It's more of a dark grey, mixed in with some white, black, and even a bit of orange — and all this is caused by its geology. Apparent color and true color The moon appears to shine because it. Calcium, Silicon, Feldspar, Pyroxene. Curiously, the common point of all these minerals is that, in the form of dust, they are all grey. The other thing is that, like all moons and planets, our moon doesn't emit its own light… Moon light comes from the reflection of the light coming from the sun.
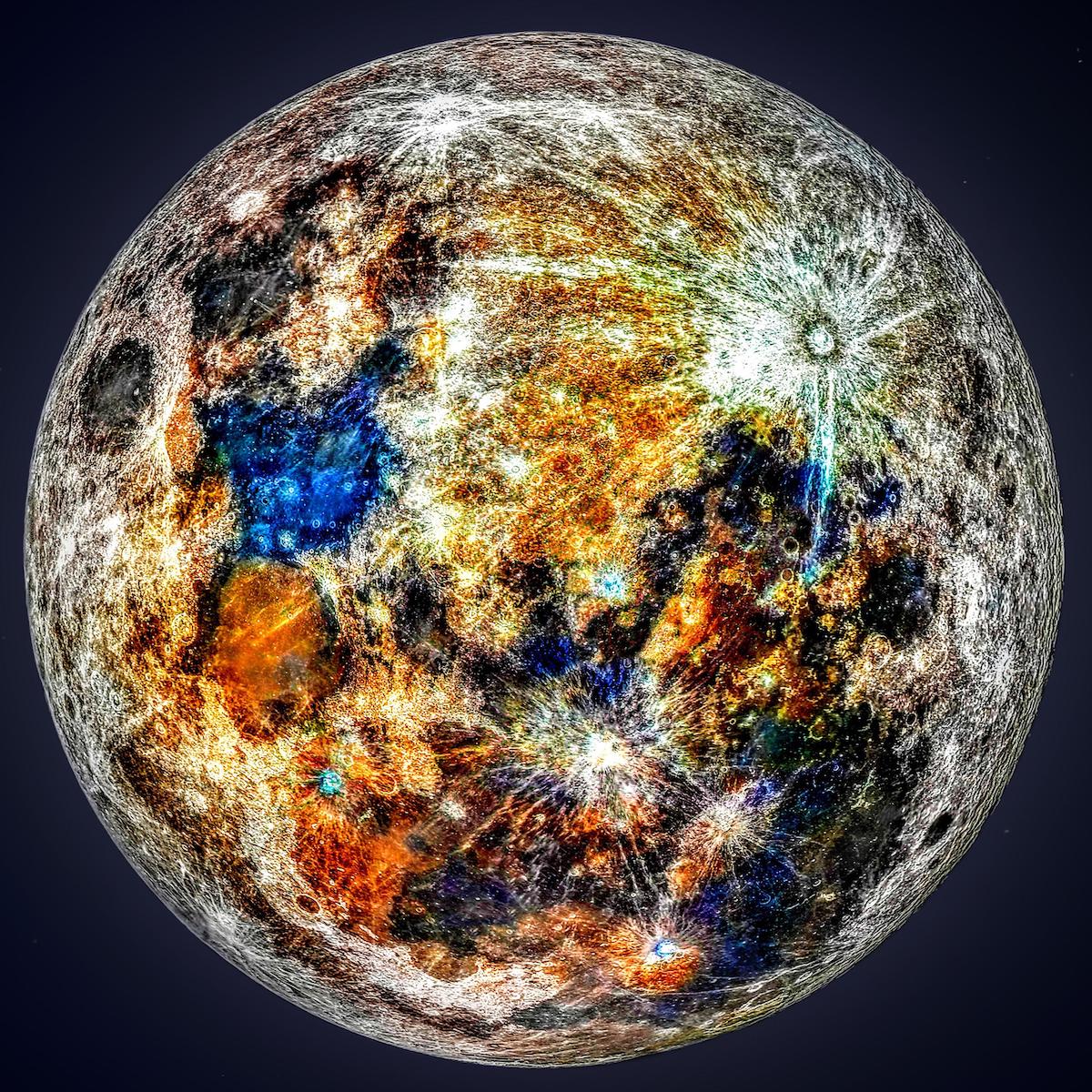
150,000 Photos Used Show the Hidden Colors of the Moon
August 22, 2023 The constant presence of Earth's Moon has captivated humans throughout our relatively short tenure on this planet. There are still mysteries that plague us about this tantalizingly close ball of rock. One common question we hear a lot is "what color is the Moon?" What colour is the Moon? - BBC Sky at Night Magazine The Moon has many glorious shades, just ripe for observing, photographing and even sketching. Kevin Kilburn explains how you can see them. What color is the Moon? The photographs of the Moon, taken from space are the best true-color views of the Moon. That gray color you see comes from the surface of the Moon which is. The moon's actual color is an off-white brown-gray when its dusty surface is sunlit. But Earth's atmosphere modifies our views of the moon, altering colors and shape. Italian photographer.

LUNAR LIGHTS ON A HOLLOW MOON? Red Shaman Intergalactic Ascension Mission
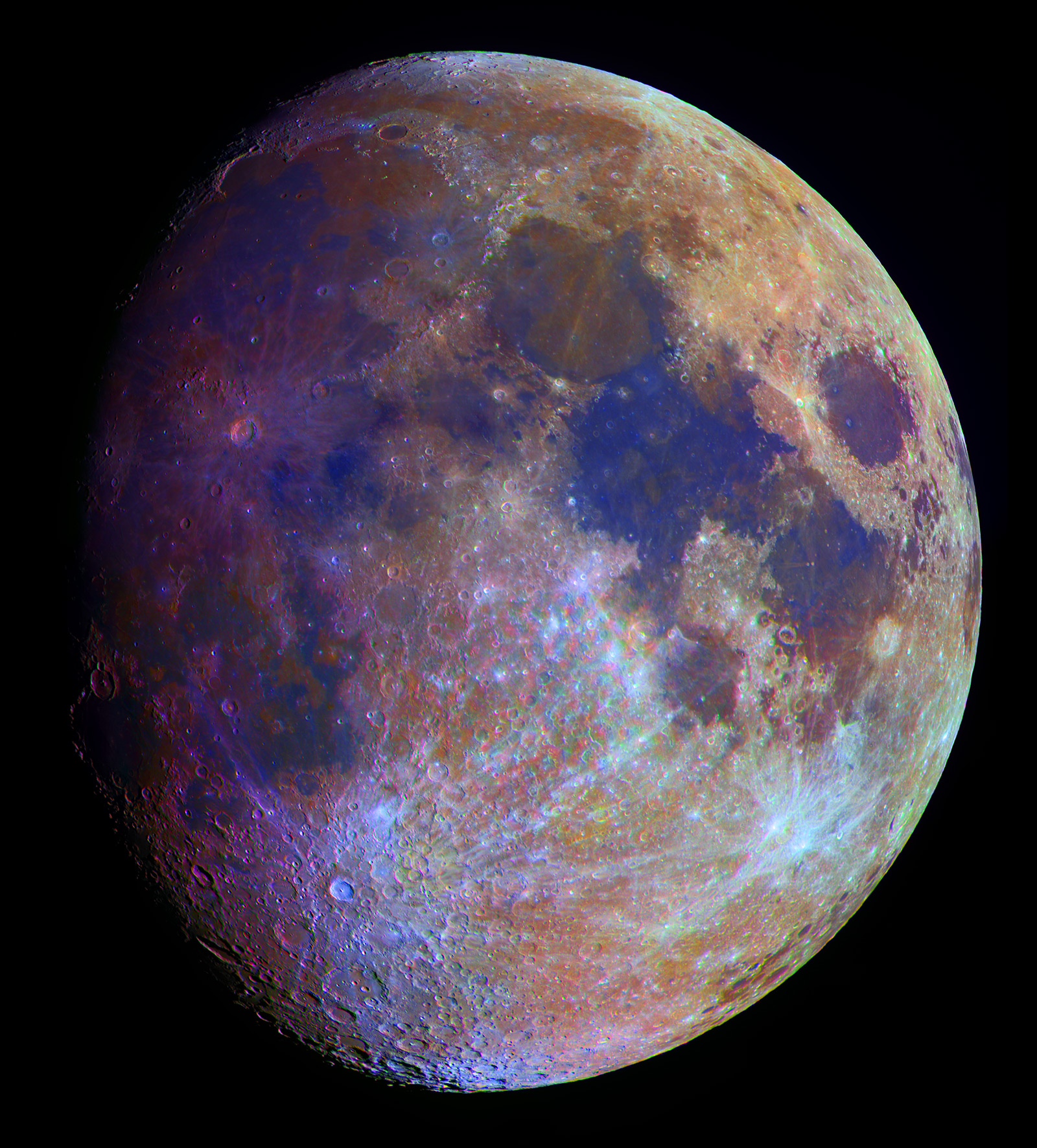
Explanation: What color is the Moon? It depends on the night. Outside of the Earth's atmosphere, the dark Moon, which shines by reflected sunlight, appears a magnificent ly brown-tinged gray. Viewed from inside the Earth's atmosphere, though, the moon can appear quite different. What Are All Of The Possible Types Of Moon Colors? The more the Moon climbs in the sky, its color changes from red to orange, to yellow and possibly white, if it climbs high enough in the sky. While climbing high in the sky, the Moon changes color. Image credit: Stefano Moschini. What color is the moon? The 4 dominant types of rocks on the moon are mare basalts, breccia, anorthosite, and regolith. Altogether, the moon has mostly grey colors with dark spots known as Lunar Maria. The Moon appears gray or whitish-gray when viewed from Earth. This color is due to the surface materials on the Moon, which are primarily. The Moon's Real Color Home Multimedia Gallery The Moon's Real Color. The Moon may look black and white to the naked eye, but the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera's filters show its true colors in this image. ID#: WEB15286-2016 Source: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center/Arizona State University.

GeoSphere Some Facts about the Moon
What Color is the Moon? From here on Earth, the sunlit part of the Moon usually looks bright, almost white. This is an illusion. The brightness of the Sun's reflected light makes it difficult to see the Moon's actual color from a distance. Does it really? Is the moon a chameleon? Read on to find out if our moon changes color. Every couple of years we hear in the news about a Pink Moon or a Blue Moon and in some cases a Red Moon. We know that the moon actually does not turn color.
What color is the Moon? The actual color of the Moon is a combination of various shades of gray. We know this from the days of the NASA missions. Photographs, lunar rocks, and soil samples were taken by Apollo Astronauts while on the surface of the Moon. If gray is its primary color, why do we see so many different colors of the Moon? To some the Moon appears colourless, or even grey.

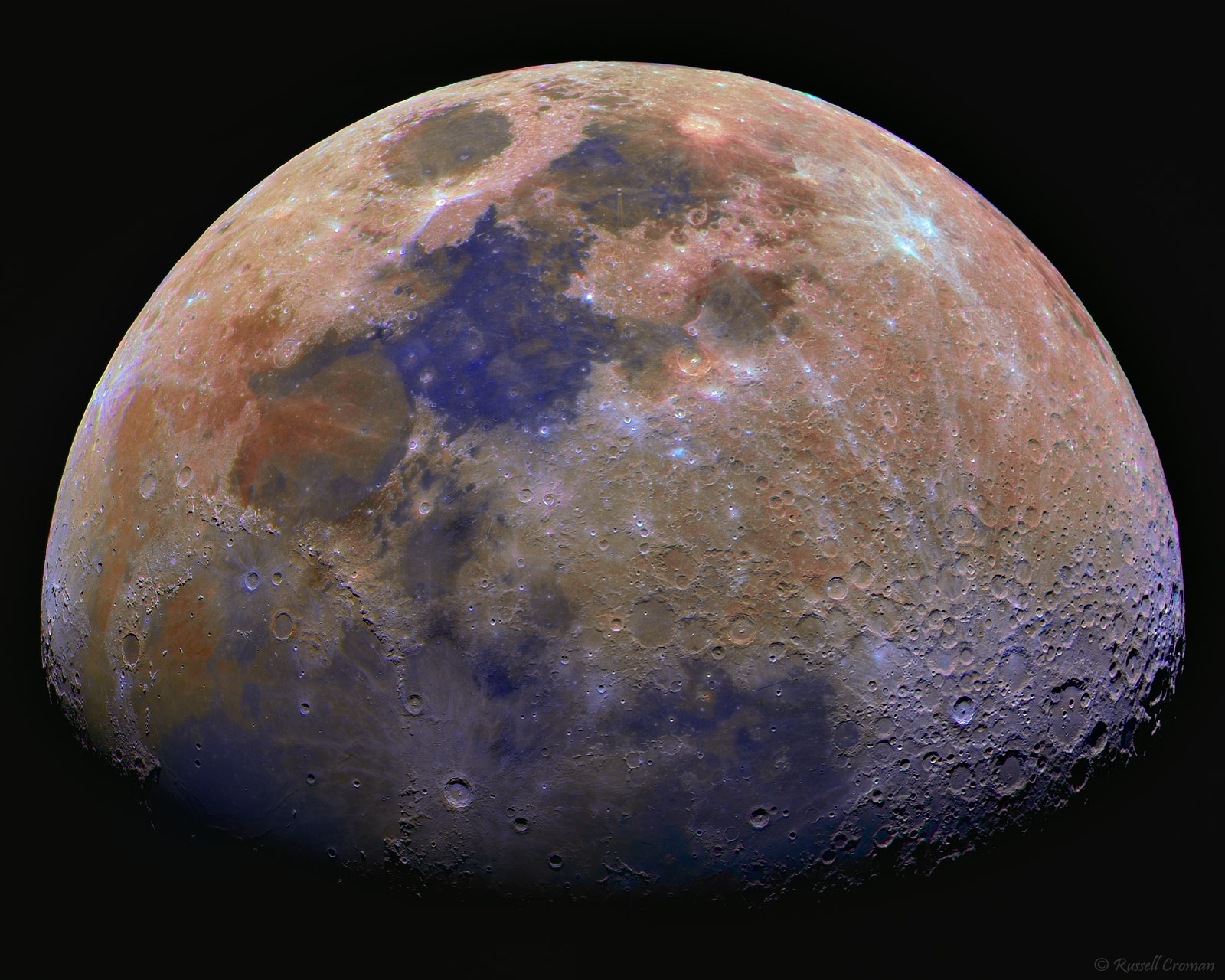
Full Moon (enhanced color) The Society
Yellow or Orange "Harvest moon" is the name for a yellow or orange moon, which usually occurs in late summer or early fall. A harvest moon usually occurs when our dusty neighbor is sitting close to the horizon, meaning that the light reflecting off the Moon has to travel through more of the atmosphere to reach our eyes. Lunar Surface in Color Image Credit: NASA/Goddard/Arizona State University Published: October 9, 2017 A color composite mosaic showing most of the Moon's surface, based on images from NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, photometrically normalized. Note that small "holes" in the mosaic are due to shadows or satauration in the original observations.




