Thermoforming is a manufacturing process where a plastic sheet is heated to a pliable forming temperature, formed to a specific shape in a mold, and trimmed to create a usable product. A plastic sheet is heated in an oven then stretched into or onto a mold and cooled to a finished form. Guides 15 minutes read Table of Contents What is Thermoforming? Plastic comes in different sizes, types, colors, and with different material characteristics. The wide variety of plastic makes it a crucial material for manufacturers interested in producing both prototypes and end-use parts for use.

Accelerating Growth with Thermoforming Equipment SupplyOne
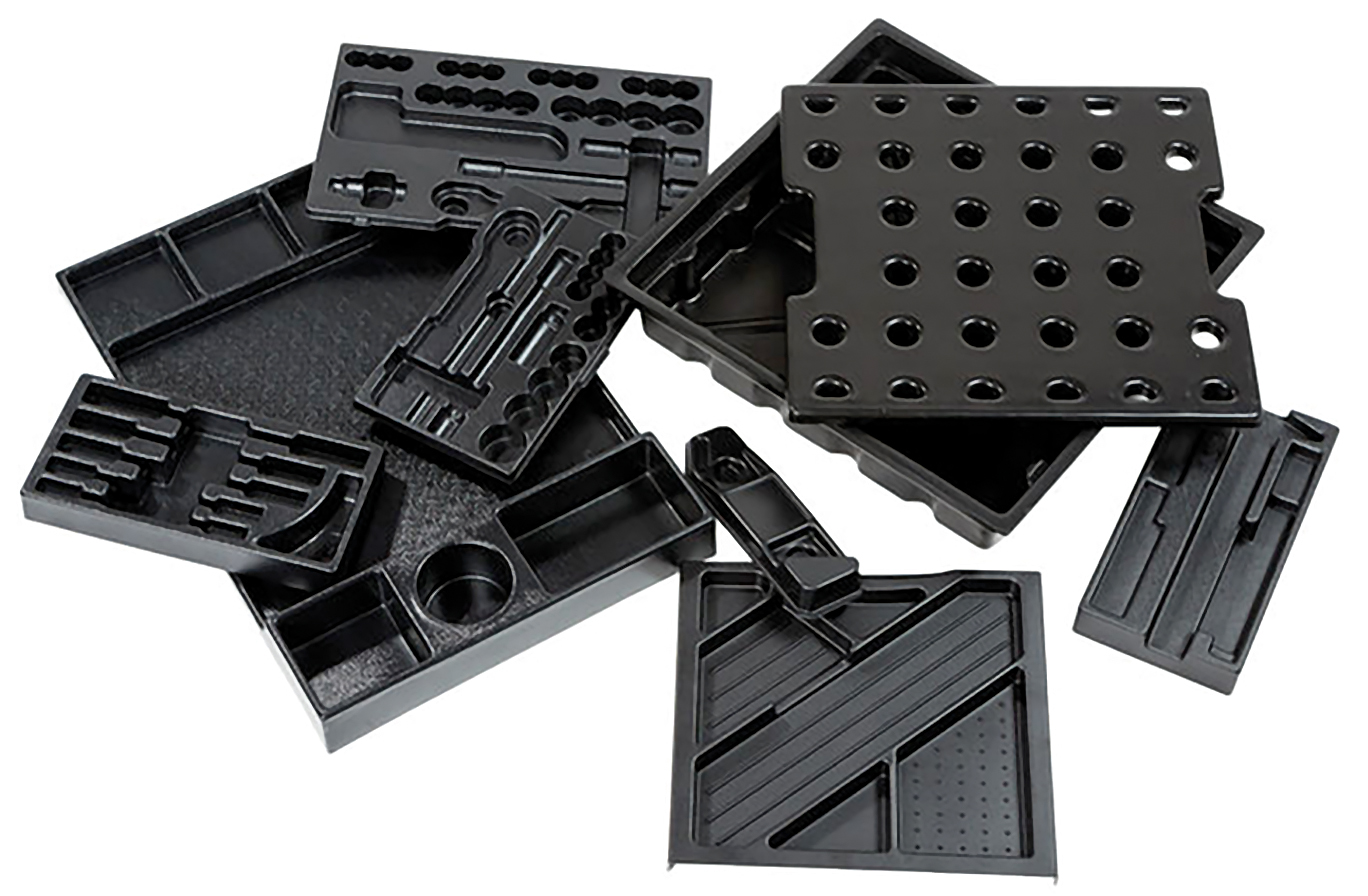
Plastic Thermoforming is a plastic manufacturing process that applies a force (vacuum or pressure) to stretch a sheet of heated thermoplastic material (thermo) over an engineered mold to create a 3-dimensional shape or part (forming). PETG Plastic PETG, or polyethylene terephthalate - glycol modified has good clarity, impact strength, and moderate resistance to acids and alkalis. PETG is relatively easy to thermoform and can be heat or RF (radio frequency) sealed without getting cloudy. The process of evacuating air from the sealed space between the hot sheet and the mold, thus allowing atmospheric pressure (14.7 p.s.i.) to force the sheet to conform with the contour of the mold. Applications: Non-critical appearance covers, dunnage trays, internal covers. Competes with sheet metal and fiberglass. A low- to medium-volume process. Procedure A person holds a mold in an open vacuum bed. A sheet of hot plastic will be placed on top and the bed sealed, pulling the plastic down over the mold.

INTECH Thermoforming
A thermoforming primer. First, some basics: The process takes the form of either vacuum or pressure forming. In the former, a heated, pliable plastic sheet is pulled against the contours of the mold by vacuum pressure. "Since pressure is only applied to one side of the sheet," explains Formed Plastics Inc., "vacuum forming is typically. Resin is a really good example of a thermoset plastic. None of these plastics can be recycled. Thermoplastic Thermoplastics is a plastic polymer which becomes soft when heated and hard when cooled. Thermoplastic materials can be cooled and heated several times: when they are heated, they melt to a liquid and when they cool they become hard. forming can be ideal when you need durable plastic parts that don't require sharp non-tool side features. Applications: • Non-critical appearance covers, dunnage trays, internal. Thermoforming Design Guide • www.Thermoform.com. Example #2. Assume a part size of 10" x 11" x 5" deep. Surface Area = 2(10" x 5") + 2(11" x 5. The process of thermoforming. In the thermoforming process, a thermoplastic sheet is heated to a temperature where it is pliable. It is, then, stretched over a mould and held in place while it cools and solidifies into the desired shape. The thermoplastic sheet is clamped and heated by an oven using either convection or heat until it is melted.
Professional Plastics Thermoforming Video YouTube
Some of the most common are: Introduction Vacuum Forming: This is the most basic process. In vacuum forming, vacuum alone is used to mold the part. The forming "pressure" is thereby limited to atmospheric pressure, about 14.7 psi. Pressure Forming: In pressure forming a pressure box is used on the side of the part opposite the mold. First, a plastic sheet is heated to a temperature at which it becomes pliable. Then, the malleable plastic is cooled so it can harden into the desired shape. Types of thermoforming Pressure forming and vacuum forming are the most common thermoforming techniques.
Step 1 is to heat the plastic sheet to a pliable temperature, then shape it to the mold using vacuum pressure, air pressure or a combination of both. Once the material has formed to the mold, it's cooled and removed from the mold, keeping its final shape. Since the final project cools against the mold surface under ambient temperatures. Vacuum forming, a low-cost thermoforming process, offers an economical method of creating large-size, low-volume plastic parts. As a custom thermoforming specialist, Universal Plastics has all the answers to your vacuum forming questions. Read through the most frequently asked questions below, or call us at 800-553-0120 for more information.

a row of plastic stadium seats
The process is accomplished by applying heat and pressure (positive or negative) to stretch and conform a two dimensional thermoplastic sheet material onto temperature controlled molds to create custom three dimensional shaped structures and parts. PRIMARY FORMING TECHNIQUES Noryl® Engineering plastic with outstanding strength, stiffness, and electrical insulating properties. PETG Transparent plastic sheet with good impact resistance and outstanding thermoforming characteristics. Polycarbonate Transparent, strong and stiff thermoplastic with outstanding impact resistance. Polycarbonate Film




