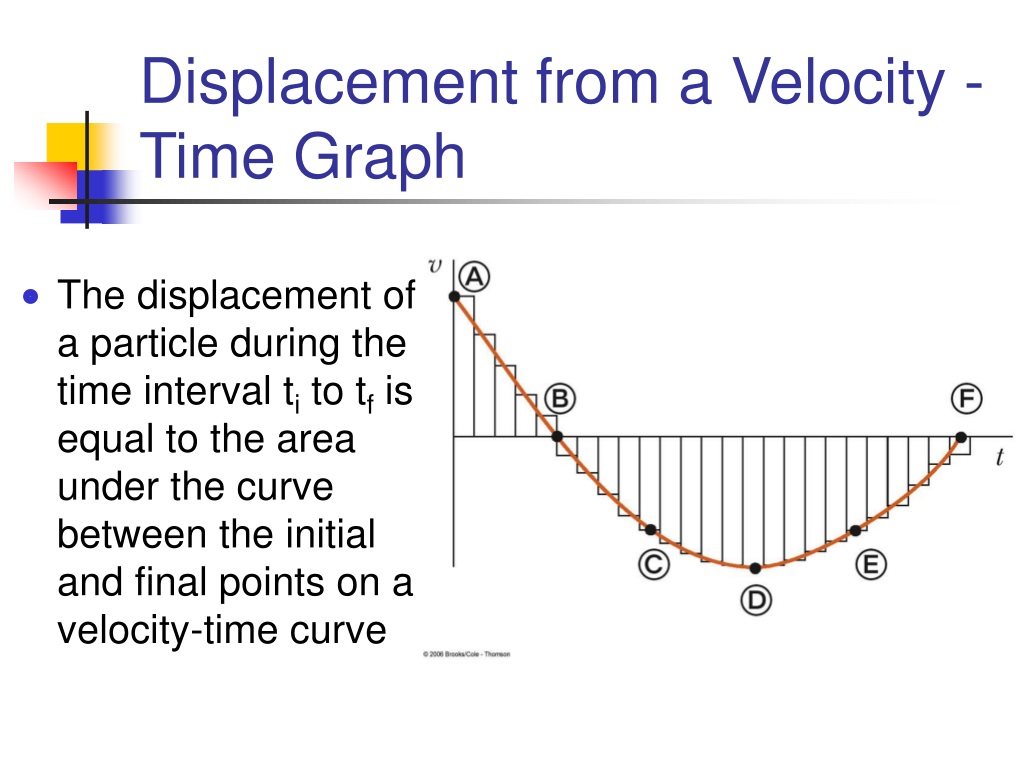
It works because displacement is the product of velocity and time. And in our graph when you multiply velocity and time you're basically multiplying two lengths in our graph and that gives us the area. And so that's the secret to calculating displacements and from a velocity time graph. The displacement close displacement A distance measured in a specified direction. of an object can be calculated from the area under a velocity-time graph. The area under the graph can be.

Velocity Time Graph And Position Time Graphs
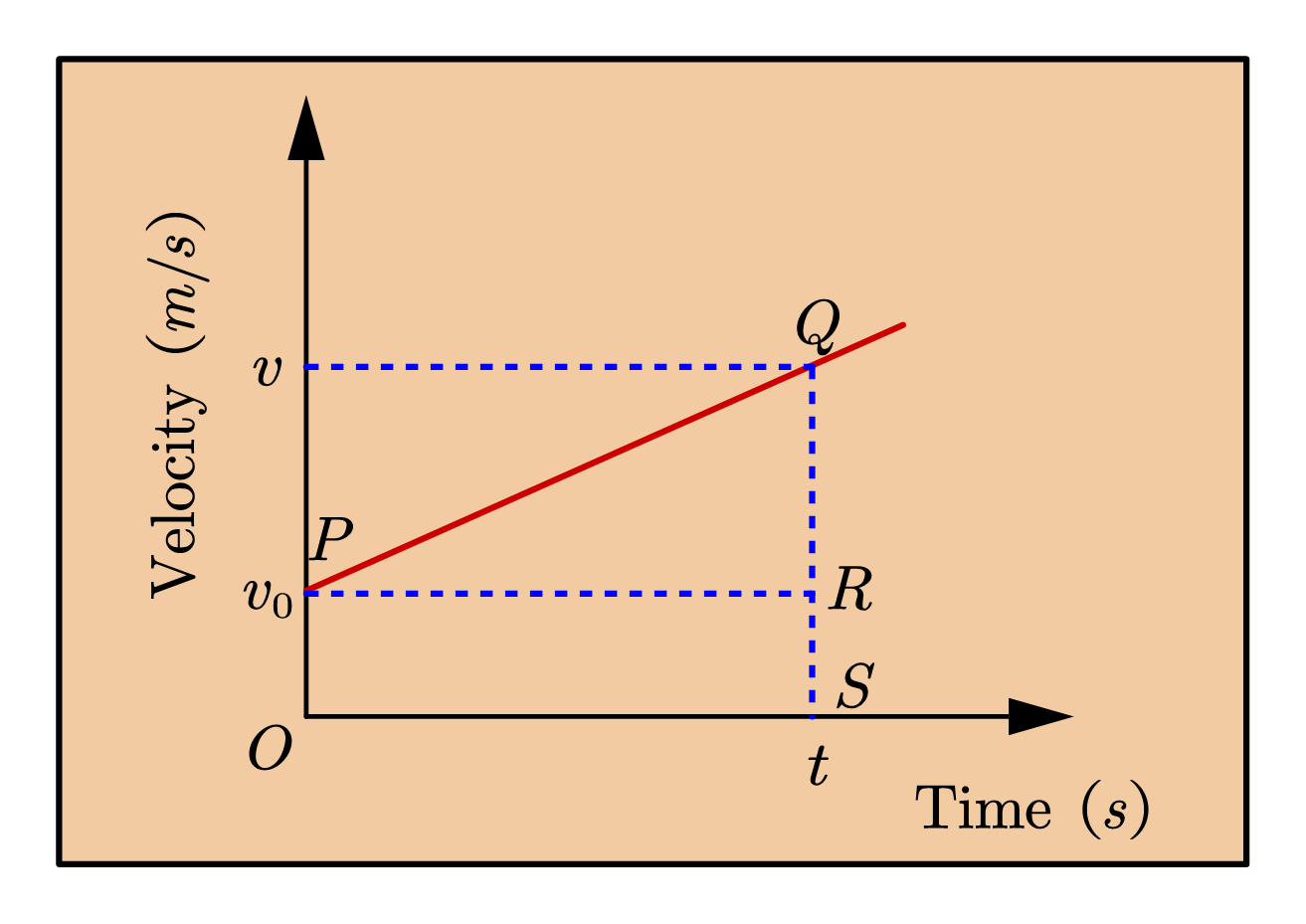
The first answer was correct, displacement does need a quantity and direction. Displacement can be calculated by measuring the final distance away from a point, and then subtracting the initial distance. Displacement is key when determining velocity (which is also a vector). Velocity = displacement/time whereas speed is distance/time. The slope of a velocity graph represents the acceleration of the object. So, the value of the slope at a particular time represents the acceleration of the object at that instant. The slope of a velocity graph will be given by the following formula: slope = rise run = v 2 − v 1 t 2 − t 1 = Δ v Δ t. v ( m / s) t ( s) r i s e r u n t 1 t 2. The gradient of a displacement-time graph is velocity 2.Velocity-timegraphs. Any point on such a graph will have coordinates (t,v), in which v is the velocity after a time t. WorkedExample2. Figure 2 shows the velocity-time graph for the motion of the tennis ball described in example 1. It was thrown into the air with a velocity of 7 m s−1. Finding displacement from velocity graphs. An eagle is flying around and its velocity v as a function of time t is given in the graph below where rightwards is the positive velocity direction. What is the eagle's displacement Δ x from t = 1.0 s to 4.0 s ?
What is Velocity time graph? physicscatalyst's Blog
The area under a velocity-time graph is equal to the displacement of a moving object; Displacement = Area under a velocity-time graph. Acceleration is any change in the velocity of an object in a given time; As velocity is a vector quantity, this means that if the speed of an object changes, or its direction changes, then it is accelerating. An. Displacement-time graphs. Save Copy. Log InorSign Up. Explore: Try using the sliders for initial postion, s_initial, initial velocity, u, and acceleration, a. How does each one change the graph 1. s initial = 0. 2. u = 1 8. 3. a = 0. 4. Turn on the example graphs below. Each of dashed red and blue curves represent the 1D displacement of an. Additional resources for Calculating Displacement from Velocity-Time Graphs. PRACTICE PROBLEMS AND ACTIVITIES (2) FIGURE EX2.8 is a somewhat idealized graph of the velocity of blood in the ascending aorta during one beat of. (II) Given v (t) = 25 + 18t, where v is in m/s and t is in s, use calculus to determine the total displacement. Its velocity v as a function of time t is given in the graph below where rightwards is the positive velocity direction. A set of black coordinate axes are given with the vertical axis labeled "v (m/s)" and the horizontal axes labeled "t (s)".
CBSE CLASS 9TH SCIENCE(PHYSICS) CHAPTER MOTION (Graphical ) Part2
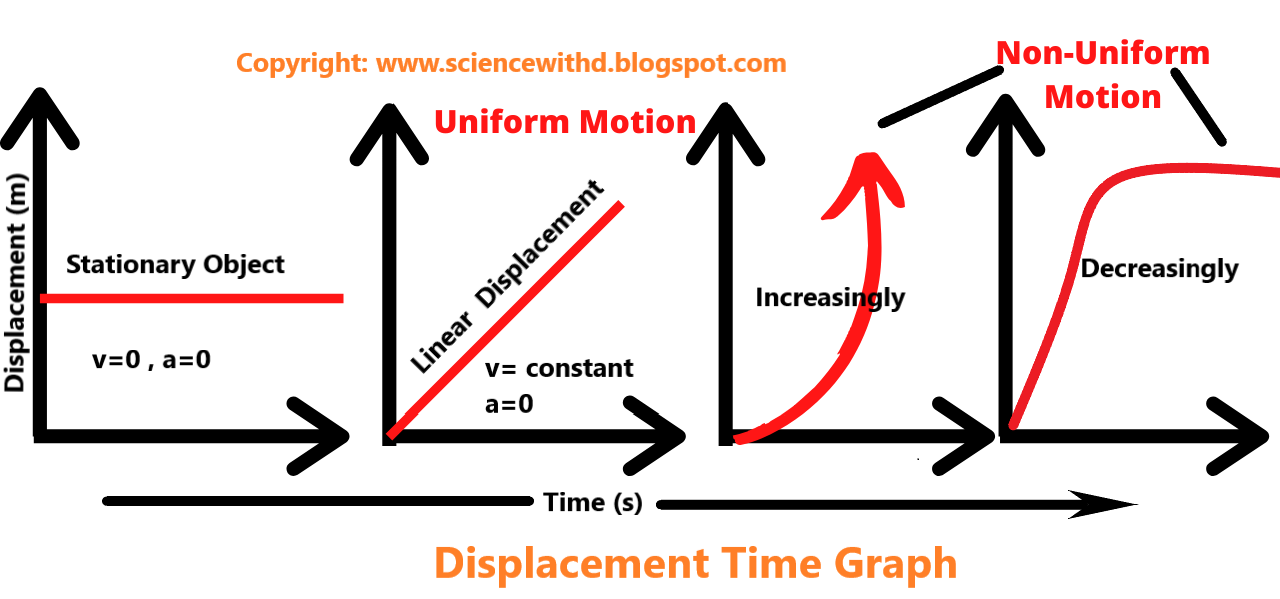
So the value of the slope at a particular time represents the velocity of the object at that instant. To see why, consider the slope of the position vs. time graph shown below: [Wait, why is the vertical axis called x?] x ( m) t ( s) r i s e r u n t 1 t 2 x 1 x 2. The slope of this position graph is slope = rise run = x 2 − x 1 t 2 − t 1 . No. Distance-vs.-time graphs only account for the total movement over time. Position-vs.-time graphs note one's position relative to a reference point (which is where x=0 on the graph in the video). Here's an example of the difference: A tennis player hits a ball to a wall 5 meters away, and the ball bounces back the same distance.
The Velocity-Time Graphs: Displacement Calculations Video Tutorial describes the significance of area on a velocity-time graph. Details about how to calculate the area between the line and the time axis are explained and modeled through numerous examples. Common pitfalls are discussed and strategies for analyzing complex situations are described. Question Video: Determining Displacement from a Velocity-Time Graph. The velocity-time graph shows the change in the velocity of a person walking in the time interval from 𝑡 = 0 s to 𝑡 = 6 s. The person's starting point is their position when 𝑡 = 0 s. What is the person's displacement from their starting point after 3 seconds?
PPT Chapter 2 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9510735
This physics video tutorial explains how to calculate displacement from a velocity-time graph.Physics - Basic Introduction: https. The displacement is given by finding the area under the line in the velocity vs. time graph. The acceleration is given by finding the slope of the velocity graph. The instantaneous velocity can just be read off of the graph. To find the average velocity, recall that vavg = Δd Δt = df−d0 tf−t0.



