The bird digestive system is a specialized and efficient process that enables birds to extract maximum nutrition from their food. Let us take a look at some of its most important features: Unlike mammals, birds lack teeth and have a leathery, thin tongue that is sometimes sticky. Their salivary glands are not well-developed, and they produce a. The Bird Digestive System: Saliva, Gizzard & Alimentary Canal. Digestion as a concept covers the passage of food items into and through the body and includes the elimination of wastes as well as the uptake of nutrients. Birds are often small with high energy needs - and for this reason they can digest food very quickly. This high digestive.

behaviour Why does ostrich and other birds like pigeon swallow stones? Biology Stack Exchange
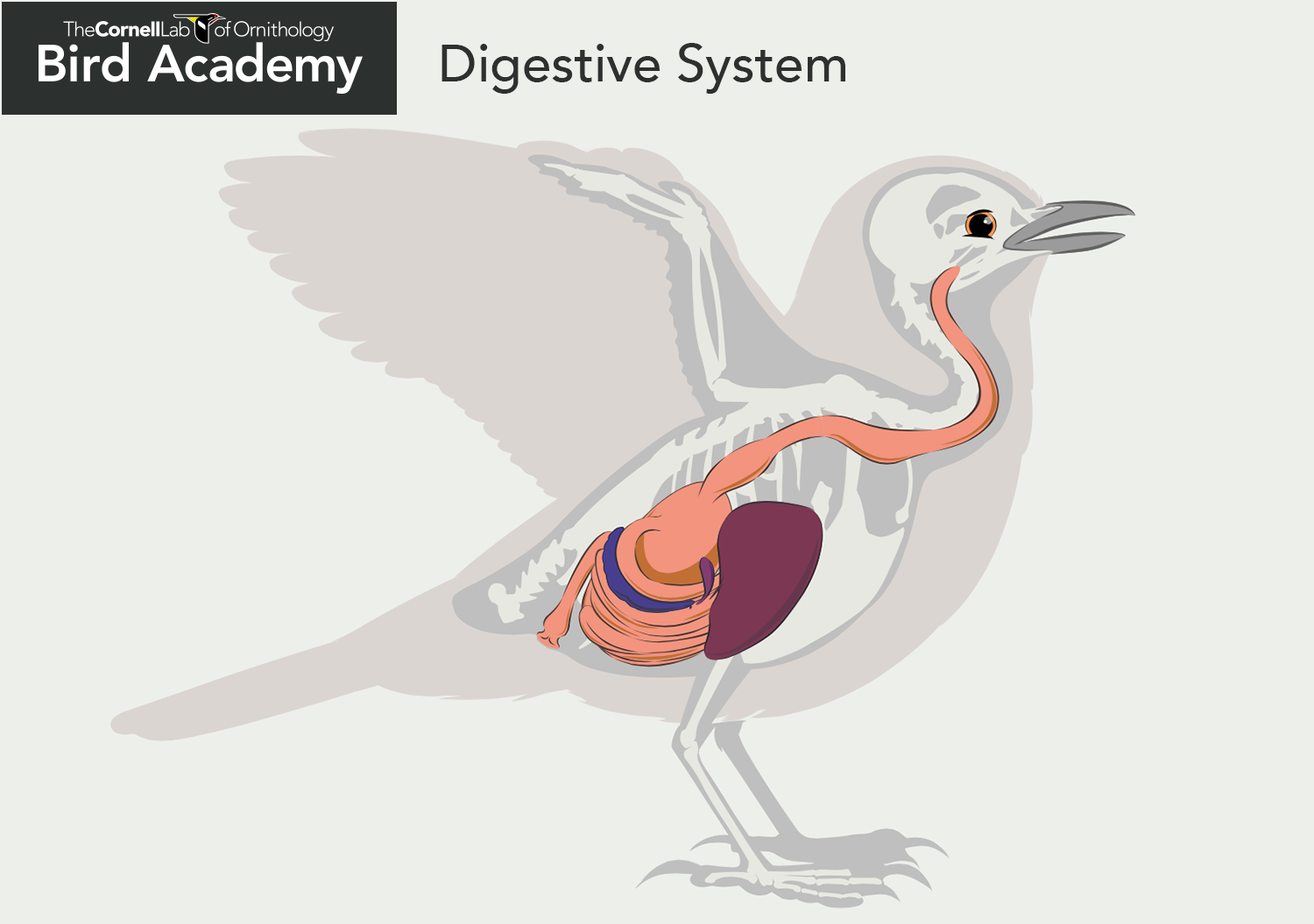
The digestive system of birds has adaptations to facilitate flight. Many birds operate on a thin margin of metabolic safety and may require a constant source of feed to sustain activity. Birds cannot afford to store heavy food materials for long periods and digest their food rather quickly relative to mammals. In addition, the avian intestinal. The digestive order is as follows: bill, mouth, tongue, pharynx, esophagus, crop, proventriculus, gizzard, small intestine, caeca, rectum, cloaca. Bills come in all different sizes and shapes and are used for scooping, pecking, tearing and generally picking up the bird's food. The bird's mouth is the opening where the digestive process starts. The digestive system of any animal is important in converting the food the animal eats into the nutrients its body needs for growth, maintenance, and production (such as egg production).. The ventriculus, or gizzard, is a part of the digestive tract of birds, reptiles, earthworms, and fish. Often referred to as the mechanical stomach, the. Birds have a small intestine that seems very similar to the small intestine of mammals. A duodenum, jejunum and ileum are defined, although these segments are not as histologically distinct as in mammals. The proximal small intestine receives bile from the liver and digestive enzymes from the pancreas, and the absorptive epithelial cells are.

19.5 Birds Guest Hollow
Digestive System of Birds (Avian GI Tract) is elaborated to understand key functions of each part to learn and remember for critical Exams. Easy and Impressi. A bird's gastrointestinal (GI) tract morphology, digestive strategy, and metabolic capability have been intimately intertwined during evolution to match the nutrient content and physical at- tributes of foods available in its natural habitat. When compared across species, the GI tract is the most anatomically diverse organ system. Digestive system of a bird. In these topics. Pet Owner Version: Description and Physical Characteristics of Birds. Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA (known as MSD outside of the US and Canada) is dedicated to using leading-edge science to save and improve lives around the world. The Veterinary Manual was first published in 1955 as a service to. The digestive system of the birds includes more regions than ours. The first region is the beak with the fleshy tongue, followed by the esophagus. As seed-eaters, budgies have a crop. This is a sack-like pouch of the esophagus located at its lower section. The crop fulfills two different tasks: First, the food is moistened in it, but the actual.

Bird Digestion
The digestive system of birds has adaptations to facilitate flight. Many birds operate on a thin margin of metabolic safety and may require a constant source of feed to sustain activity. Birds cannot afford to store heavy food materials for long periods and digest their food rather quickly relative to mammals. The crop stores food temporarily and starts the digestion process before it enters the stomach. It is a thin-walled pouch at the base of the esophagus where birds can store food before it is sent the rest of the way to the stomach. When the crop becomes empty, hunger signals are sent to the brain telling the bird it is time to eat.
The major components of the avian digestive system are the alimentary canal plus several accessory structures. The 'canal' includes the oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus (which includes a crop in some birds), stomach (proventriculus & gizzard), small intestine, & large intestine.. birds received a high digestive quality diet of the flesh from. Courtesy of Soerfm, Wikimedia Commons. Not considered part of the actual digestive system itself, the crop acts more as a holding area.Being able to consume a large amount at once but not digest it straight away is advantageous in many situations, such as when feeding out in the open, a big risk to many birds.. Instead of returning time and again to take small amounts, they can make off with.
All About Bird Anatomy Bird Academy • The Cornell Lab
Bird Lung (left), Bird Digestive Tract (right) Nervous System and Sense Organs. Birds have a large brain relative to the size of their body. Not surprisingly, the part of the brain that controls flight is the most developed part. The large brain size of birds is also reflected by their high level of intelligence and complex behavior. Figure 34.4.1 34.4. 1: Bird digestive system: The avian esophagus has a pouch, called a crop, which stores food. Food passes from the crop to the first of two stomachs, called the proventriculus, which contains digestive juices that break down food. From the proventriculus, the food enters the second stomach, called the gizzard, which grinds food.




