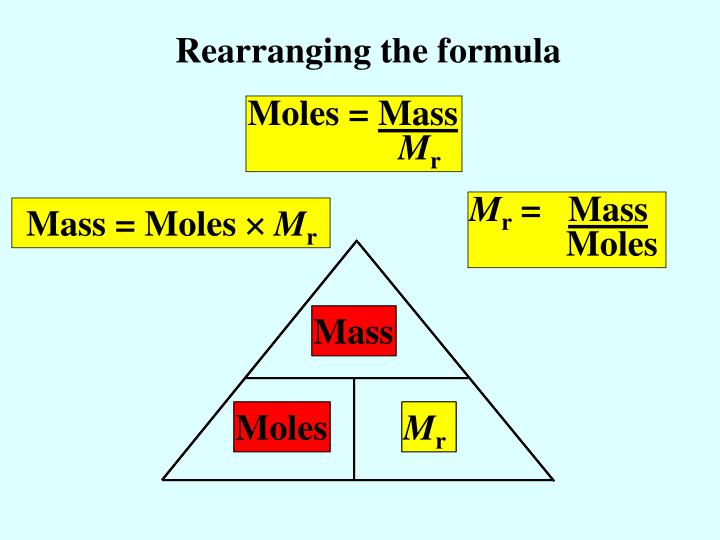
PPT Mole Calculations PowerPoint Presentation ID902714
Moles and masses , and relative formula mass are closely related. \ (moles = \frac {mass~ (g)} {M_r}\) You can imagine these properties of a substance in a triangle. You can reconfigure the. David Park. 4 years ago. First, you can calculate the molar mass of FeCl2 by adding the molar masses of Fe (55.845 g/mol) and 2 atoms of Cl (2 times (35.446 g/mol). This gives a molar mass of 126.737 g/mol. Since each mole is 126.737 grams, you multiply 3.5 mols by 126.737 grams, giving you 443.58 grams. One mole is the formula mass (Mr) of any substance in grams, and it is Avogadro's number. Putting these two together, we can say that in one mole of the mass of any substance, there are 6.02 x 10 23 particles. We can use the equations to find the number of particles in any given mass of substance: Number of moles = Mass/ Mr = given number of. The molar mass of a substance is defined as the mass of 1 mol of that substance, expressed in grams per mole, and is equal to the mass of 6.022 × 10 23 atoms, molecules, or formula units of that substance. KEY TAKEAWAY. To analyze chemical transformations, it is essential to use a standardized unit of measure called the mole.

Reacting amounts calculations YouTube
Mass and Mole Calculations. The mole is a unit in chemistry that tells us the amount of a substance. It gives an indication of how many particles are present in a substance.. We can also work out the masses of the products using the mass = moles x Mr equation. 0.1 x 63.5 = 6.35 g of copper. 0.05 x 44 = 2.2 g of carbon dioxide. View fullsize. The molar mass of any substance is the mass in grams of one mole of representative particles of that substance. The representative particles can be atoms, molecules, or formula units of ionic compounds. This relationship is frequently used in the laboratory. Suppose that for a certain experiment, you need 3.00 moles of calcium chloride \(\left.
Mass from Moles. Mr. Causey shows you step by step how to use molar mass to find the mass of a compound in moles. http://www.yourCHEMcoach.comLearn more and. ⚛ 1 mole of a pure substance has a mass equal to its molecular mass (1) expressed in grams. · This is known as the molar mass, M, and has the units g mol-1 (g/mol, grams per mole of substance) ⚛ The relationship between molar mass, mass and moles can be expressed as a mathematical equation as shown below:
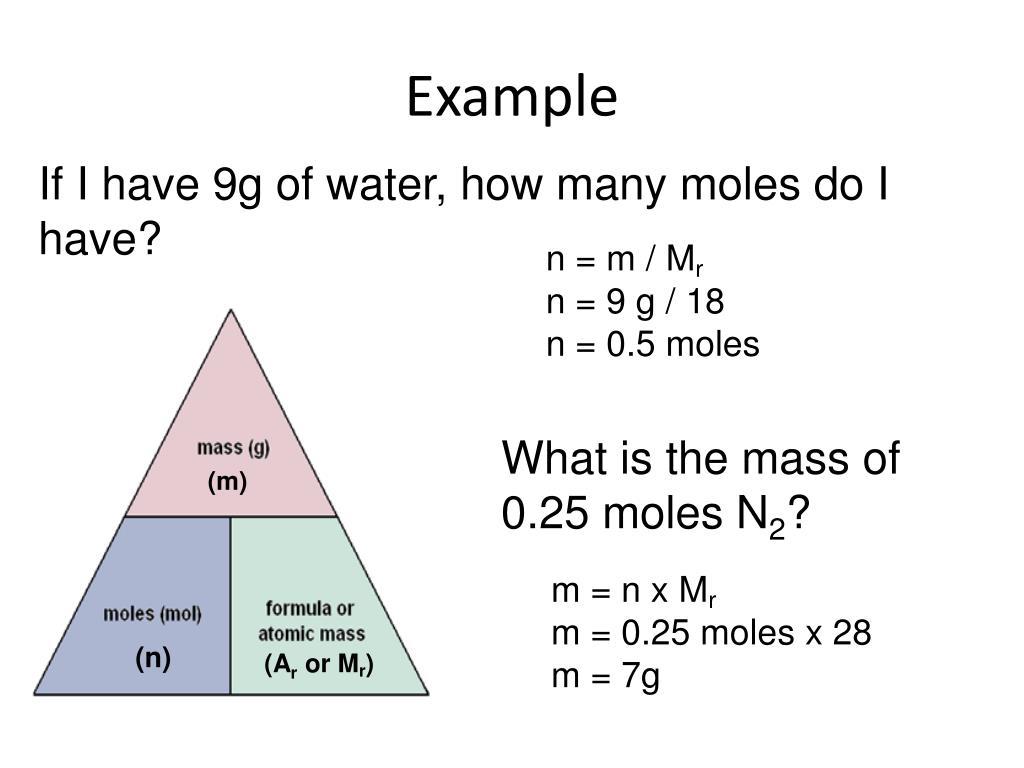
PPT Moles and reacting masses PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2568915
The molar mass of a substance is defined as the mass of 1 mol of that substance, expressed in grams per mole, and is equal to the mass of 6.022 × 10 23 atoms, molecules, or formula units of that substance. Key Takeaway. To analyze chemical transformations, it is essential to use a standardized unit of measure called the mole. The molar mass of a substance is defined as the mass of 1 mol of that substance, expressed in grams per mole, and is equal to the mass of 6.022 × 10 23 atoms, molecules, or formula units of that substance. Key Takeaway. To analyze chemical transformations, it is essential to use a standardized unit of measure called the mole.




