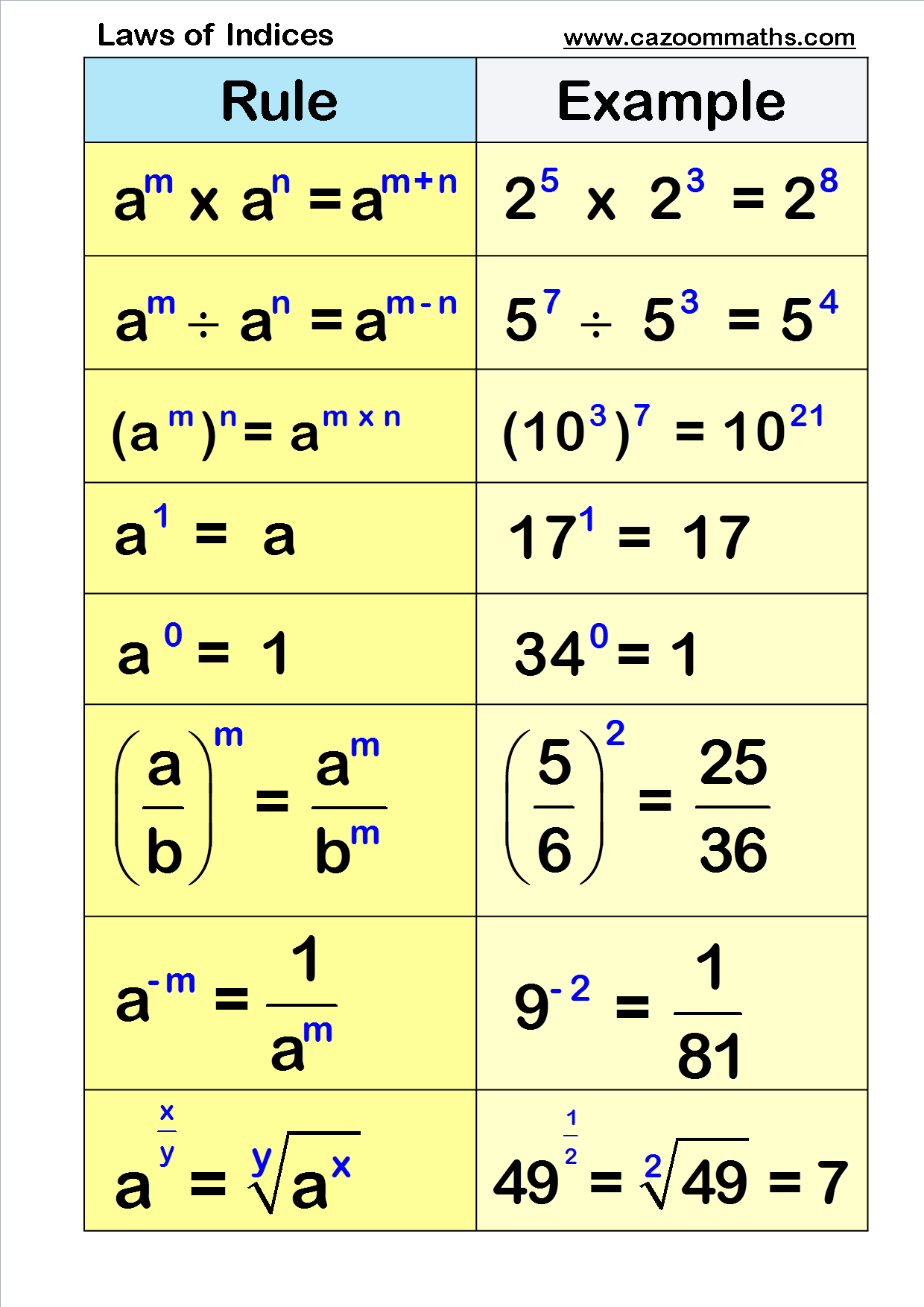
Law 1: Multiplying indices When multiplying indices with the same base, add the powers. am ×an = am+n a m × a n = a m + n Step-by-step guide: Multiplying indices Law 2: Dividing indices When dividing indices with the same base, subtract the powers. am ÷an =am−n a m ÷ a n = a m − n Step-by-step guide: Dividing indices National 5 Simplifying expressions using the laws of indices Rules of indices Indices show where a number has been multiplied by itself, eg squared or cubed, or to show roots of numbers, eg.
Maths Unit 1 Revision Cards in GCSE Mathematics
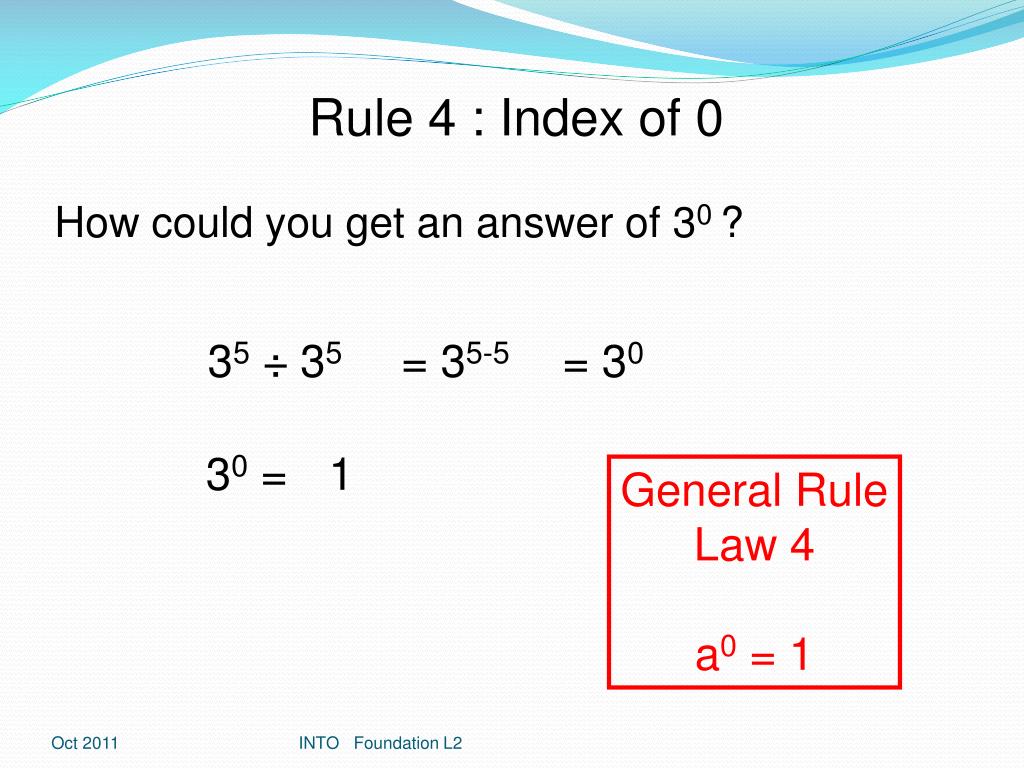
Laws of Exponents Here are the Laws (explanations follow): Laws Explained The first three laws above ( x1 = x, x0 = 1 and x-1 = 1/x) are just part of the natural sequence of exponents. Have a look at this: Six rules of the Law of Indices Rule 1: Any number, except 0, whose index is 0 is always equal to 1, regardless of the value of the base. An Example: Simplify 2 0: Rule 2: An Example: Simplify 2 -2: The laws of indices are a set of fundamental rules that govern the way indexes or indices are to be dealt with mathematically. Indices are not just used to improve the ease of writing the numbers mathematically but also have a specific function and therefore these indices rules are of utmost importance. This video demonstrates several examples of the 'rules of indices' (aka exponents or powers).I hope you find the lesson useful! Subscribe to my YouTube chann.
PPT The Rules Of Indices. PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID7103579
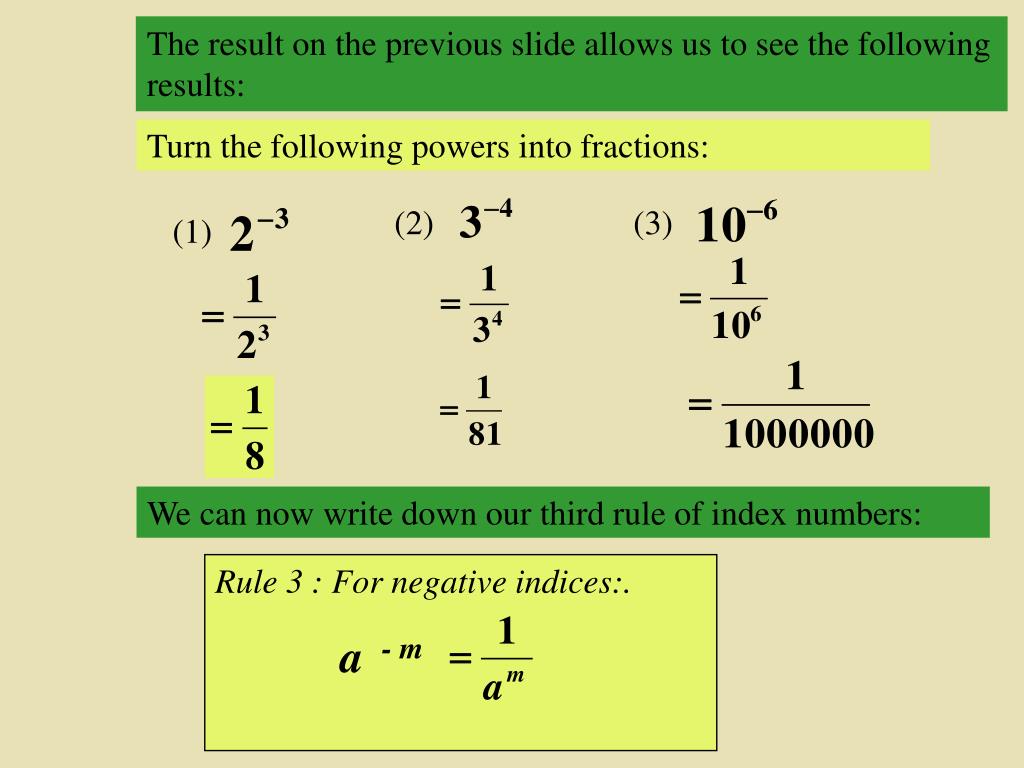
Rule 1: If a constant or variable has index as '0', then the result will be equal to one, regardless of any base value. a0 = 1 Example: 5 0 = 1, 12 0 = 1, y 0 = 1 Rule 2: If the index is a negative value, then it can be shown as the reciprocal of the positive index raised to the same variable. a-p = 1/ap Example: 5 -1 = ⅕, 8 -3 =1/8 3 Evaluate Expressions Involving Powers / Exponents / Index using this rule of indices calculator. First Indices Rule. Second Indices Rule. Third Indices Rule. Fifth Indices Rule. Sixth Indices Rule #1. Sixth Indices Rule #2. Evaluating Expressions Involving Powers / Exponents / Index are made easier here. HHS first published a regulation implementing the Church, Coats-Snowe, and Weldon Amendments in 2008. 73 Fed. Reg. 78,072 (Dec. 19, 2008). In 2011, HHS revised the conscience rule to be narrower and handle conscience matters on a case-by-case basis. 76 Fed. Reg. 9968 (Feb. 23, 2011). In 2019, HHS finalized a sweeping revision of the rule that. Simplifying Surds. Advanced Trigonometry 1. HCF and LCM. Rounding and Estimating. Types of numbers. Higher Vectors 1. Higher Vectors 2 and Congruent Triangles. Enlargement and Similarity. Unit: Rules of Indices.
PPT Lesson 2 Laws of Indices PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2747003
Indices or Powers. mc-TY-indicespowers-2009-1. A knowledge of powers, or indices as they are often called, is essential for an understanding of most algebraic processes. In this section of text you will learn about powers and rules for manipulating them through a number of worked examples. In order to master the techniques explained here it is. Laws of indices Indices are used to show numbers that have been multiplied by themselves. They can also be used to represent roots, such as the square root, and some fractions. The laws of.
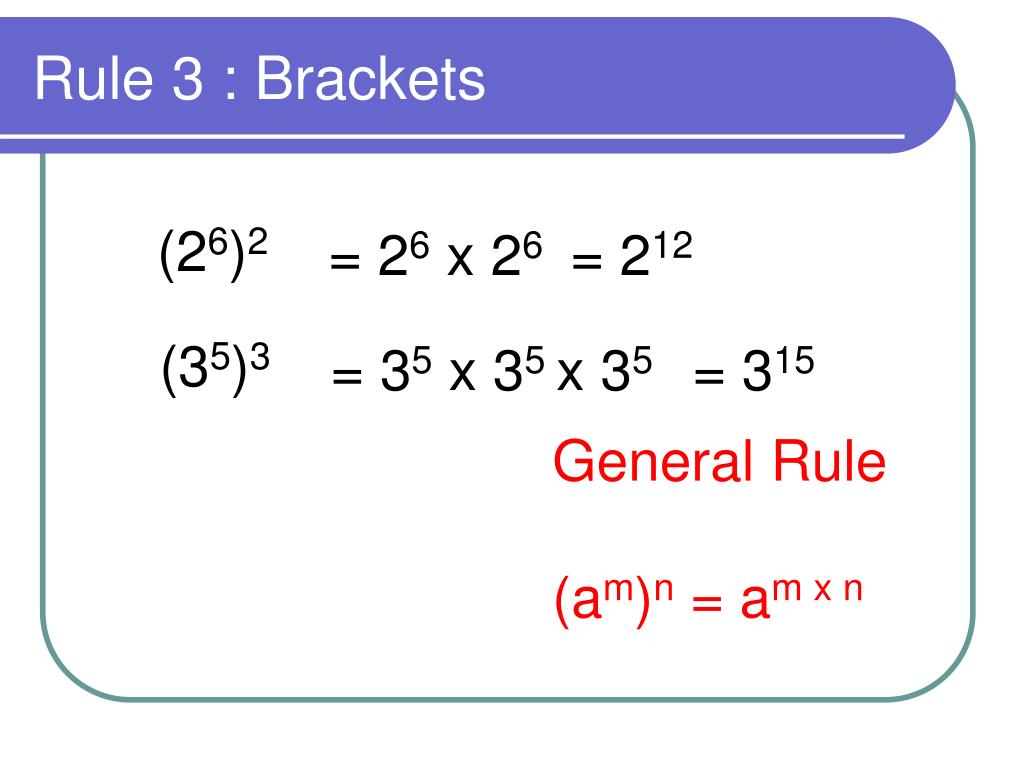
The exponent laws, also called the laws of indices (Higgens 1998) or power rules (Derbyshire 2004, p. 65), are the rules governing the combination of exponents (powers). The laws are given by x^m·x^n = x^(m+n) (1) (x^m)/(x^n) = x^(m-n) (2) (x^m)^n = x^(mn) (3) (xy)^m = x^my^m (4) (x/y)^n = (x^n)/(y^n) (5) x^(-n) = 1/(x^n) (6) (x/y)^(-n) = (y/x)^n, (7) where quantities in the denominator are. is the base and 5 is the index. Also, 10 × 10 × 10 × 10 = 10 4 And, × × = = 10 3 Generally, in a n = a × a × a × × a a multiplied by itself n times a is the base and n is the index or power. Therefore, a n is in index form, where a 0. Laws of indices To do calculations with indices we follow certain rules. These rules are called the.
PPT Laws of Indices PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1005891
The laws of indices Introduction A power, or an index, is used to write a product of numbers very compactly. The plural of index is indices. In this leaflet we remind you of how this is done, and state a number of rules, or laws, which can be used to simplify expressions involving indices. 1. Powers, or indices We write the expression 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 corbettmaths 184K subscribers Subscribe Subscribed Like 445K views 9 years ago OCR Higher - Paper 5 & 6 - June 2019 Corbettmaths - This video goes through the laws of indices needed for both the.




