Duck Life Cycle: Incubation Period Most ducks create a nest out of vegetation. Mallards, for example, don't pluck or collect material and carry it to their nest but pull up all the vegetation that they can reach from the edge of the nest. Some ducks also pull the overhanging grasses and shrubbery over themselves to hide from predators. Explore the complete life cycle of ducks, including nesting, migration, molting, and more. Gain insights into their breeding habits and wintering patterns. April 04, 2006 • 6 min read In the space of one year a duck experiences the full spectrum of seasonal changes that usher in opportunities and challenges.
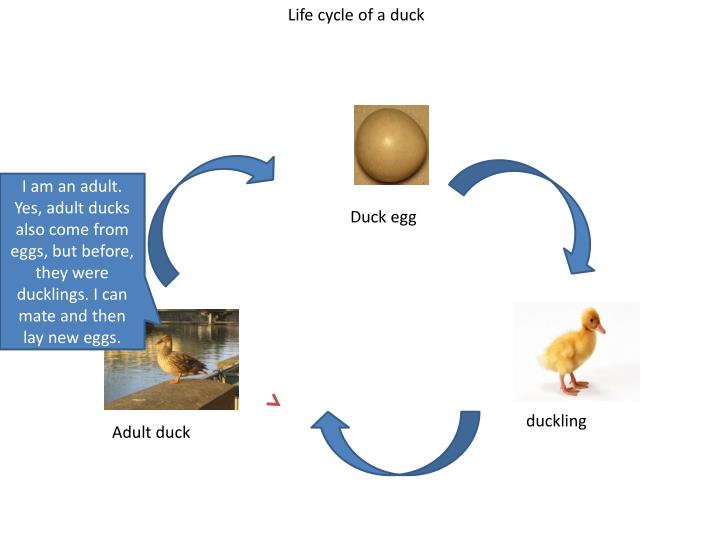
PPT Life cycle of a duck PowerPoint Presentation ID4915278
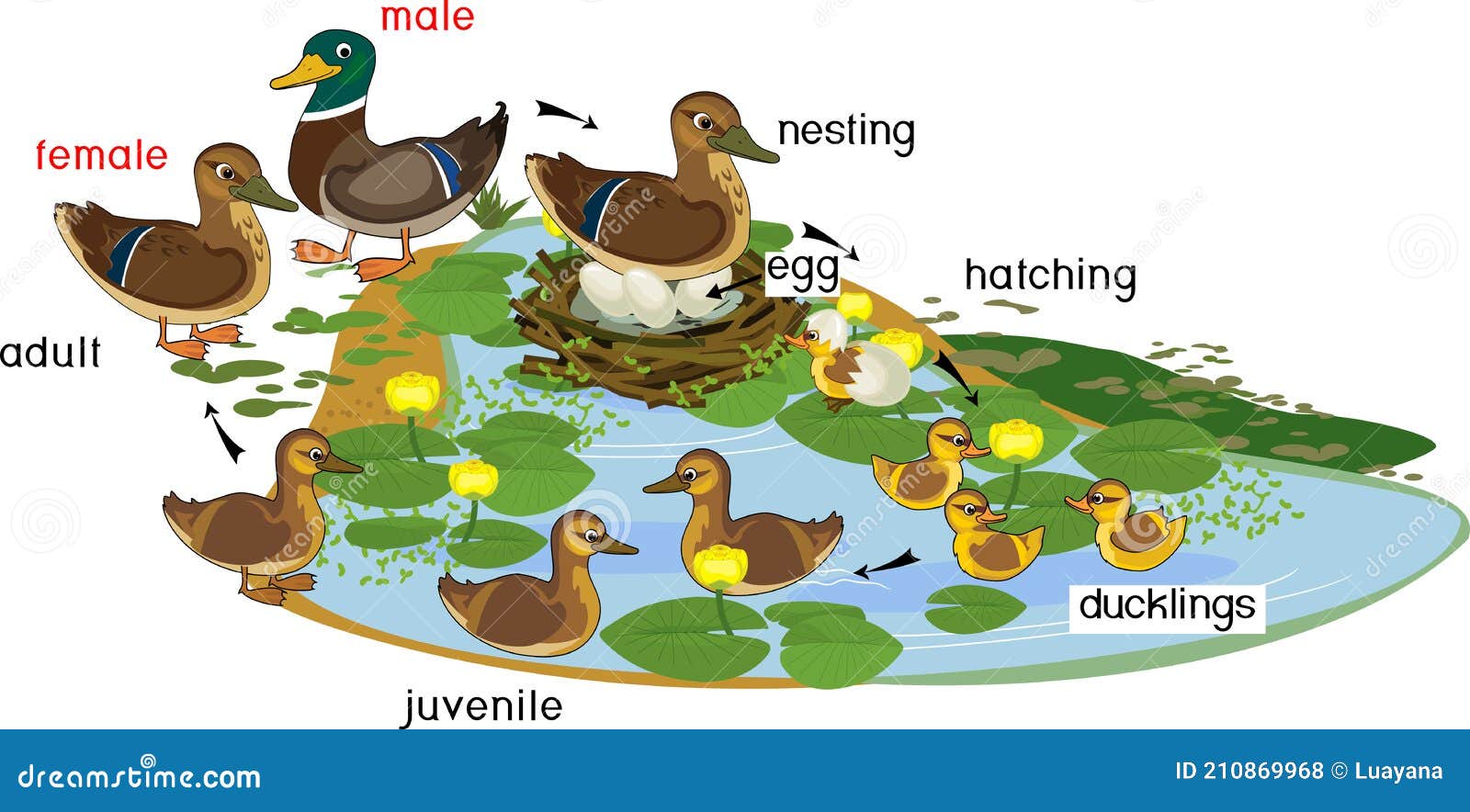
Duck Lifecycles Ducks Unlimited 54.6K subscribers Subscribe 110 19K views 5 years ago Ducks Unlimited CEO Dale Hall discusses the fascinating and complex lifecycles of ducks, and how DU. A duck's life cycle consists of four main stages: the egg-laying period, incubation and hatching, duckling development, and maturity and reproduction. The Four Stages of a Duck's Life. As mentioned earlier, the life cycle of a duck can be divided into four main stages. Each stage has its own challenges and opportunities, and understanding. The life cycle of a duck includes nesting, brood rearing, post-breeding, molting, fall migration, winter migration, spring migration and pre-nesting. These cycles occur yearly until death, with most domestic ducks living no more than seven years. Ducks look for their mates in the fall and are usually part of an established pair by winter. Perhaps the most familiar of all ducks, Mallards occur throughout North America and Eurasia in ponds and parks as well as wilder wetlands and estuaries. The male's gleaming green head, gray flanks, and black tail-curl arguably make it the most easily identified duck. Mallards have long been hunted for the table, and almost all domestic ducks.

Cycle De Vie De Loiseau Étapes De Développement Du Canard Sauvage De
It takes 50-70 days for ducklings to attain flight status, and survival during this period is highly variable, ranging from less than 10 percent to as high as 70 percent. The most common causes of duckling mortality include predation, adverse weather conditions, starvation, disease, and parasites. Mallard Tracking Facts. The average distance traveled by satellite-marked mallards during spring migration was more than 730 miles. The average distance traveled by individual birds during fall migration was almost 875 miles. One of the first mallards (a drake) ever marked with a GPS satellite transmitter in Arkansas flew more than 500 miles. April 25, 2016 • 3 min read By John M. Coluccy, Ph.D., and Ed Farley For waterfowl, the cycle of life begins anew each year with the eggs that are laid and carefully nurtured by nesting birds on their breeding grounds. An egg consists of three main parts: the yolk, albumen (egg white), and shell. April 23, 2009 • 5 min read by Bruce Batt Ph.D. Nothing in nature is more critical to waterfowl reproduction than the eggs that are laid each spring. Each egg has all the vital components needed to produce a new life in the form of a developing embryo, a duckling, and ultimately, an adult duck capable of producing its own eggs.
Anas Cartoons, Illustrations & Vector Stock Images 171 Pictures to
Last updated: Sep 20 2023 Click to Skip Ahead Why Do Some Ducks Live Longer Than Others? Life Stages of a Duck How To Tell Duck's Age Although ducks are raised for their eggs and meat, many homeowners enjoy keeping them as pets. Updated Dec 7, 2021 Ducks follow a yearly life cycle of ducks that includes growth, migration and parenting. Independent of motherly supervision by a few months of age, young ducklings must fly south for the winter at four or five months of age.
Outdoor classroom walks through the life cycle from a duckling to a duck. The mallard is also the ancestor of the domestic duck which is a common poultry and ornamental bird all over the globe. Mallards have been recorded to live for nearly 30 years in the wild, although the average individual is not likely to reach the age of two. In captivity, mallards are likely to survive longer than wild birds if given good care.

Female Mallard Duck Laying Eggs
The embryonic life cycle of ducks is a remarkable process that allows for the development of a new life from the essential components within each egg. From embryo to duckling to adult, this intricate journey ensures the continuation of the species and highlights the fascinating nature of these waterfowl creatures. The Five Stages of Duck. What is the life cycle of a mallard duck? The adulthood age for mallards is fourteen months, and the average life expectancy is three years, but they can live to twenty. Several species of duck have brown-plumaged females that can be confused with the female mallard. Do ducks get pregnant?




