Woodland Food Chain Any woodland food chain begins, as most food chains do, with the producers. Trees produce seeds, which are eaten by first order consumers like squirrels and birds. Grasses and shrubs provide additional food for first order consumers including mice and deer. What Is the Food Chain for the Woodlands Ecosystem? | Sciencing Food chains describe "what eats what" in an ecosystem. The woodland food chain is like most food chains in that it has primary producers and tiered-levels of consumers; however, the woodland food chain is complex.

Forest Food Chain
The woodland ecosystem food chains food webs and the plant animal and decomposition subsystems - Rain Forests Ecology Center Survival (current) Water Freedom System Miracle Farm Blueprint Air Fountain Water Harvester The Lost Superfoods Christian Prepper Backyard Liberty Blackout USA Survival MD DIY Survival Sanctuary Survive the 2020s Food chains Can you find different food chains in a woodland habitat? First, find a producer - a plant that makes its own food from sunlight. Next, find a consumer that eats the. Several distinct types of woodland habitats exist on Earth, such as conifer, deciduous and mixed. A study of the deciduous forest shows how a food chain functions within an ecosystem that experiences distinct seasonal changes. The Deciduous Forest Cycle Woodland Foodchains Squirrel Rabbit Bat Toad Frog My favourite food is acorns. I eat other nuts, hard fruit, fungi and grains. I make stores of food for the winter. Unfortunately, I cannot always remember where I have put them. My favourite food is grass. I also eat other green crops. I can eat 180 kg of food in a year. I have lived in Britain.

Ecosystems by Readfield 3rd Graders [licensed for use only] / Woodland Food Chain
Food Chain The food chain describes who eats whom in the wild. Grades 5 - 12+ Subjects Biology, Ecology Photograph Secondary Consumers A fish, caught by a heron in the U.S. city of Nokomis, Florida, has another fish in its mouth. These secondary consumers in the food chain prey on other organisms. 1. What does a food chain start with? 2. What is shown by the arrows in a food web? Ecology Ecology is the study of living organisms and the places that they live. An ecologist studies the. Aimed at primary learners, this resource aims to develop an understanding of some of the food chains within a woodland habitat. Linked to the topics of animals and all living things, it includes a matching activity, a game and a simulation of a food web. Teacher guidance on running the activities is provided along with cards for the matching. Three types out woodlands are coniferous, leaf and princess. Any woodland eat chain starter with producers like trees, shrubs, plants both grasses. Primary consumers include mice, insects, birds and deer. Secondary users is minor predators. Tertiary consumers include bears and cops.
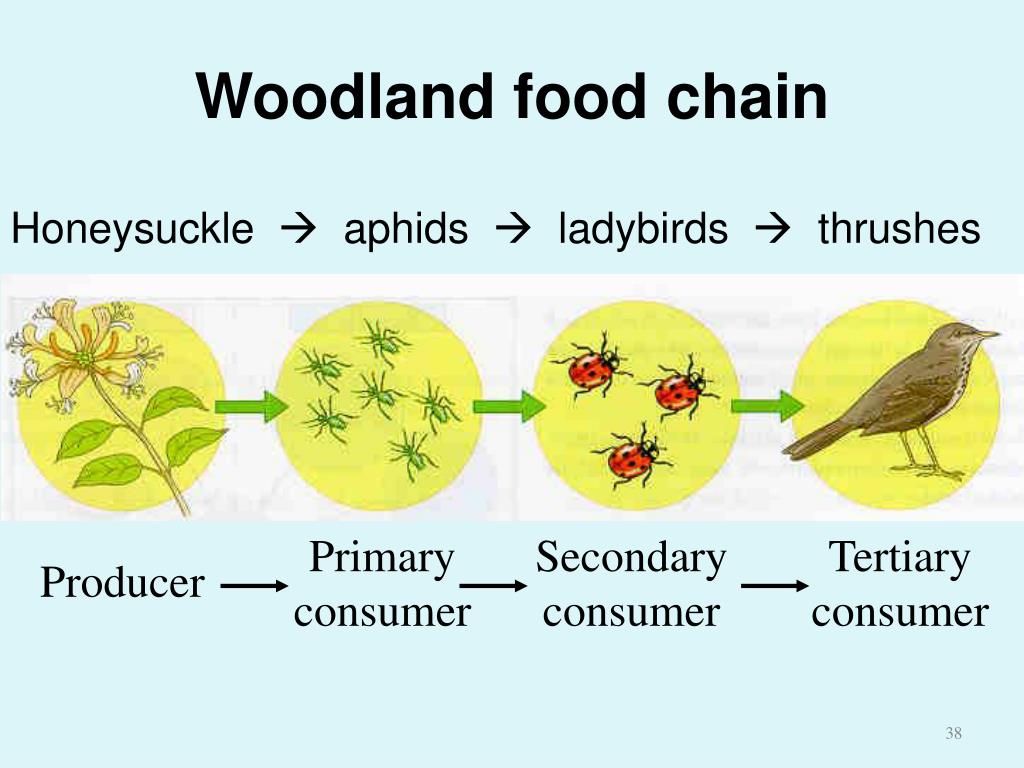
PPT Ch 3 Introduction to Ecology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID7037264
Food chains in a woodland. Can you spot the food chain? In this science worksheet, your child identifies two food chains and their parts in a picture of a woodland. SCIENCE | GRADE: 5th . Print full size . Print full size . Skills Animals, Food chains, Guided inquiry, Living versus non-living, Observational skills, Predators and prey, Science. Trees dominate the woodland both forest social to which they grow but hosts of other organisms - including fungi and bacteriological - which evolved in parallel Ecology Center Stay (current)
Food Chains Woodland Food Chains Teacher's notes This activity can be run with varying degrees of complexity depending on the age and ability of your pupils. For all versions, each child is. The Effects of Biotic Factors in British Deciduous Woodland Decomposers and food chains A saprophyte is an organism that lives on decaying organic matter. There are many other decomposers in. Give an example of a forest food-chain with a primary producer 'link', a herbivore 'link' and two 'links' of predator. Q.7. Give an example.

food web for temperate deciduous forests Google Search Temperate deciduous forest, Mule deer
What is the food chain in The Woodlands?. Woodland Food Chain Trees produce seeds, which are eaten by first order consumers like squirrels and birds. Grasses and shrubs provide additional food for first order consumers including mice and deer. Second (secondary) and third (tertiary) order consumers feed off the first and second order consumers. Examples of large woodland forest herbivores are white-tailed deer, mule deer and elk. Herbivores are more plentiful than carnivores and are the bottom rung of the food chain. Most small herbivores overwinter. Insects survive in cocoons or protected hiding places. Small mammals dig dens or burrows.




