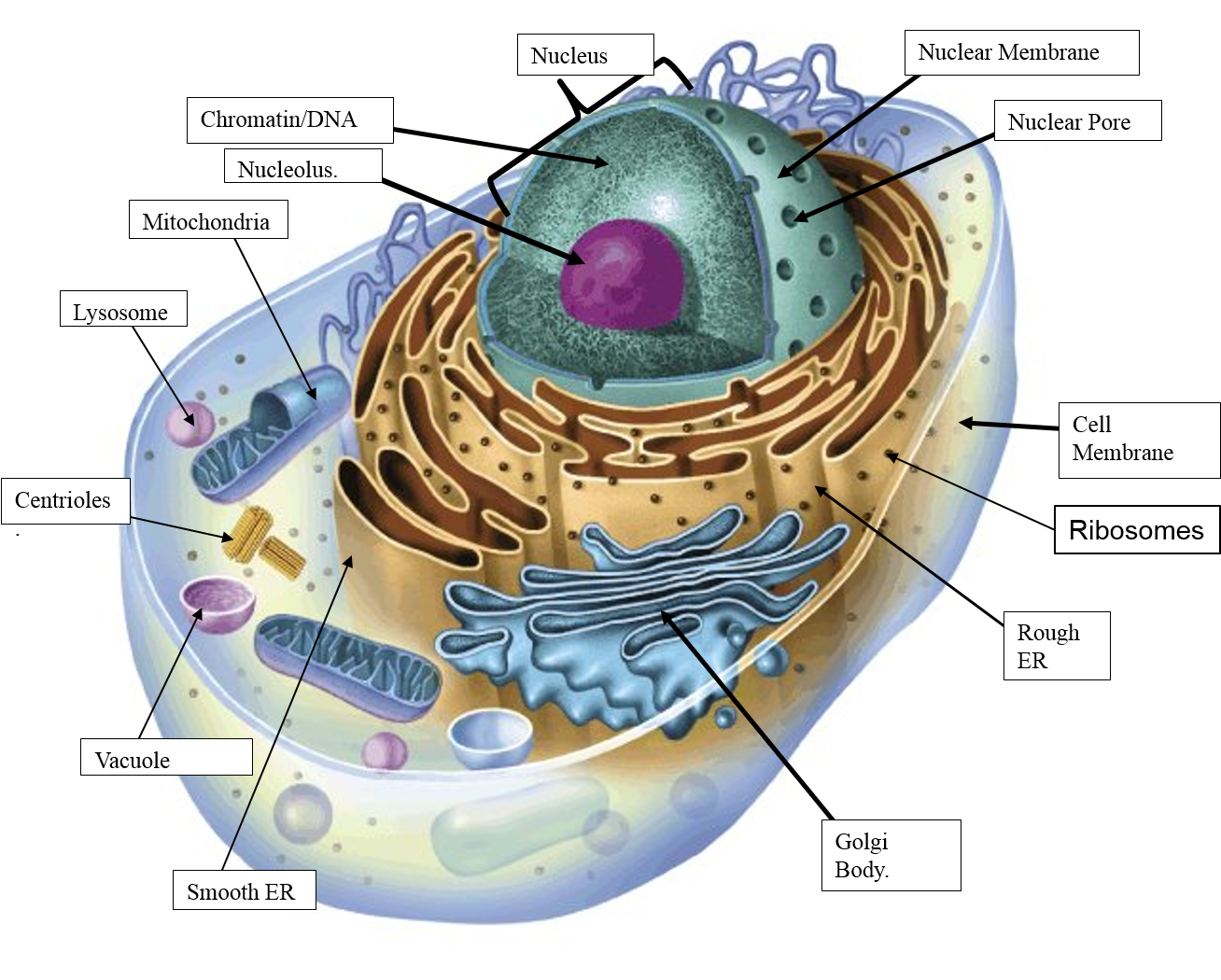
Key points: All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out. The cell membrane surrounds a cell's cytoplasm, which is a jelly-like substance containing the cell's parts. Cells contain parts called organelles. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell. Definition Animal cells are the basic unit of life in organisms of the kingdom Animalia. They are eukaryotic cells, meaning that they have a true nucleus and specialized structures called organelles that carry out different functions.
South Pontotoc Biology Plant and Animal Cell Diagrams
An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall, and it is enclosed by the plasma membrane. The cell organelles are enclosed by the plasma membrane including the cell nucleus. Unlike the animal cell lacking the cell wall, plant cells have a cell wall. Animal cells are eukaryotic cells, meaning they possess a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not have cell walls, allowing for more flexibility in shape and movement. A plasma membrane encloses the cell contents of both plant and animal cells, but it is the outer coating of an animal cell. Plant Cell Anatomy Animal Cell Anatomy The cell is the basic unit of life. All organisms are made up of cells (or in some cases, a single cell). Most cells are very small; in fact, most are invisible without using a microscope. Cells are covered by a cell membrane and come in many different shapes. Are you learning about animal cells in 5th grade science or biology? If so, you may need to memorize the animal cell, its organelles, and their functions. To help you do this, I've created a printable animal cell diagram. Use this convenient study aid in preparation for your upcoming test or quiz. There are six animal cell diagrams to choose from.

Animal Cell Diagrams Labeled Printable 101 Diagrams
Diagram Structure Types Conclusion Let us have a detailed overview of the animal cell, its types, diagram and structure. Animal Cell Definition "An animal cell is a type of eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall and has a true, membrane-bound nucleus along with other cellular organelles." Explanation Animal Cell Definition. Animal cells are the types of cells that make up most of the tissue cells in animals. Different kinds of animals have different numbers of cells, but most have millions and millions. Human beings, for instance, have over 40 trillion cells. Animal cells are eukaryotic, which means they have a nucleus that holds DNA. Animal cells are typical of the eukaryotic cell, enclosed by a plasma membrane and containing a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles.. Illustrated in Figure 2 are a pair of fibroblast deer skin cells that have been labeled with fluorescent probes and photographed in the microscope to reveal their internal structure. The nuclei are stained. How are cells structured? Learn about the size and function of plant and animal cells for GCSE Combined Science, AQA.

Animals cell labeled Biological Science Picture Directory
A Labeled Diagram of the Animal Cell and its Organelles There are two types of cells - Prokaryotic and Eucaryotic. Eukaryotic cells are larger, more complex, and have evolved more recently than prokaryotes. Where, prokaryotes are just bacteria and archaea, eukaryotes are literally everything else. Packages and ships materials to move out of the cell. Moves things around in the cell. HAS ribosomes. Makes protein. A gel-like fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended. Provides cushion and support. Sign up and see the remaining cards. It's free! Start studying Animal Cell Labeling.
Diagram of a typical plant cell: Image modified from OpenStax Biology. Both animal and plant cells have mitochondria, but only plant cells have chloroplasts. Plants don't get their sugar from eating food, so they need to make sugar from sunlight. This process (photosynthesis) takes place in the chloroplast. Color according to the directions below; the numbers correspond to the numbers on the cell diagram. The cell membrane surrounds the cell and acts as a barrier. It controls what comes in and out of the cell. Color the membrane light brown. The membrane can have structures on its surface that help the cell move, or move particles within the body.

animal cell labeled Classical Conversations Cycle 1 Classical
Animal Cell; Animal Cell - Map Quiz Game. Centrosome; Chromatin; Cytoplasm; Endoplasmic reticulum; Golgi apparatus; Lyosome; Microtubule; Mitochondria; Nucleolus; Nucleus; Ribosome; Vacuole; You need an account to play. Create challenge. 0/0 0 % Game mode: Pin Type Show more game modes. Learn. Restart---Your high score (Pin) An animal cell is defined as the basic structural and functional unit of life in organisms of the kingdom Animalia. They have a distinct nucleus with all cellular organelles enclosed in a membrane, and thus called a eukaryotic cell.




