Understanding Rivers A river is a large, natural stream of flowing water. Rivers are found on every continent and on nearly every kind of land. Grades 5 - 12+ Subjects Earth Science, Biology, Ecology, Geography, Physical Geography, Geology Loading. Powered by Background Info Vocabulary Advertisement Rivers are flowing bodies of water with distinct boundaries that drain into another body of water, usually an ocean or another river. They are used to generate electricity and are used as the lifelines of cities and towns throughout the world. Yet, rivers aren't simply a homogenous form of water that appear out of nowhere.
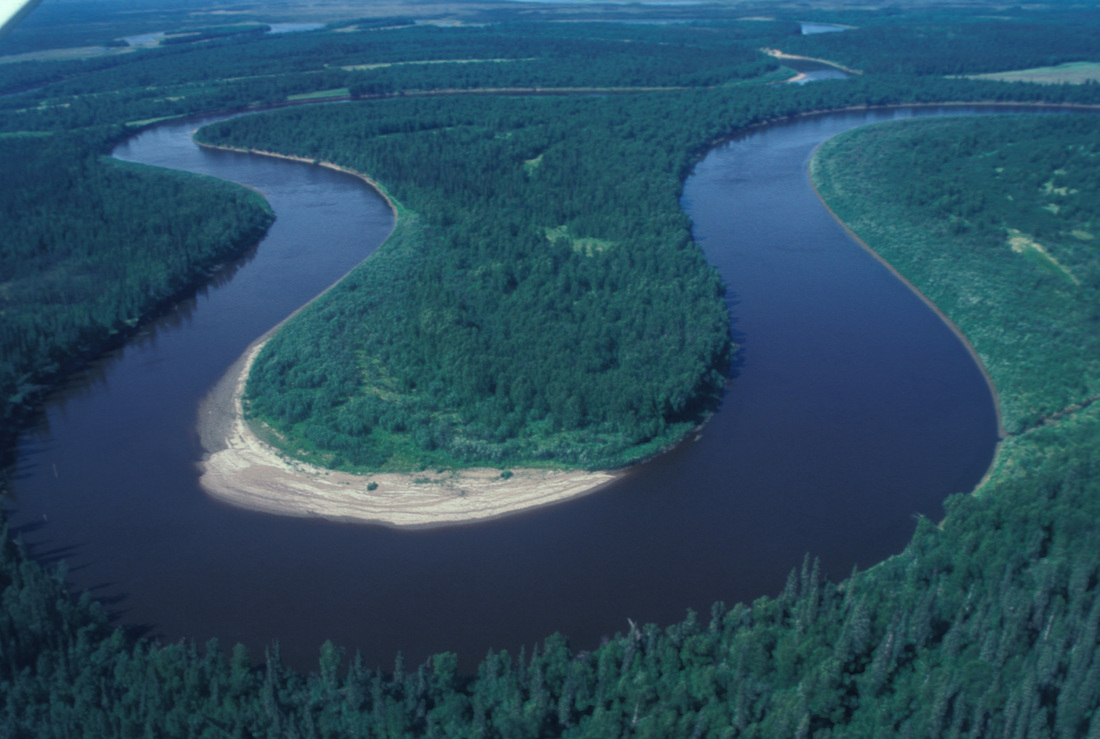

meanders river features
Vocabulary A river is a ribbon-like body of water that flows downhill from the force of gravity. A river can be wide and deep, or shallow enough for a person to wade across. A flowing body of water that is smaller than a river is called a stream, creek, or brook. What are they? Roads? Paths? Strange shaped fields? Now, check out the short video below from Liverpool University. This is a simple model that shows how rivers 'move' and change their course over time. How are rivers formed? Rivers meander where there is the least resistance. In this diagram, the river is moving around the rocks. Rivers usually begin in upland areas, when rain falls on. river, (ultimately from Latin ripa, "bank"), any natural stream of water that flows in a channel with defined banks . Modern usage includes rivers that are multichanneled, intermittent, or ephemeral in flow and channels that are practically bankless. The concept of channeled surface flow, however, remains central to the definition. The word stream (derived ultimately from the Indo-European.
2.1 River Features GEOGRAPHY FOR 2020 & BEYOND
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually a freshwater stream, flowing on the earth's land surface or inside caves towards another waterbody at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, sea, bay, lake, wetland, or another river. A river is often divided into three parts or stages and has features that are specific to each stage. The table below explains the main features of each stage. Stage. Main activity. Main features. 5.5: The Morphology of Rivers. Page ID. John Southard. Massachusetts Institute of Technology via MIT OpenCourseware. Figures 5-17 and 5-18 are simplified flow-transverse cross sections through a representative single-channel alluvial river of medium to large size. Figure 5-17 shows the entire stream valley, and Figure 5-18 shows details of the. A river is a moving body of water that drains the land. It flows from its source on high ground, across land, and then into another body of water. This could be a lake, the sea, an ocean or even.
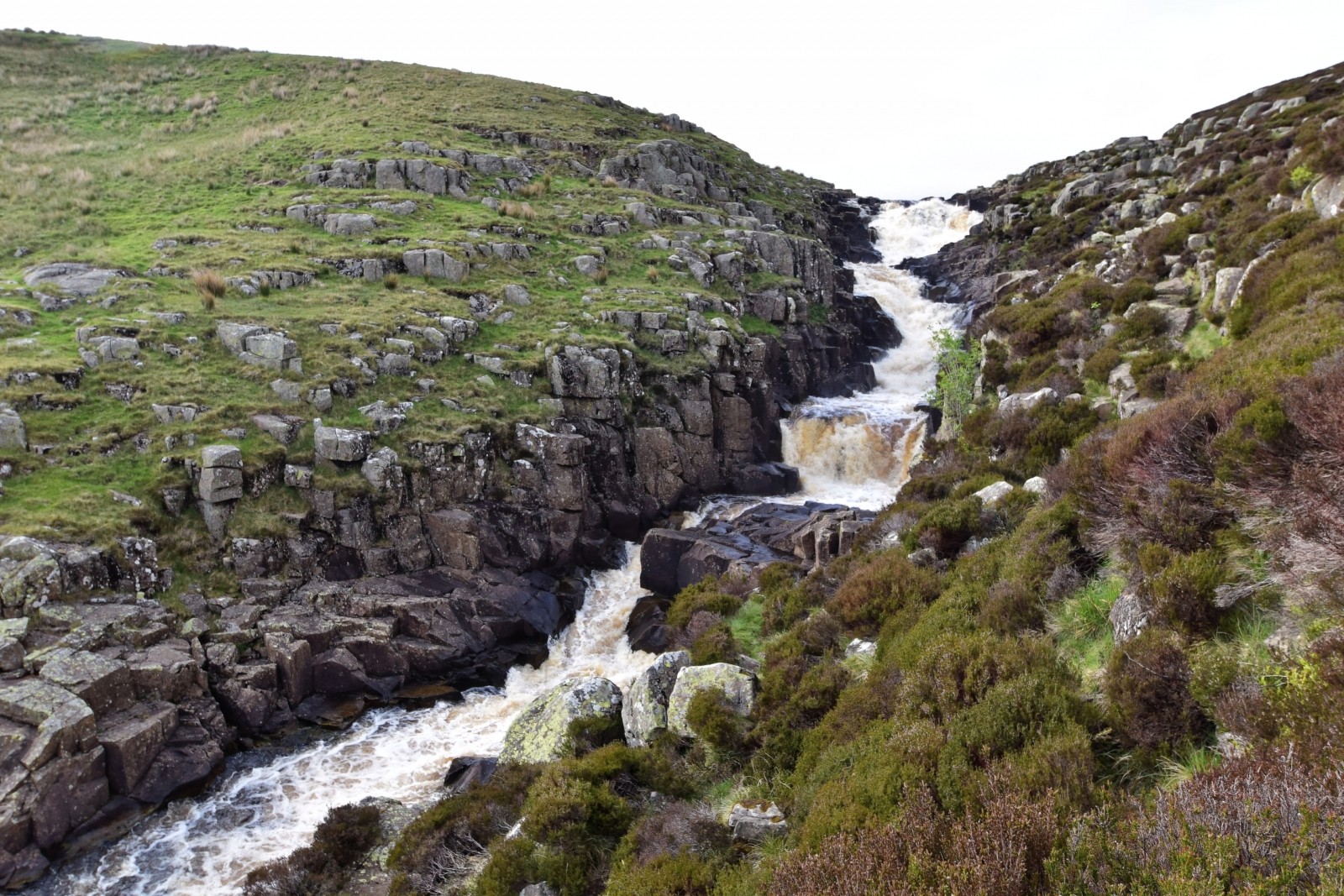

Landforms in the upper course of a river Geography
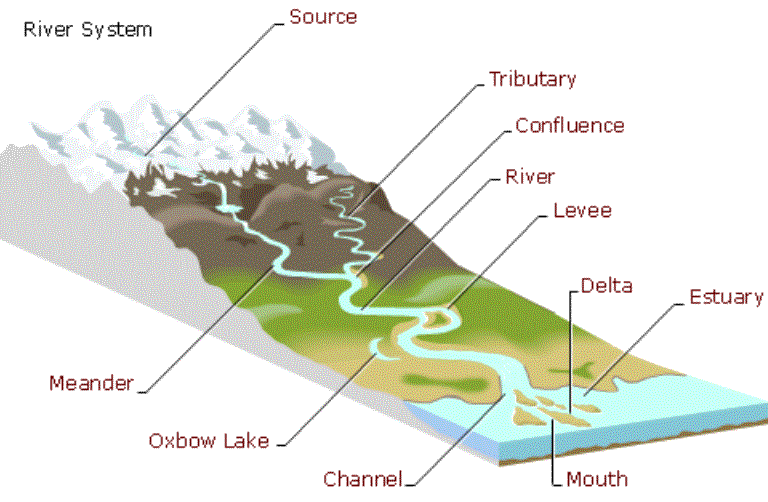
Follow Us: A river is characterized by continuously flowing water from an upland source into lakes, wetlands or the sea. Rivers are fed by tributary streams or springs, and they include a river channel, shoreline and a floodplain. All rivers have a river bed, which all differ from one another. River Features Typically, a river valley can be divided into three sections; the upper course, the middle course and the lower course. There are particular river features which we can expect to find in each of these sections. We shall examine each section of the river along with their various features in some detail.
This is also known as river beheading or river piracy. Its development is dependant on the different rate of headward erosion (back-cutting) into a divide. For example - if one side of the divide has more gradient or receives more precipitation than the other, the process given below will follow. Stream A will cut back more rapidly than. Introduction Water current pervades every facet of existence for life in lotic (flowing water) habitats. Maintaining position in the face of flow can be energetically costly, but provides access to.

VUDEEVUDEE'S GEOGRAPHY BLOG RIVER LANDFORMS
What are the characteristics of rivers? Changing-channel characteristics Downstream changes Rivers perform three key tasks: they wear away their channels, carry materials, and form new landscapes through erosion and deposition. 15 facts about rivers 1) The Nile River is widely accepted as the world's longest river. Found in north Africa, it flows through 11 different countries and stretches a whopping 6,695km - that's as long as 65,000 football pitches!




