History of ancient Israel and Judah Approximate map of the Northern Kingdom of Israel (blue) and the Kingdom of Judah (gold) with their neighbors (tan) during the Iron Age (9th century BCE) Part of a series on the History of Israel Early history Ancient Israel and Judah Second Temple period Late Antiquity and Middle Ages Modern history By topic (c. 733 BCE) Maps of the Middle East, BCE: Middle East, BCE Maps: Table of Contents Sources: World History Encyclopedia of Jewish and Israeli history, politics and culture, with biographies, statistics, articles and documents on topics from anti-Semitism to Zionism.

Pin on Bible Study
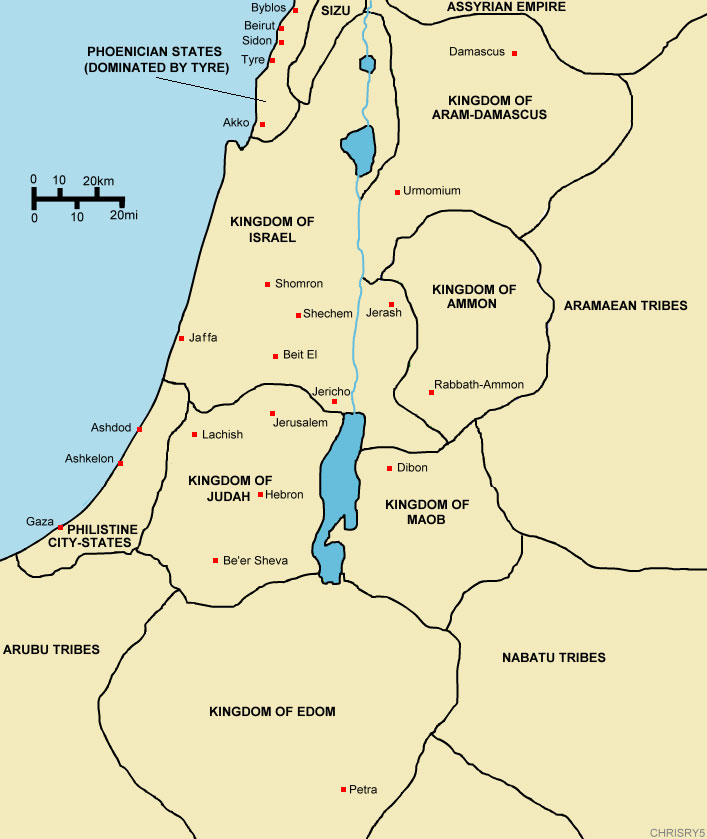
Approximate map showinhjjjg the Kingdoms of Israel (blue) and Judah (orange), ancient Southern Levant borders and ancient cities. The map shows the region in the 9th century BCE. I, the copyright holder of this work, hereby publish it under the following licenses: English: This category is intended for old maps of the divided kingdoms of ancient Israel and Judah, that means in the times after the supposed "United Monarchy" under David and Salomon (for those, see Category:Old maps of the United Monarchy ). Jerusalem Stepped Stone Structure seen from the Large Stone Structure The status of Jerusalem in the 10th century BCE is a major subject of debate. [8] The oldest part of Jerusalem and its original urban core are the City of David, which does show evidence of significant Israelite residential activity around the 10th century. [27] Category:Maps of the Kingdom of Judah From Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository Subcategories This category has only the following subcategory. O Old maps of the ancient kingdoms of Judah and Israel (14 F) Media in category "Maps of the Kingdom of Judah" The following 16 files are in this category, out of 16 total.

Staff Portal Resources for Schools Geography
Israel, either of two political units in the Hebrew Bible ( Old Testament ): the united kingdom of Israel under the kings Saul, David, and Solomon, which lasted from about 1020 to 922 bce; or the northern kingdom of Israel, including the territories of the 10 northern tribes (i.e., all except Judah and part of Benjamin ), which was established i. English: Approximate map showing the Kingdoms of Israel (blue) and Judah (orange), ancient Southern Levant borders and ancient cities such as Urmomium and id.The map shows the region in the 9th century BCE. Israel and Judah were from the Canaanite culture of the late Bronze Age, and were based on villages that formed and grew in the southern Levant highlands (today for the region between the coastal plain and the Jordan Valley) between c. 1200-1000 BCE. The Israel Antiquities Authority stated, "The excavations at Khirbat Qeiyafa reveal an urban society that existed in Judah already in the late eleventh century BCE. It can no longer be argued that the Kingdom of Judah developed only in the late eighth century BCE or at some other later date." [34]
Pathways to Current Beliefs The Human Journey
Judaism: The period of the divided kingdom. The southern Kingdom of Judah thrived until 587/586 bc, when it was overrun by the Babylonians, who carried off many of the inhabitants into exile. When the Persians conquered Babylonia in 538 bc, Cyrus the Great allowed the Jews to return to their homeland, where they soon set to work to replace the. Both names are tied to the ancient Israelite kingdoms: the former corresponds to part of the Kingdom of Judah, also known as the Southern Kingdom; and the latter corresponds to part of the Kingdom of Samaria, also known as the Northern Kingdom.
The name Judea is a Greek and Roman adaptation of the name "Judah", which originally encompassed the territory of the Israelite tribe of that name and later of the ancient Kingdom of Judah. Nimrud Tablet K.3751, dated c. 733 BCE, is the earliest known record of the name Judah (written in Assyrian cuneiform as Yaudaya or KUR.ia-ú-da-a-a). The area is small, maybe only 100 miles north to south and 40 or 50 miles east to west. Israel and Judah were from the Canaanite culture of the late Bronze Age, and were based on villages that formed and grew in the southern Levant highlands (today for the region between the coastal plain and the Jordan Valley) between c. 1200-1000 BCE. Israel.

Old map of Israel ancient and historical map of Israel
Category:Ancient Israel and Judah - Wikimedia Commons Help Category:Ancient Israel and Judah From Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository Subcategories This category has the following 34 subcategories, out of 34 total. * Maps of ancient Israel (10 C, 54 F) A Adullam (6 C, 53 F) B Babylonian Exile (3 C, 1 F) The following article is reprinted with permission from Ancient Israel: From Abraham to the Roman Destruction of the Temple, edited by Hershel Shanks (Biblical Archaeology Society). Solomon's Successor: Rehobaom. When Solomon died, his son Rehoboam (c. 930-913 B.C.E.) succeeded him as king of Judah, apparently without incident (1 Kings 11:42).




