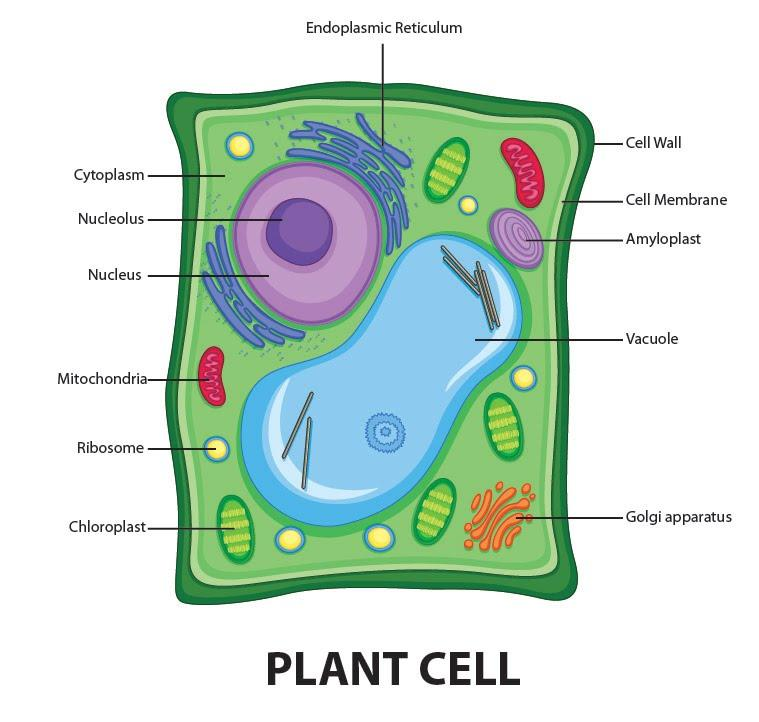
Plant Cell Diagram The plant cell is rectangular and comparatively larger than the animal cell. Even though plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and share a few cell organelles, plant cells are quite distinct when compared to animal cells as they perform different functions. Diagram of a plant cell Above: Diagram of the structure of a plant cell Note: The diagram above is a general plant cell - so not a particular part of any specific plant. The labels in pink are links to pages of further information about the part of the plant cell indicated.
Draw a welllabelled diagram of a plant cell.
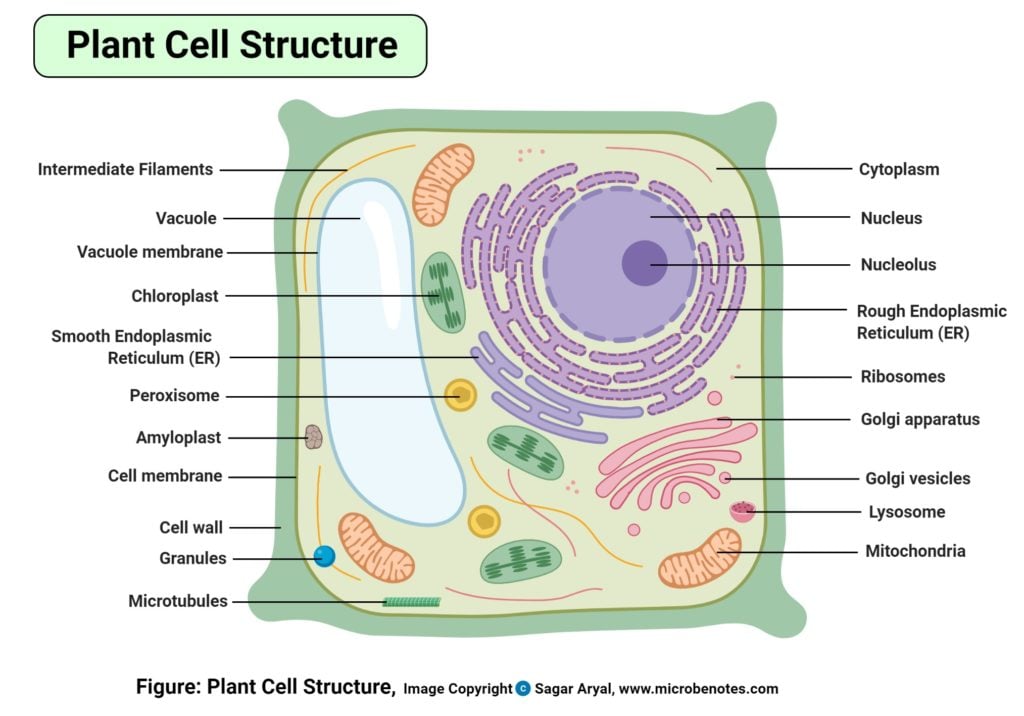
A diagram to show the cell wall and middle lamella of one plant cell Plasmodesmata Narrow threads of cytoplasm (surrounded by a cell membrane) called plasmodesmata connect the cytoplasm of neighbouring plant cells This allows substances to be transported between plant cells and facilitates cell to cell communication Pits Plant cells are eukaryotic cells, that are found in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae which means they have a membrane-bound nucleus. They have a variety of membrane-bound cell organelles that perform various specific functions to maintain the normal functioning of the plant cell. Table of Contents Plant cells are eukaryotic cells, found in plants and algae. Most plant cells have the same organelles as animal cells, plus a few extra. The ultrastructure of a plant cell is as follows: Cell wall - surrounds the cell outside of the cell surface membrane and is made of a polysaccharide called cellulose. 3. DNA, the heredity information of cells, which can be found in a nucleus of eukaryotic cells and the a nucleoid region of prokaryotic cell. 4. ribosomes, or protein-synthesizing structures composed of ribosomes and proteins. These structures can be found on the image of the plant cell (Figure 3.1.2.1 3.1.2. 1 ).
Plant Cell vs. Animal Cell (25 Major Differences)
Special Structures in Plant Cells. Most organelles are common to both animal and plant cells. However, plant cells also have features that animal cells do not have: a cell wall, a large central vacuole, and plastids such as chloroplasts.. Plants have very different lifestyles from animals, and these differences are apparent when you examine the structure of the plant cell. Figure 10.1.5 10.1. 5: A micrograph of a cell nucleus. The nucleolus (A) is a condensed region within the nucleus (B) where ribosomes are synthesized. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope (C). Just oustide the nucleus, the rough endoplasmic reticulum (D) is composed of many layers of folded membrane. The cell wall is found in plant cells, algal cells, and certain fungal cells. The cell wall is a very strong structure that is made up of the carbohydrate polymer cellulose. In fungal cells, it is made of chitin. Some bacteria also can have cells walls. The main function of the cell wall is to support the cells. What is a plasma membrane? What are the different organelles found in animal cells? What are chloroplasts? What is the outermost covering in plant and animal cells? Reference Plasma Membrane The plasma membrane is a thin, permeable membrane which surrounds the cell. It controls any exchange in or out of the cell.

What is a cell? Definition, Functions & types FAQ Plant cell diagram, Cell diagram, Plant cell
It consists mainly of cellulose. Plasma Membrane: This is a semi-permeable membrane that controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell. Nucleus: The nucleus is the control center of the cell, containing DNA that directs all cell activities. plant cell, the basic unit of all plants. Plant cells, like animal cells, are eukaryotic, meaning they have a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. The following is a brief survey of some of the major characteristics of plant cells. For a more in-depth discussion of cells, see cell. Unlike animal cells, plant cells have a cell wall surrounding.
A diagram to show the cell wall and middle lamella of one plant cell Plasmodesmata Narrow threads of cytoplasm (surrounded by a cell membrane) called plasmodesmata connect the cytoplasm of neighbouring plant cells This interconnected system of cytoplasm between plant cells is known as the symplast Pits These are very thin regions of the cell wall The plant cell will store water in the central vacuole, which expands the vacuole into the sides of the cell. The cell wall then pushes against the walls of other cells, creating a force known as turgor pressure. While animals rely on a skeleton for structure, turgor pressure in plant cells allows plants to grow tall and reach more sunlight.
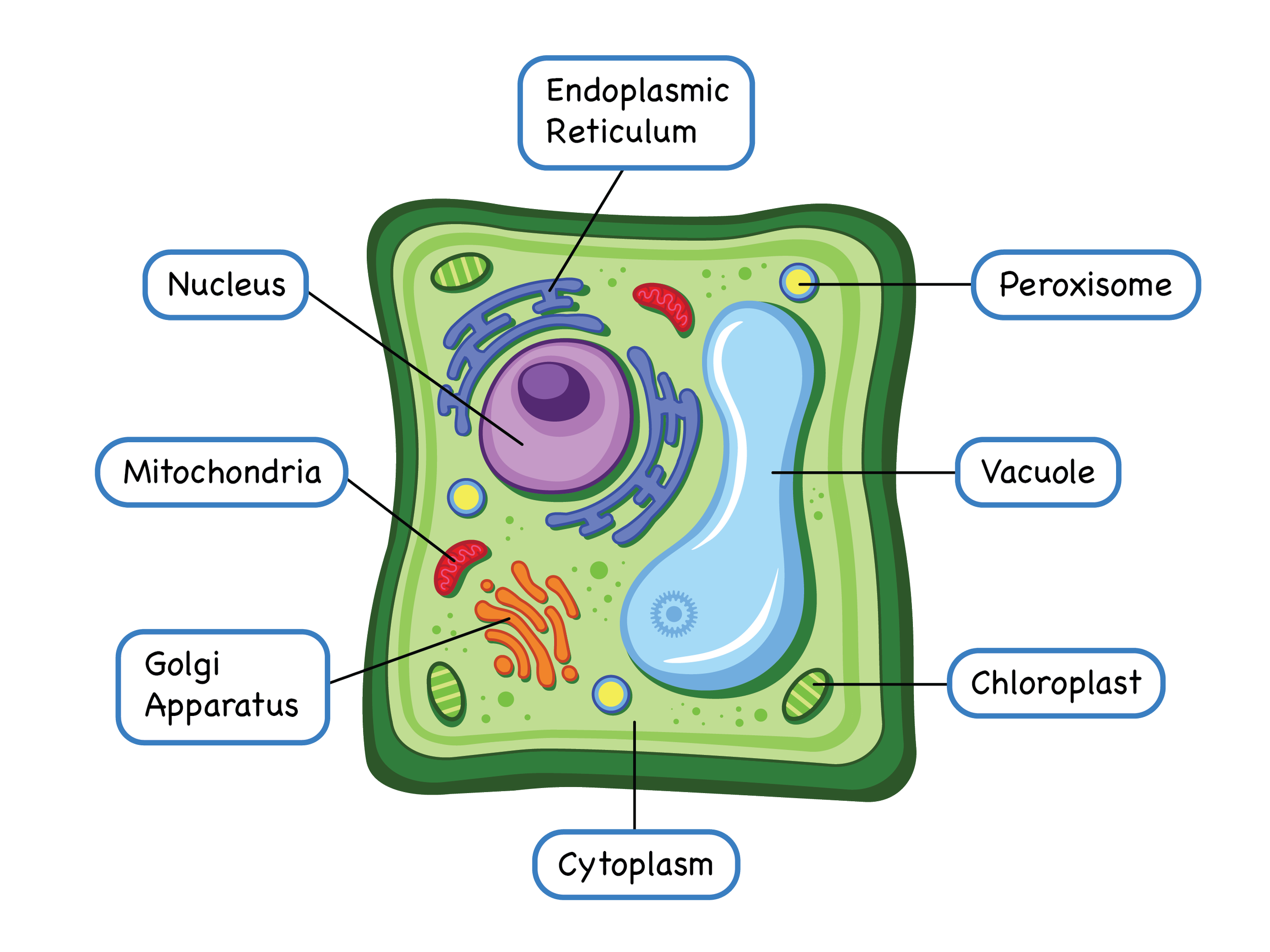
Students can stick and organise contents inside a cell and study biology with fun. — Elena
Structure of Animal & Plant Cells. The only structures found in animal cells but not plant cells are the centrioles and microvilli. Plant cells also have additional structures: the cellulose cell wall, large permanent vacuoles and chloroplasts. The ultrastructure of an animal cell shows a densely packed cell - the ER and RER and ribosomes. Cell diagrams showing a typical animal cell and plant cell. Image created with Biorender.com. Questions Tips & Thanks Want to join the conversation? Sort by: Top Voted lillianjohnson a year ago has there ever been anything that had both animal and plant cells? • 12 comments ( 67 votes) Barrs Julianna a year ago




