¡Precios increíbles y alta calidad aquí en Temu. Envío gratuito en todos los pedidos. No deslizar. Enormes descuentos en nuestros productos aquí - ¡hasta un 90% de descuento! eBay is here for you with Money Back Guarantee and Easy Return. Get your Biology Today! 75 of the Top 100 Retailers can be found on eBay. Find Biology from the Top Retailers.

9.3 Transpiration a level biology student
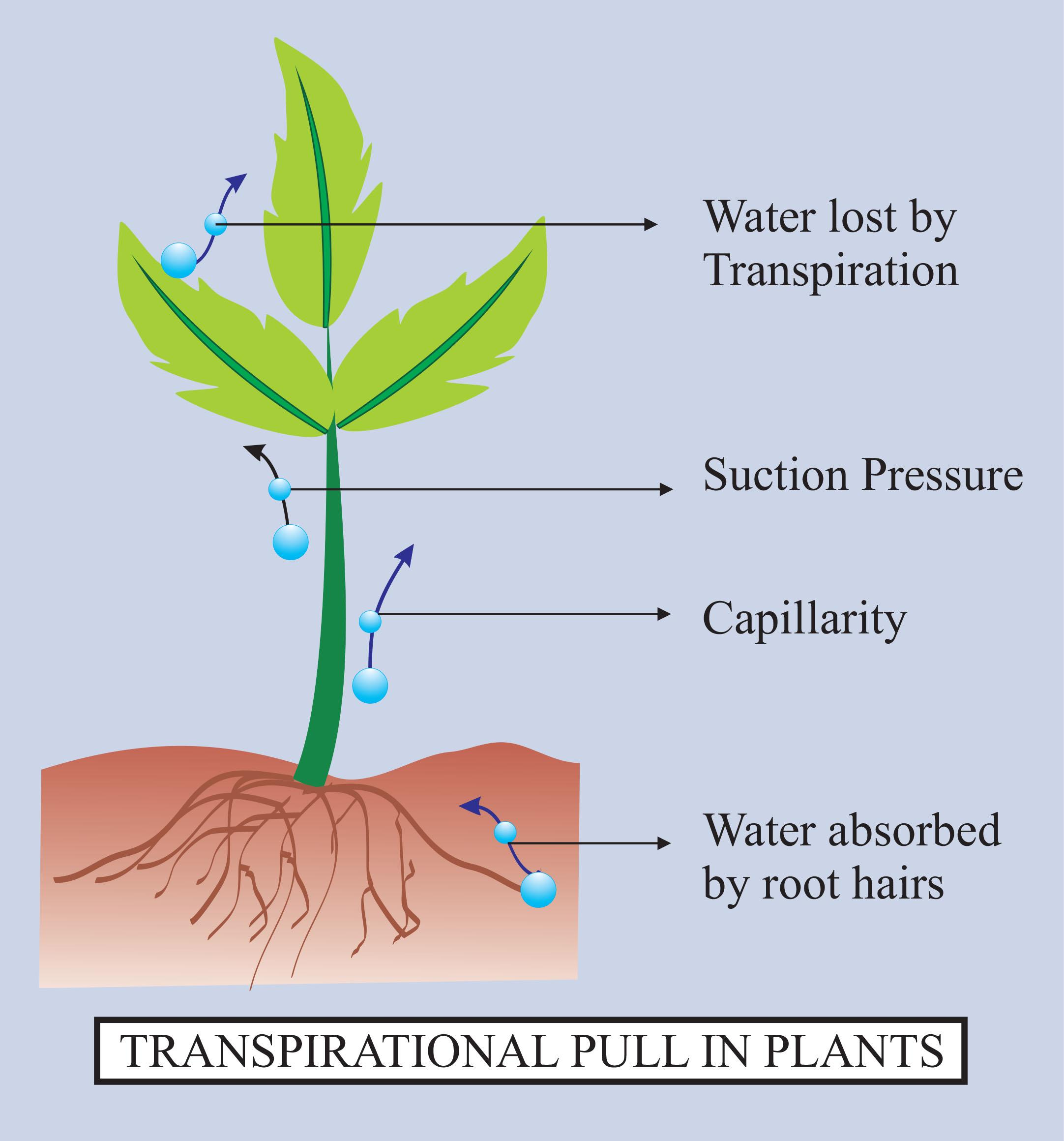
Transpiration refers to the loss of water vapour via the stomata by diffusion Note that this is different to the transpiration stream which is the movement of water from the roots to the leaves Transpiration is important to the plant in the following ways It provides a means of cooling the plant via evaporative cooling Introduction to Transpiration (A-level Biology) Introduction to Transpiration Transpiration Transpiration is where plants absorb water through the roots. It then travels up through the plant, in the xylem vessels, getting released into the atmosphere as water vapour through the leaves' pores. The role of the stomata Transpiration is mainly controlled by the pairs of guard cells that surround stomata (singular stoma) Guard cells open the stomata when they are turgid and close the stomata when they lose water When the stomata are open there is a greater rate of transpiration and of gaseous exchange Freesciencelessons 651K subscribers 5K views 5 months ago A Level Biology "Exchange and Transport in Plants" In this video, we look at transpiration and the cohesion-tension theory of water.

Transpiration and translocation
Transpiration involves several cellular structures in the leaf (Figure 4.5.1.2.1 4.5.1.2. 1 ). Water on the surface of mesophyll cells saturates the cellulose microfibrils of the primary cell wall. The leaf contains many large intercellular air spaces for the exchange of oxygen for carbon dioxide, which is required for photosynthesis. Transpiration is the evaporation of water from plants. Most of the water absorbed by the roots of a plant—as much as 99.5 percent—is not used for growth or metabolism; it is excess water, and it leaves the plant through transpiration. Transpiration is very important for maintaining moisture conditions in the environment. Transpiration is the process of evaporation of water at the spongy mesophyll surface in the leaves, where the water vapour is lost through the stomata. There are four main reasons and processes for the importance of transpiration. They are photosynthesis, cooling, support and movement of minerals: Learn how a potometer shows the rate of transpiration and the associated calculation. Learn how to set up the equipment, collect the data and try some commo.
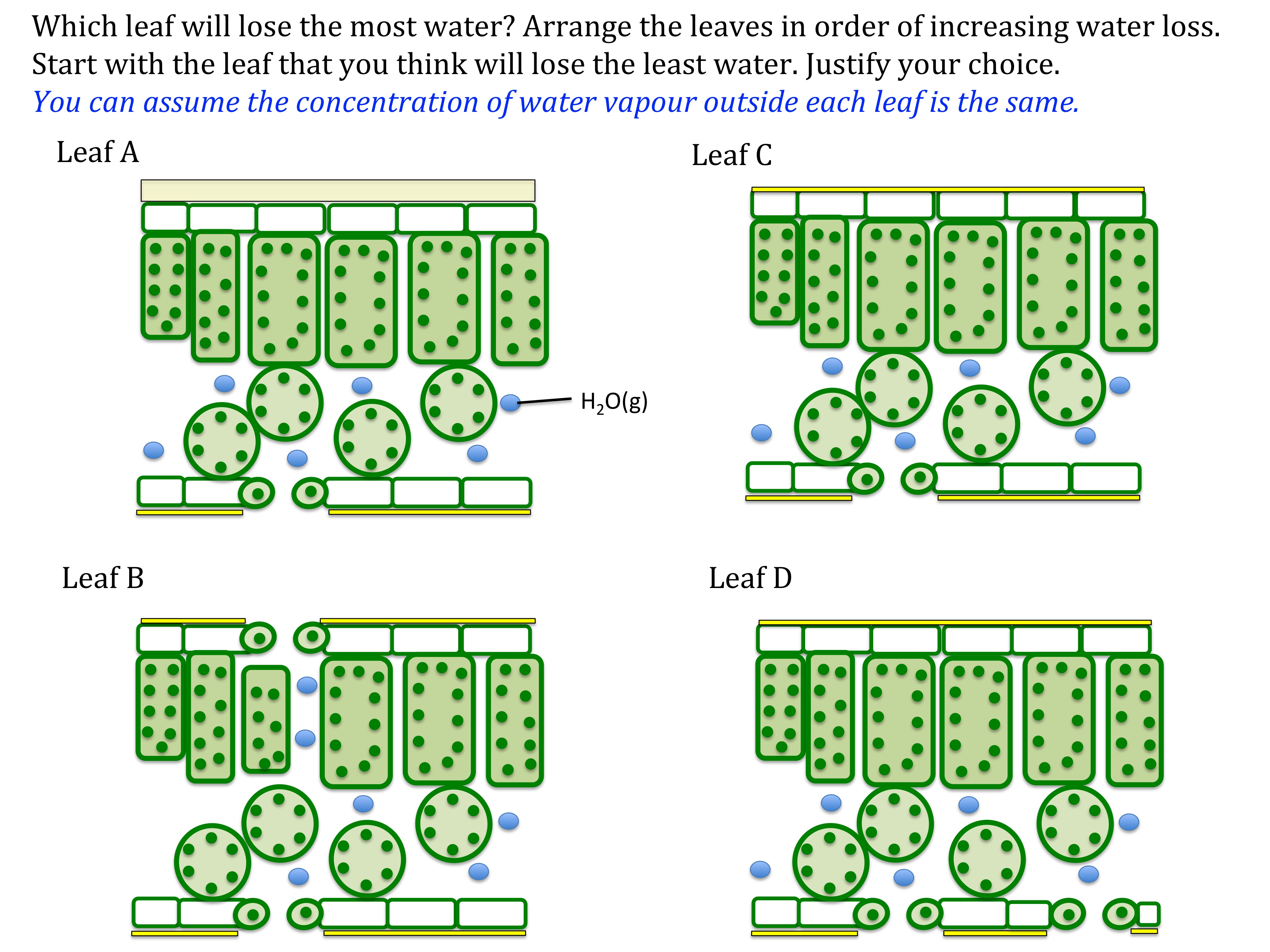
Maximum transpiration takes place from(a)Stem(b)Leaves(c)Roots(d)Flowers and fruits
16.2C: Transpiration. Page ID. John W. Kimball. Tufts University & Harvard. Transpiration is the evaporation of water from plants. It occurs chiefly at the leaves while their stomata are open for the passage of CO 2 and O 2 during photosynthesis. How does water move up a plant? We start with the leaf and work backwards to find out.
Exam Tip When answering questions about transpiration it is important to include the following keywords: Water potential gradient (between leaves and roots), Diffusion (water vapour through the stomata) Transpiration pull (evaporation of water from the mesophyll cells pulls other water molecules from the xylem tissue) This is expressed as ΔΨ. Transpiration is the loss of water from the plant through evaporation at the leaf surface. It is the main driver of water movement in the xylem. Transpiration is caused by the evaporation of water at the leaf-atmosphere interface; it creates negative pressure (tension) equivalent to -2 MPa at the leaf surface.
Transpiration teaching resources the science teacher
Transpiration refers to the loss of water vapour from a plant to its environment by evaporation and diffusion Transpiration is a consequence of gaseous exchange at the stomata The advantage of transpiration is that: It provides a means of cooling the plant via evaporative cooling The transpiration stream is helpful in the uptake of mineral ions True or false: transpiration is useless to plant function. false. Give four examples of how transpiration is useful to plant functions: it transports useful mineral ions up the plant, maintains cell turgidity, supplies water for growth, cell elongation and photosynthesis, supplies water that evaporates and keeps the plant cool.




