Classification Grade 1 to 3 have been described on MRI: grade 1: small focal area of hyperintensity, no extension to the articular surface grade 2: linear areas of hyperintensity, no extension to the articular surface 2a: linear abnormal hyperintensity with no extension to the articular surface Diagram MRI grading system for abnormal high meniscal signal intensity reported by Lotysch et al. Normal meniscus should appear as a uniform low-signal (dark) triangular structure in sagittal MRI images. normal: No abnormal signal intensity 1: small focal area of increased signal intensity, with no extension to the articular surface
Meniscus Tear Local Physio
Meniscal tears are the failure of the fibrocartilaginous menisci of the knee. There are several types and can occur in an acute or chronic setting. Meniscal tears are best evaluated with MRI. Pathology Meniscal tears are common sports-related injuries in young athletes and can also present as a degenerative condition in older patients. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with joint line tenderness and a positive Mcmurray's test, and can be confirmed with MRI studies. Though initially described as a functionless remain of a leg muscle [ 1 ], extensive scientific investigations in recent decades have described the meniscus as a vital part of the knee joint with anatomical, biomechanical, and functional importance [ 2 ]. Normal meniscus has uniformly low signal intensity on T2-weighted images (T2W). Grade I and II lesions can be a normal appearance of ageing in older patients. Classifications, online calculators, and tables in radiology. Martin C, Crues JV 3rd, Kaplan L, Mink JH. Meniscal tears: pathologic correlation with MR imaging. Radiology. 1987 Jun;163.
Meniscal Tear Types
Meniscal injuries are a common problem in sports; they are the most frequent injury to the knee joint. Such injuries are especially prevalent among competitive athletes, particularly those. Meniscal tears are a common pathology and diagnosis relies on a detailed clinical history and clinical examination, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and arthroscopy. Some types of meniscal tears (e.g. horizontal or oblique tears) may not always be related to clinical symptoms, and they are frequently encountered in asymptomatic knees [ 1 ]. Occasionally, meniscal tears can be difficult to detect at imaging; however, secondary indirect signs, such as a parameniscal cyst, meniscal extrusion, or linear subchondral bone marrow edema, should increase the radiologist's suspicion for an underlying tear. Awareness of common diagnostic errors can ensure accurate diagnosis of meniscal tears. The lateral and medial menisci are crescent-shaped fibrocartilaginous structures that collectively cover approximately 70% of the articular surface of the tibial plateau and primarily function in load transmission and shock absorption through the tibiofemoral joint.

MR Imagingbased Diagnosis and Classification of Meniscal Tears RadioGraphics
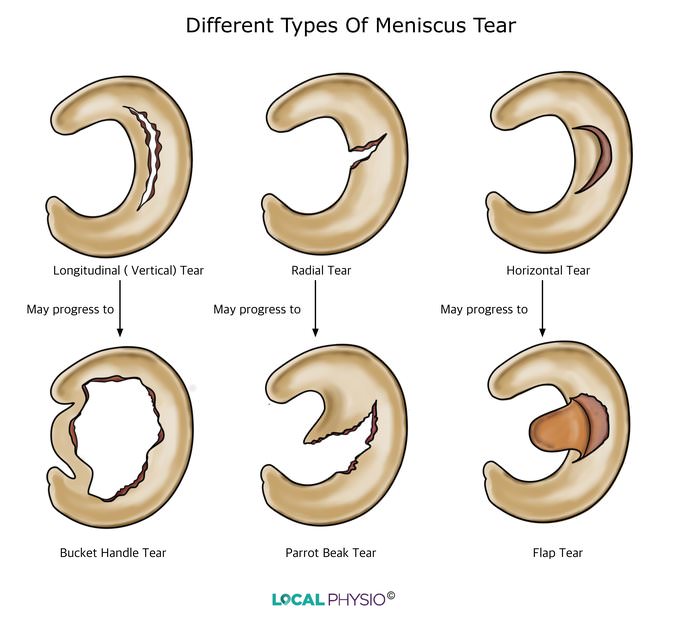
. MRI grading system classifies tears based on their appearance on an MRI scan (Fig. 8). Grade 0 represents an intact, normal meniscus. Grade I and Grade II signals do not intersect. The meniscus a tissue that sits between the femur and tibia bone. It can tear in many different ways, and no two tears ever look the same. There are a few varieties frequently seen in MRI reports. Radial meniscus tear A radial tear is a tear across the fibers of the meniscus.
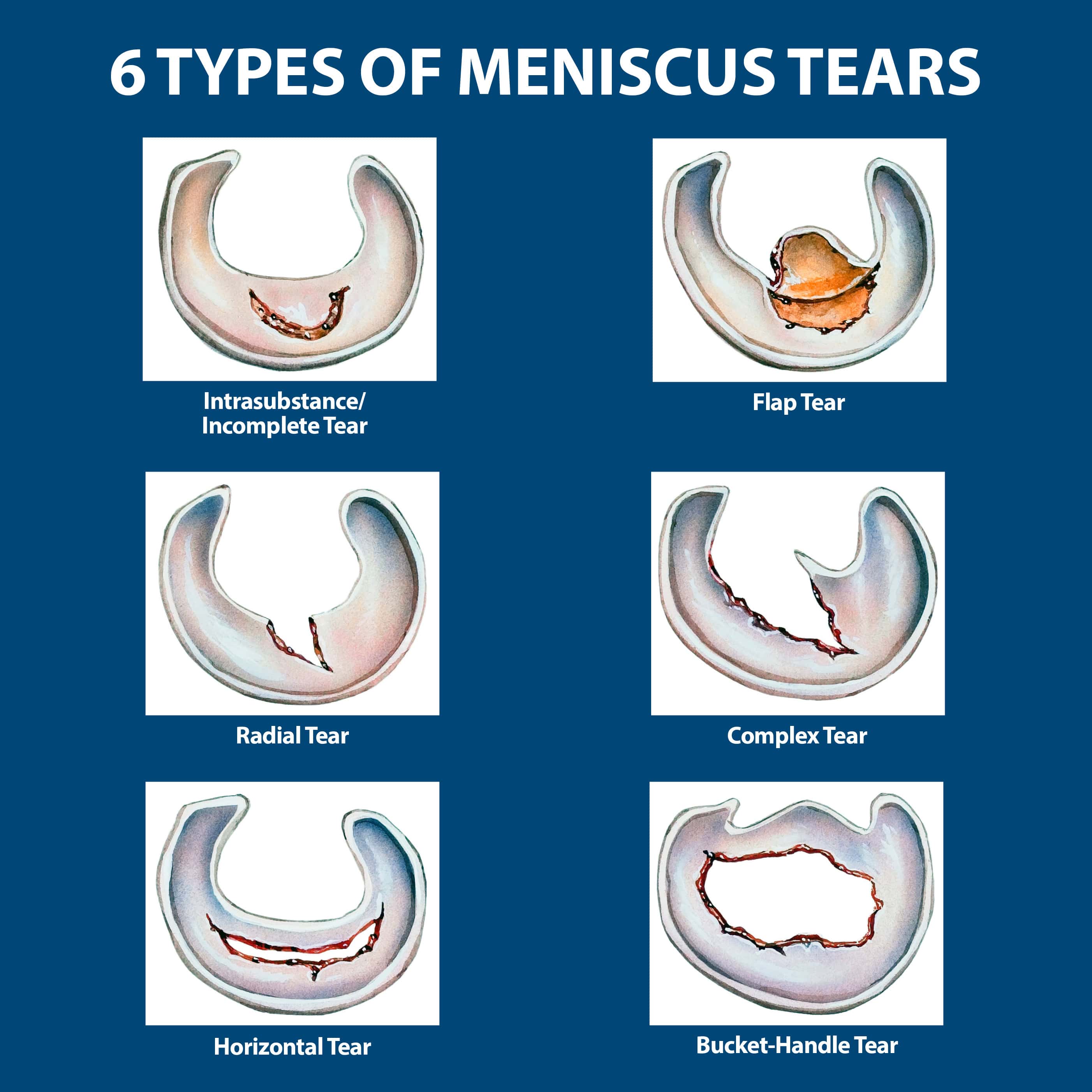
There are six types of meniscus tears: radial, intrasubstance, horizontal, flap, complex, and bucket-handle. All can compromise the knee, where this C-shaped cartilage is found. The part of the meniscus these tears affect, the patterns they exhibit, and their complexity differ, however. Symptoms & causes Diagnosis & treatment Doctors & departments On this page Diagnosis Treatment Self care Preparing for your appointment Diagnosis A torn meniscus often can be identified during a physical exam.

Meniscal Tear Causes, Presentation and Treatment Bone and Spine
The menisci — the medial meniscus and lateral meniscus - are crescent-shaped bands of thick, rubbery cartilage attached to the shinbone (tibia). They act as shock absorbers and stabilize the knee. The medial meniscus is on the inner side of the knee joint. The lateral meniscus is on the outside of the knee. Download scientific diagram | Grading scale for meniscal tears on MRI. Grade 0 is a normal meniscus. Grades I and II have an intrameniscal signal that does not abut the free edge. Grade III has a.




