Pemphigus Foliaceus - Pemphigus foliaceus is the most common autoimmune skin disease in dogs and cats. It is often observed in middle-aged and older patients. Pemphigus foliaceus typically causes hair loss, scabs, and ulcers (open sores) around the head, face and ears. Pemphigus foliaceus is the most common autoimmune skin disease in dogs, although it remains rare. In this article, Dr. Michael Kearley discusses the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for pemphigus foliaceus in dogs.
Pemphigus Foliaceus The Skin Vet
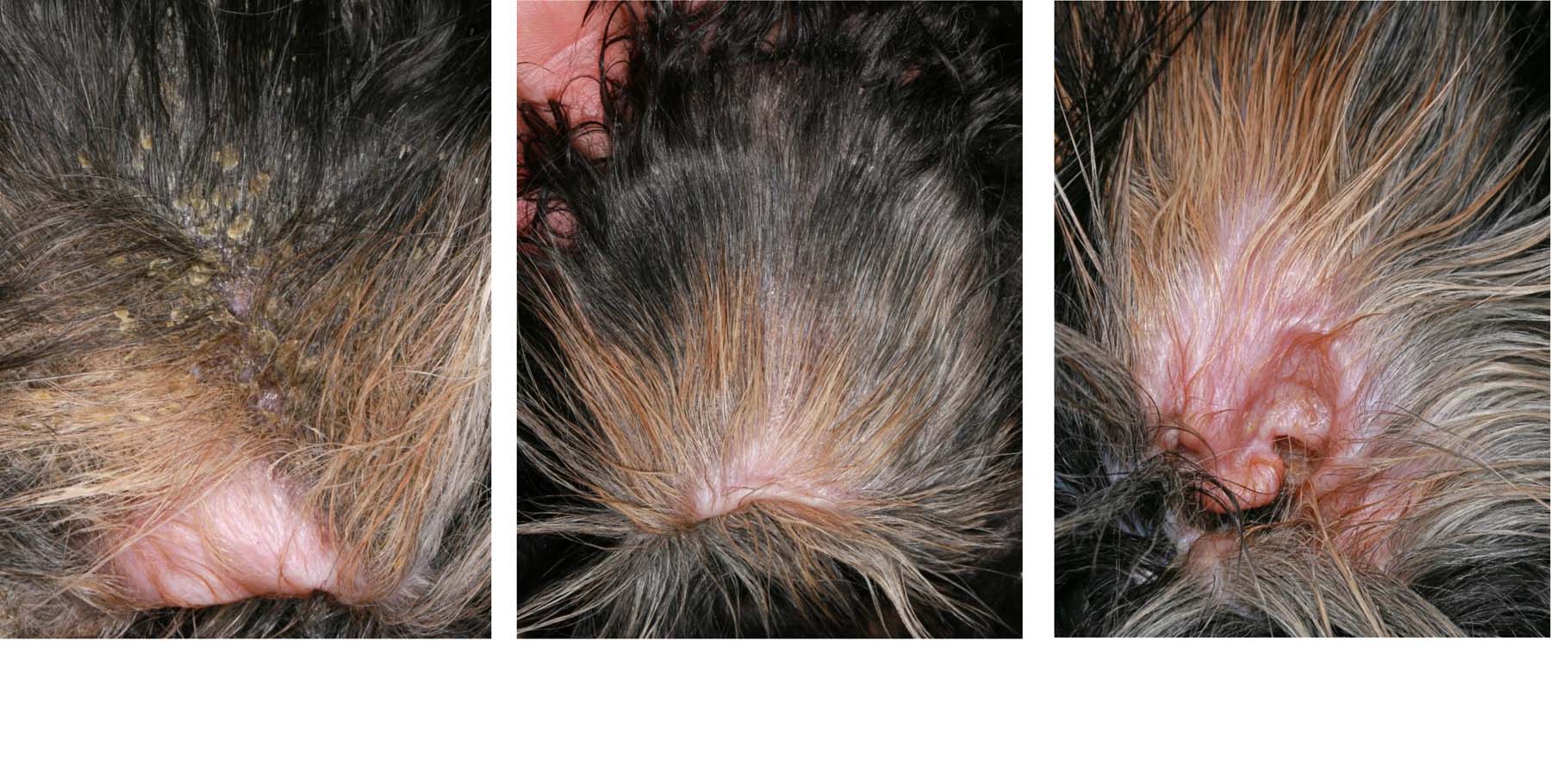
Pemphigus foliaceus (PF) is the most common autoimmune skin disease in dogs and cats. It is also the most common variant of pemphigus diseases,1,2 which are characterized by autoantibodies that target keratinocyte desmosomal proteins, leading to loss of cell-to-cell adhesion (acantholysis). Pemphigus foliaceus (PF) is the most common autoimmune disease in dogs. It is characterized by pustules, ulcers and crusts (scabs) developing on the canine's skin surface. Symptoms of Pemphigus Foliaceus in Dogs Redness Blisters Pus Yellow-brown crust (scabs) Depression Lethargy Fever Sometimes itchy Hair loss Ulcers Lack of appetite Pemphigus in dogs is an autoimmune condition of the skin. Pemphigus causes the connections between a dog's skin cells to break down.. Pemphigus foliaceus usually appears on the head, face, and ears with symmetrical lesions on both sides of the head. A dog's footpads are often affected as well. The trunk of their body is sometimes. Pemphigus foliaceus (PF) is a type of autoimmune disease of the skin. Other skin diseases besides PF also have the word "pemphigus" in their name, but are different from PF. What Species or Breeds get Pemphigus Foliaceus? Although an uncommon skin disease in dogs and cats, any breed of dog or cat can develop PF.
Generalized pemphigus foliaceus dog
Pemphigus in Dogs Estimated Reading Time: 4 minutes Pemphigus can best be described as an immune-mediated skin disease in dogs where a dog's own immune system begins to attack the connection between the normal layers of skin cells. There are different types of pemphigus that involve different areas of the skin. Pemphigus Foliaceus is an autoimmune vesicobullous to pustular skin disease in dogs characterized by acantholysis or loss of adhesion between keratinocytes within the epidermis and hair follicles. The disease is characterized by production of autoantibodies against intercellular connections of the keratinocytes. Pemphigus foliaceous is the most common autoimmune disease in dogs and is most often caused by autoantibodies targeting desmocollin-1 ( 2, 3 ). Go to: Clinical presentation The classical lesions of pemphigus foliaceous are large pustules that span multiple hair follicles ( 1, 4 ). Pemphigus foliaceus (PF) is the most common autoimmune skin disease in dogs and cats. It is also the most common variant of pemphigus diseases,1,2 which are characterized by autoantibodies that target keratinocyte desmosomal proteins, leading to loss of cell-to-cell adhesion (acantholysis). Acantholysis of keratinocytes causes separation and.

TCVM for Treating Autoimmune Skin Diseases Today's Veterinary Practice
Pemphigus foliaceus is the most common of these diseases, occurring more often in dogs than in cats and horses. It is characterized by the development of erosions, ulcerations, and thick encrustations of the skin and mucocutaneous junctions. 1. Pemphigus Foliaceus Canine pemphigus encompasses four variants: pemphigus foliaceus, pemphigus vulgaris, pemphigus vegetans and paraneoplastic pemphigus. Pemphigus foliaceus is the most common variant and also the most common autoimmune skin disease affecting dogs and cats. Pathomechanism
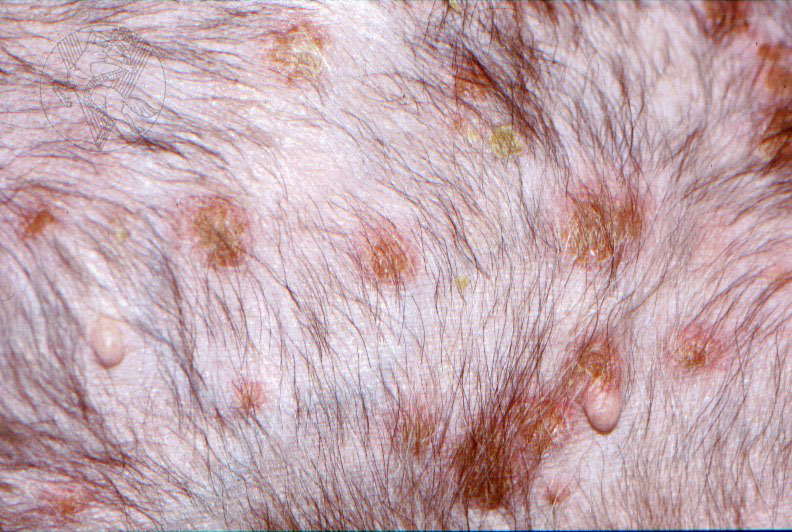
Canine Pemphigus Foliaceus. Pemphigus foliaceus, the most common autoimmune dermatosis in dogs, presents with primary large, superficial pustules. Pustules may be punctate or span multiple follicles, and contents may appear translucent to yellow ( Figure 1). Because they are thin-roofed, pustules tend to rapidly rupture and form crusts with. Pemphigus is a group of autoimmune skin diseases that can be found in humans, cats, dogs, and even horses. There are three main types, all of which affect the skin: Pemphigus Vulgaris (PV). The first to ever be described in veterinary medicine in 1989, and the most severe.
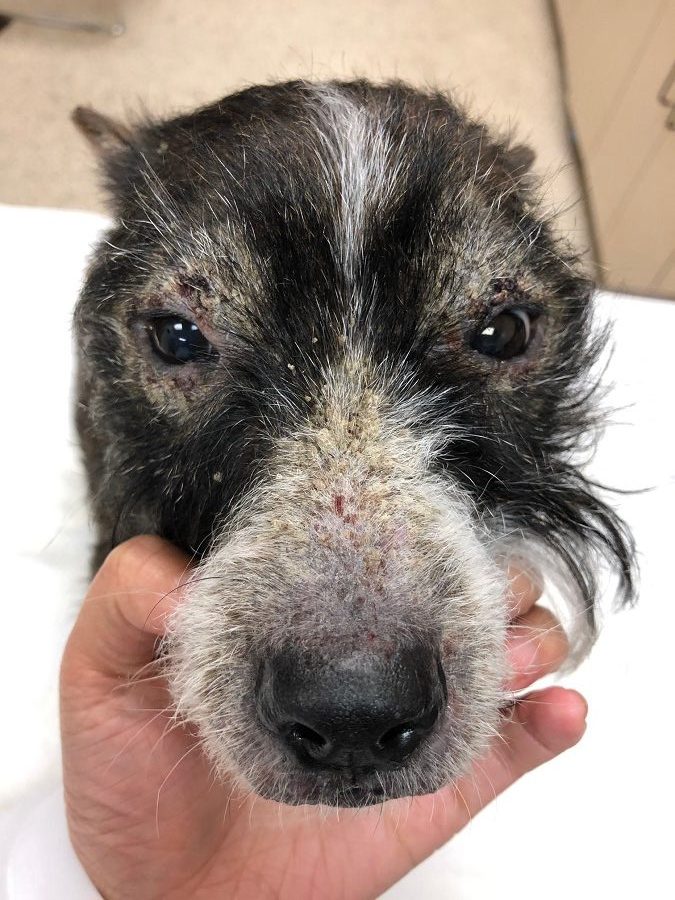
Pet Case Study Rocky’s Pemphigus Animal Dermatology Referral Clinic (ADRC)
Pemphigus foliaceus (PF) is the most common form of the pemphigus complex in small animals and the most common autoimmune skin disease in dogs.1,2 This review aims to provide an update on the pathogenesis of pemphigus foliaceus, as well as its clinical manifestations, diagnosis and therapeutic approach. Pathogenesis. Clinical signs. Pemphigus foliaceus is a severe skin disease that is characterized by pustules and blisters that rupture, causing damage to the skin of the face, ears, feet and eventually the entire skin in dogs. Pemphigus Foliaceus in dogs is commonly shortened and referred to as just "Pemphigus". This disease results when the animal recognizes a specific.




