human muscle system, the muscles of the human body that work the skeletal system, that are under voluntary control, and that are concerned with movement, posture, and balance. Broadly considered, human muscle—like the muscles of all vertebrates—is often divided into striated muscle (or skeletal muscle), smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle. human body maps muscular system Muscular The primary job of muscles is to move the bones of the skeleton, but muscles also enable the heart to beat and constitute the walls of other vital.

Muscle Diagram Most Important Muscles Of An Athletic Male Body Anterior And Posterior View
PowerPoint Presentation THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM COMPILED BY HOWIE BAUM 1 Muscles make up the bulk of the body and account for 1/3 of its weight.!! Blood vessels and nerves run to every muscle, helping control and regulate each muscle's function. The muscular system creates body heat and also moves the: Bones of the Skeletal system Last Updated: Oct 10, 2021 2D Interactive NEW 3D Rotate and Zoom Anatomy Explorer HEAD AND NECK CHEST AND UPPER BACK ABDOMEN AND LOWER BACK ARM AND HAND LEG AND FOOT HEAD AND NECK Clavicular Head of Sternocleidomastoid Muscle Depressor Anguli Oris Muscle Depressor Labii Inferioris Muscle Frontal Belly of Epicranius Muscle (Frontalis Muscle) The musculoskeletal system (locomotor system) is a human body system that provides our body with movement, stability, shape, and support. It is subdivided into two broad systems: Muscular system, which includes all types of muscles in the body. Skeletal muscles, in particular, are the ones that act on the body joints to produce movements. Muscular system functions include mobility, stability, posture, circulation, and more. Muscles allow a person to move, speak, and chew. They control heartbeat, breathing, and digestion. Other.

Simple Human Muscles Diagram / Learn All Muscles With Quizzes And Labeled Diagrams Kenhub
Muscular System / In these topics. Muscles. Brought to you by Merck & Co, Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA (known as MSD outside the US and Canada)—dedicated to using leading-edge science to save and improve lives around the world. Learn more about the MSD Manuals and our commitment to Global Medical Knowledge. Skeletal muscles and synovial joints. Flexion and extension. Abduction and adduction. Pronation and supination. Elevation and depression. Protraction and retraction. Inversion and eversion. Dorsiflexion and plantar flexion. Prime movers, synergists, stabilizers, and antagonists. The muscular system is made up of muscle tissue and is responsible for functions such as maintenance of posture, locomotion and control of various circulatory systems. This includes the beating of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive system. The muscular system is closely associated with the skeletal system in facilitating. The Muscular System A diagram illustrates an anterior view of muscles in the human body with the major muscle groups labeled cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and skeletal muscle. An anterior view of the heart is illustrated in the thoracic region and an anterior view of the stomach is illustrated in the abdominal region.

Major Muscle Groups Body muscle anatomy, Muscle anatomy, Human body muscles
Definition The muscular system is a set of tissues in the body with the ability to change shape. Muscle cells connect together and eventually to elements of the skeletal system. When the muscle cells contract, force is created as the muscles pull against the skeleton. Overview Muscle contraction Neuromuscular junction and motor unit Osmosis Muscles high-yield notes offers clear overviews with striking illustrations, tables, and diagrams. Make learning more manageable.
Image Credit: Wikiemedia. Biology definition: The muscular system is an organ system responsible for providing strength, keeping up the balance, maintaining posture, allowing movement, and producing heat. It includes all the muscle tissues, such as the skeletal muscle tissues, smooth muscle tissues, and cardiac muscle tissues. Muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. Skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. Skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells. The membrane of the cell is the sarcolemma; the cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm.
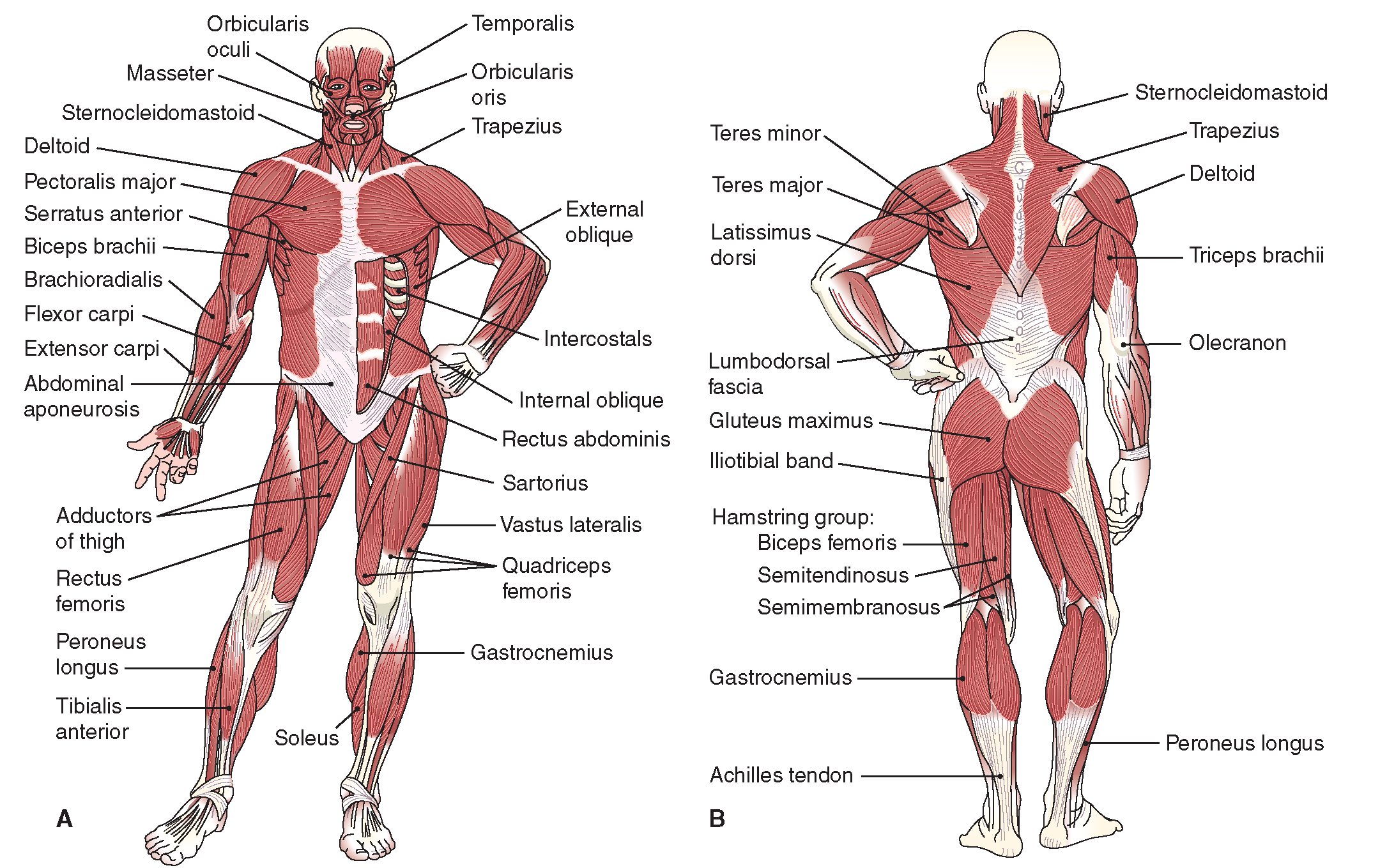
The Musculoskeletal System (Structure and Function) (Nursing) Part 4
+ Show all Skeletal system The skeletal system is composed of bones and cartilages. There are two parts of the skeleton; axial and appendicular. The axial skeleton consists of the bones of the head and trunk. The appendicular skeleton consists of the bones within the limbs, as well as supporting pectoral and pelvic girdles . The muscular system is made up of three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac and smooth. In this section, we'll focus on the skeletal muscles of the body involved in voluntary movement and maintaining posture. They are attached to bones via tendons and contract to cause movement at the joints. Learn more about the anatomy and functions of.




