Key Points. Reflexes, or reflex actions, are involuntary, almost instantaneous movements in response to a specific stimulus. Reflex arcs that contain only two neurons, a sensory and a motor neuron, are considered monosynaptic. Examples of monosynaptic reflex arcs in humans include the patellar reflex and the Achilles reflex. The primary components of the reflex arc are the sensory neurons (or receptors) that receive stimulation and in turn connect to other nerve cells that activate muscle cells (or effectors), which perform the reflex action.
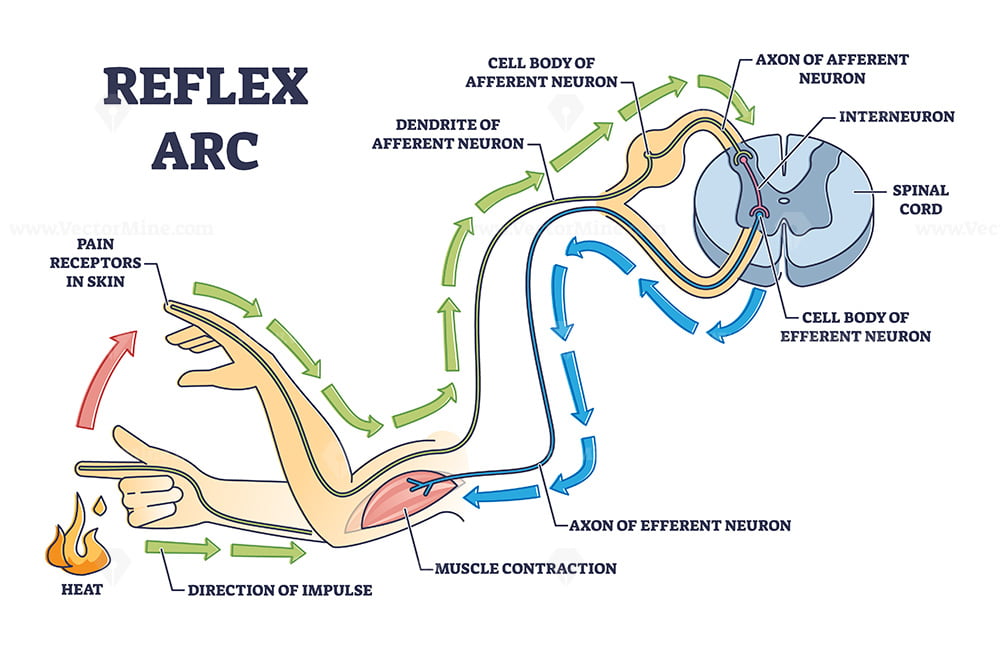
Reflex arc explanation with pain signals and receptor impulse outline diagram VectorMine
A reflex action is an automatic (involuntary) and rapid response to a stimulus, which minimises any damage to the body from potentially harmful conditions, such as touching something hot.. Definition Reflex Arc Components Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Definition The neural network that manages a reflex is known as a reflex or simple reflex arc. In vertebrates, most sensory neurons synapse in the spinal cord rather than entering the brain directly. Reflex Arc A signal travels from the organ and initiates a response to the organ that reacts to the signal. This response causes various parts of the reflex arc to work in order. A simple reflex arc has the following parts: 1. Stimulus It is any change in the environment (internal or external) detected by a receptor. The best known of the reflexes is the patellar, or knee-jerk, reflex. The DTR exam involves a healthcare provider tapping your knee with a rubber hammer (it shouldn't hurt). This tap stretches your patellar tendon and the muscle in your thigh that connects to it. That's how the leg moved on its own. Comment.
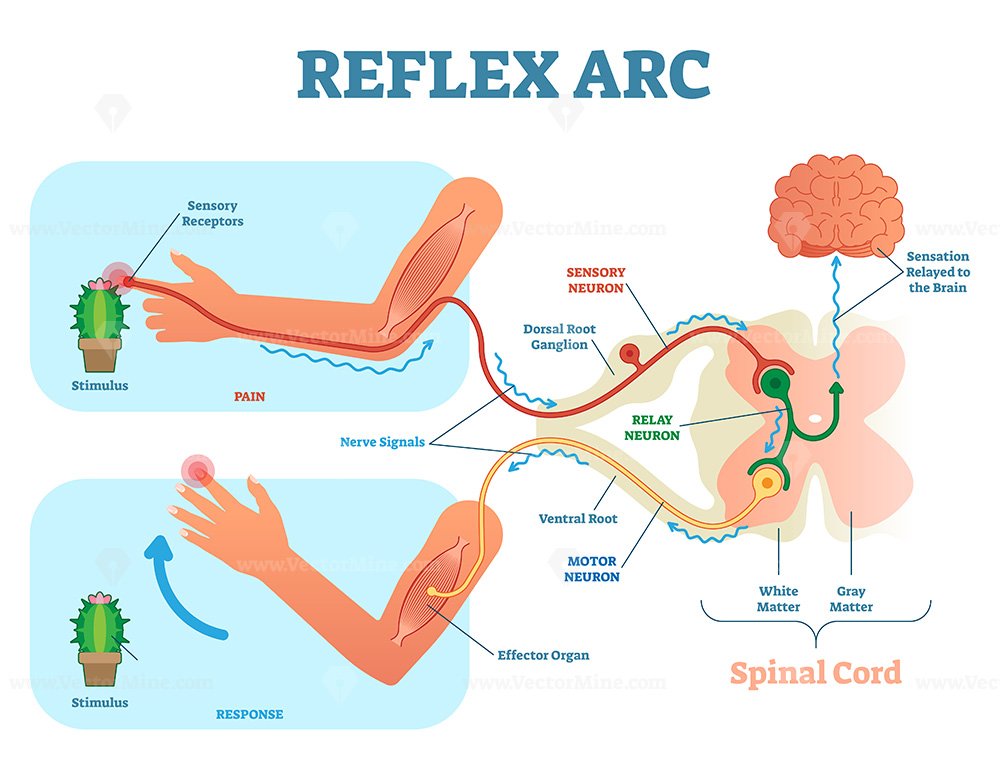
Spinal Reflex Arc anatomical scheme, vector illustration VectorMine
Understanding: • Autonomic and involuntary responses are referred to as reflexes. • Reflex arcs comprise the neurons that mediate reflexes. The basic pathway for a nerve impulse is described by the stimulus response model. A stimulus is a change in the environment (either external or internal) that is detected by a receptor. The reflex arc is the pathway that a signal follows from stimulus to response during a reflex action. The typical reflex arc of a simple reflex has seven components, which are shown in Figure 2. Figure 2: A flow chart showing the 7 components of a reflex arc, from the stimulus to the response. The pathway of a reflex action only travels through relay neurones in the spinal cord and not the brain These are the steps in the reflex arc in more detail: A receptor in the skin detects a. Download scientific diagram | Simple reflex arc. The reflex arc provides the basis for neurological examination of the limbs and trunk. At its most simple, it involves just two neurons - the.
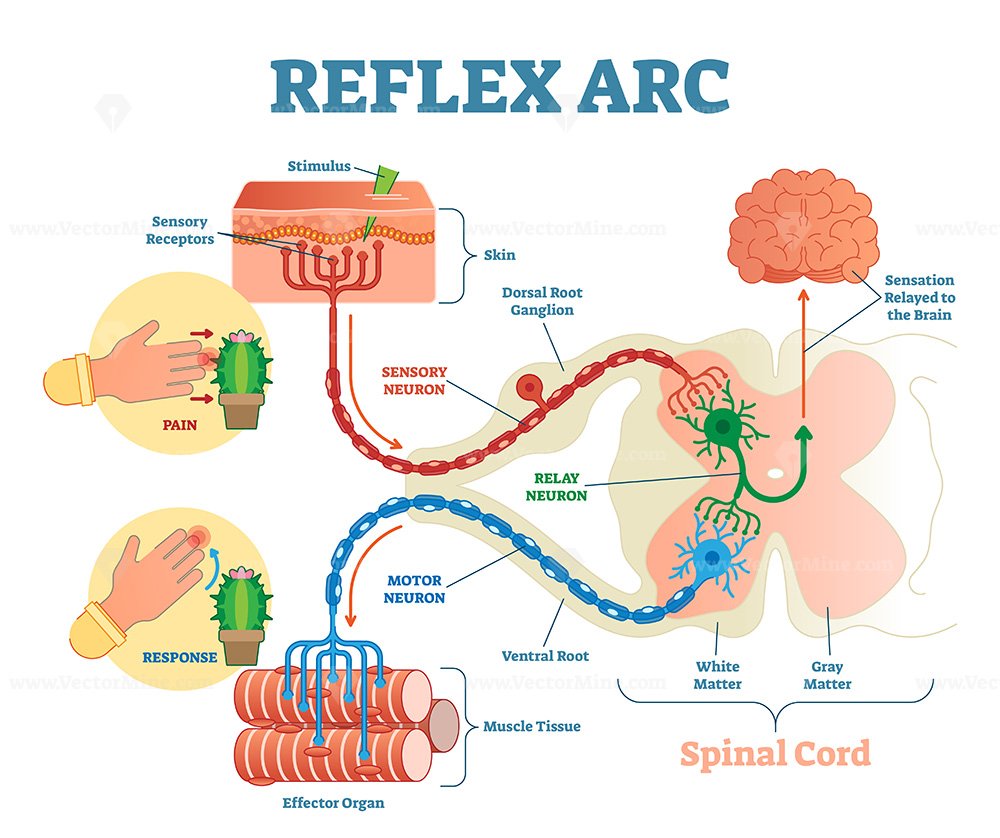
Spinal Reflex Arc anatomical scheme, vector illustration VectorMine
A reflex arc is a neural pathway that controls a reflex. In vertebrates, most sensory neurons do not pass directly into the brain, but synapse in the spinal cord. This allows for faster reflex actions to occur by activating spinal motor neurons without the delay of routing signals through the brain. reflex arc . For example, a simple reflex arc happens if we accidentally touch something hot. Receptor in the skin detects a stimulus (the change in temperature). Sensory neurone sends.
Reflex action (& reflex arc) | Control & Coordination | Biology | Khan Academy Khan Academy India - English 381K subscribers Subscribe Subscribed 19K 840K views 4 years ago Control &. Labelled Diagram Of A Reflex arc Reflex Arc Diagram This labelled diagram of a reflex arc indicates the neural pathway controlling a reflex. It clearly indicates the route adapted when a stimulus occurs and how the reaction takes place.

[Class 10 Biology] What is Reflex Action in Humans? Teachoo
The Reflex Arc works through a series of steps that involve a sensory neuron, an interneuron, and a motor neuron. When a stimulus is detected by the sensory neuron, an impulse is sent to the spinal cord, where it is processed by the interneuron. The interneuron then sends an impulse to the motor neuron, which in turn causes a muscle contraction. A 'Simple Reflex Arc' The following diagram shows the sequence of events described above in more detail, specifically for the case of the 'simple reflex arc'. That is why the diagram shows a vertebra of the spine but does not also include the brain. Figure (2): 'Simple Reflex Arc'




