The dimension of root hair cells ranges between 15-17 μm in diameter and 80-1500 μm in length. The epidermal cells present in the region of maturation of the root are responsible for the growth of root hair. A single root epidermal cell is roughly rectangular with a cytoplasmic extension on its lateral end. Fungal interaction Root hairs are essential for healthy plant nutrition, especially through their interactions with symbiotic fungi. Symbiotic fungi and root hairs produce mycorrhizal symbioses like arbuscular mycorrhiza, formed by AM fungi, and ectomycorrhiza, formed by EM fungi. [10]

Arabidopsis root structure. (A) Four distinct zones. (B) Organization
Dimensions The root hair cells vary between 15-17 micrometers in diameter and 80-1500 micrometers in length. Structure The root hair cell is roughly rectangular in shape with a cytoplasmic extension on its lateral end (the root hair). It has the following cellular components: A cell wall with intercellular spaces A semi-permeable cell membrane A layer of cells known as the endodermis borders the stele (Figure 3.2.3. 2) and is considered the innermost layer of the cortex. The endodermis is exclusive to roots, and serves as a checkpoint for materials entering the root's vascular system. A waxy substance called suberin is present on the walls of the endodermal cells. The hair root is in the skin and extends down to the deeper layers of the skin. It is surrounded by the hair follicle (a sheath of skin and connective tissue), which is also connected to a sebaceous gland. New cells are constantly forming in the hair bulb. These cells stick together and harden. Root Hair Cell Diagram A root hair cell. Root Hair Cells and the Uptake of Water The structure of a root specifically allows it to maximise absorption of water by osmosis and mineral ions by active transport. You've read 1 of your 10 free revision notes Get unlimited access to absolutely everything: Downloadable PDFs Unlimited Revision Notes
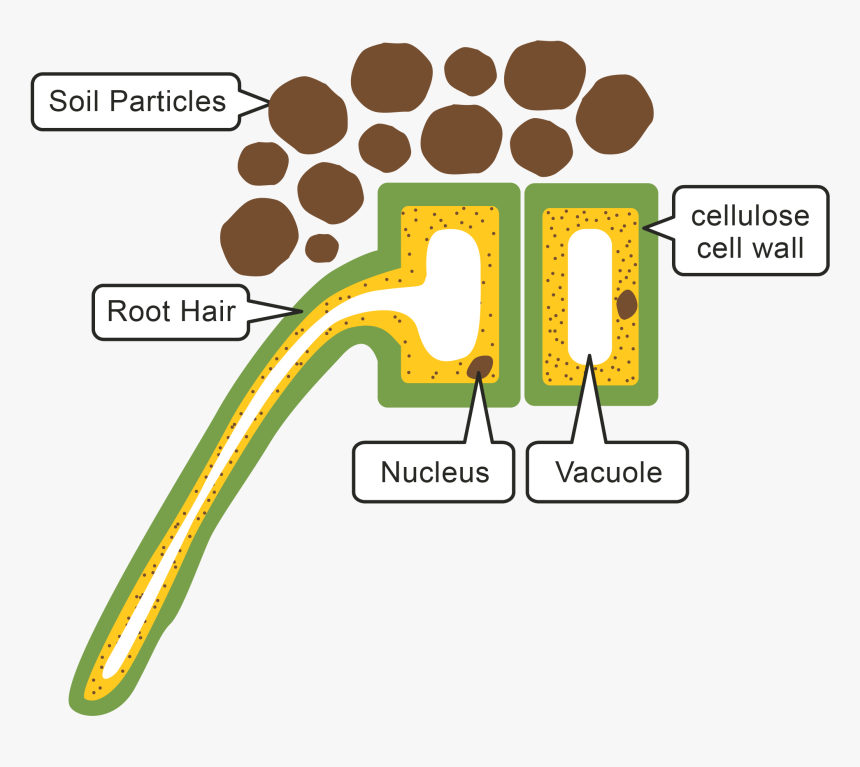
Image Of A Root Hair Cell, HD Png Download kindpng
Introduction Root hairs are long tubular-shaped outgrowths from root epidermal cells. In Arabidopsis, root hairs are approximately 10 µm in diameter and can grow to be 1 mm or more in length ( Figure 1 ). 1 Mention Explore all metrics Abstract Root hairs are tip-growing extensions from root epidermal cells that play important roles in nutrient uptake and in plant-soil interactions. In this review, we discuss the major environmental, physiological and genetic factors that regulate the differentiation and growth of root hairs in angiosperms. Root hair cells are present outside the intercellular space between two underlying cortical cells. Root Hair Tip Growth. (A) Diagram summarizing the mechanism of tip growth in Arabidopsis root hairs. The tip is packed with membrane-bound vesicles delivering new cell wall material. These vesicles are made in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and. Beginning at the first root hair is the zone of cell maturation where the root cells begin to differentiate into special cell types. All three zones are in the first centimeter or so of the root tip. Figure 30.16 A longitudinal view of the root reveals the zones of cell division, elongation, and maturation.
Active Transport In Root Hair Cells Of Plants Transport Informations Lane
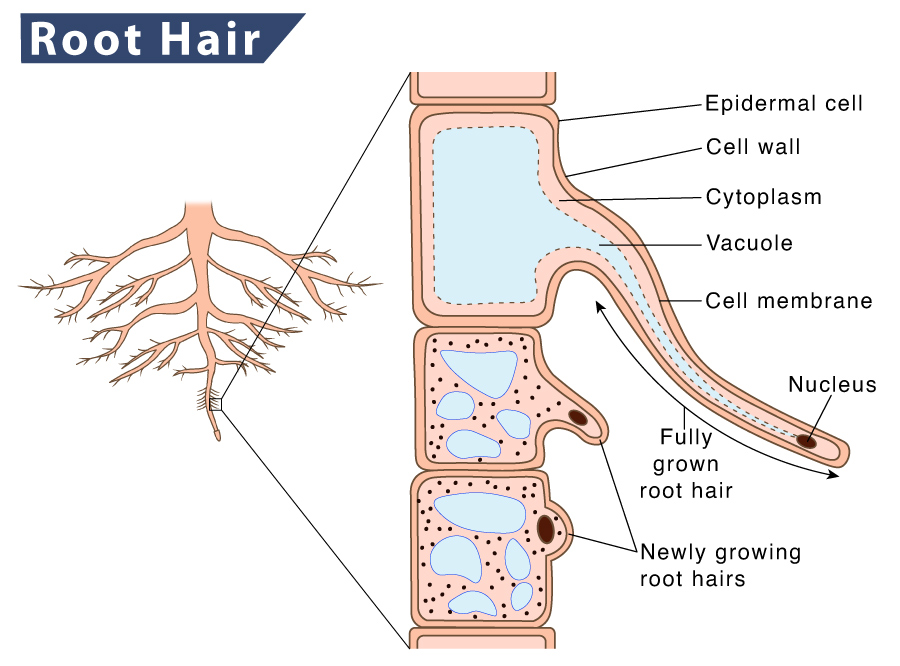
The initial step in the formation of a root hair is the specification of a newlyformed epidermal cell to differentiate as a root hair cell. This represents an example of a central problem in developmental biology; namely, how do particular cell types acquire their identity? Root hair cells Roots hold plants in place as they grow and also absorb water and minerals from the soil. Roots divide into smaller and smaller branches as they travel into the soil. The.
An overview of Root Hair formation. The Trichoblast root hair forming epidermal cells participate with the diffuse growth phase that is allied to the main root axis elongation. Growth is reorganized when the fully elongated trichoblast have exited the elongation zone and become localised to the side upon the root hair initiation process. Diagram of the root hair structure Hydrogen is combined with the carbon dioxide to produce the food (glucose) for the plant, whereas the oxygen, which is a by-product of the entire process, is let out through the stomata. If a plant does not absorb enough water, it will wilt or go floppy.

Roothaircellfromaplantfunction
What are Root Hair Cells? How Root Hair Cells Absorb Water and Mineral Ions From the Soil? Summary of the process Importance of Water for the Plant Water Transport From Root to Leaf Investigating the Water Pathway In this article, we will discuss the root hair cells of the plant in detail. The hair follicle is a skin appendage located deep in the dermis of the skin . Its function is to produce hair and enclose the hair shaft. A hair follicle consists of two main layers, an inner (epithelial) root sheath and an outer (fibrous) root sheath. At the base of the hair follicle is the hair bulb, which houses the dermal papillae and hair.




