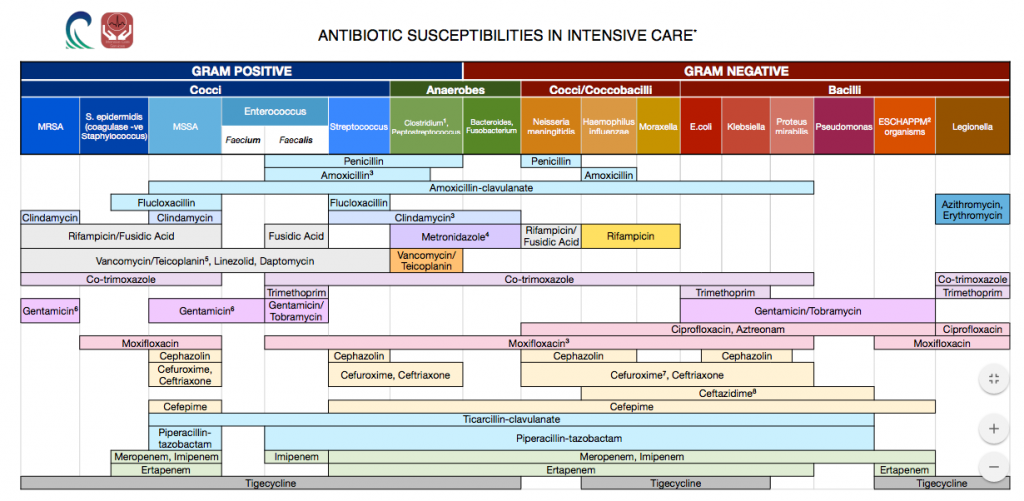
Cloxacillin and clindamycin typically have less than 40% activity for S.epidermidis, thus usage depends on local susceptibility data Enterococci has two main species - Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium; the antibiotics listed are active against E.faecalis, but have limited activity for E.faecium. Rifampin. These medications should be prioritized as key targets for antibiotic stewardship. Antibiotics that should be reserved for treatment of confirmed or suspected infections with multi-drug resistant organisms. Amoxicillin. Ampicillin. Cephalexin. Cefazolin. Dicloxacilllin. Nafcillin. Oxacillin.
Antibiotic Spectrum Chart Phartoonz
Antimicrobial spectrum. A simplified diagram showing common disease-causing bacteria and the antibiotics which act against them. The antimicrobial spectrum of an antibiotic means the range of microorganisms it can kill or inhibit. Antibiotics can be divided into broad-spectrum antibiotics, extended-spectrum antibiotics and narrow-spectrum. Fidaxomicin. Cloxacillin and clindamycin typically have less than 40% ac6vity for S.epidermidis, thus usage depends on local suscep6bility data Enterococci has two main species - Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium - the an6bio6cs listed work well for E.faecalis, but have limited ac6vity for E.faecium. Infectious Diseases Resources. IDSA Practice Guidelines. Kucers' the Use of Antibiotics. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. Sanford Guide (Web Edition) All content and media on the buganddrugs.stanford.edu is created and published online for informational purposes only. Antibiotic classification types include penicillin, cephalosporin, macrolide, tetracycline, sulfonamide, carbapenem, and fluoroquinolone. Antibiotic class chart, mnemonic, ppt, and table included on drug names, gram coverage, mechanism of action, and example uses made easy

Antibiotic Chart Antibiotic Charto, Pharmd, Antibiotics Chart, 1 275 1
CRRT: 6mg/kg IV Q24h Alt: 8 - 10mg/kg IV Q48h. No renal dose adjustment HD: 500mg IV x1 now, then QPM *For outpatient post-HD dosing, contact ID/ASP CRRT: 1g IV Q24h No renal dose adjustment HD: 100mg-400mg* IV/PO x1 now & post-HD CRRT: 200mg-800mg* IV Q24h Severe, CRRT: 800mg -1200mg IV divided q12h-24h. Antibiogram: Click on each class of antibiotics to learn more.. Pencillins: Pencillins are broadly separated into 4 classes - natural pencillins, anti-staphylococcal penicillins, broad spectrum pencillins which include aminopencillins and anti-pseudomonal penicillins.. General rules for penicillins - there is no MRSA coverage, no atypical coverage, and there is generally increasing gram. 40% activity for S.epidermidis, thus usage depends on local susceptibility data Enterococci has two main species - Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium; the antibiotics listed are active against E.faecalis, but have limited activity for E.faecium. Cloxacillin and clindamycin typically have less than. NOTE: Antibiotic dosing in this chart does not take into account renal or liver dysfunction. Empiric Antimicrobial Guidelines for Hospitalized Adults 2019 Suggested initial therapies based on guidelines 1-9 and local resistance patterns, these guidelines are not a substitution for an ID consult.

Coverage of common antibiotics used in the hospital For GrepMed
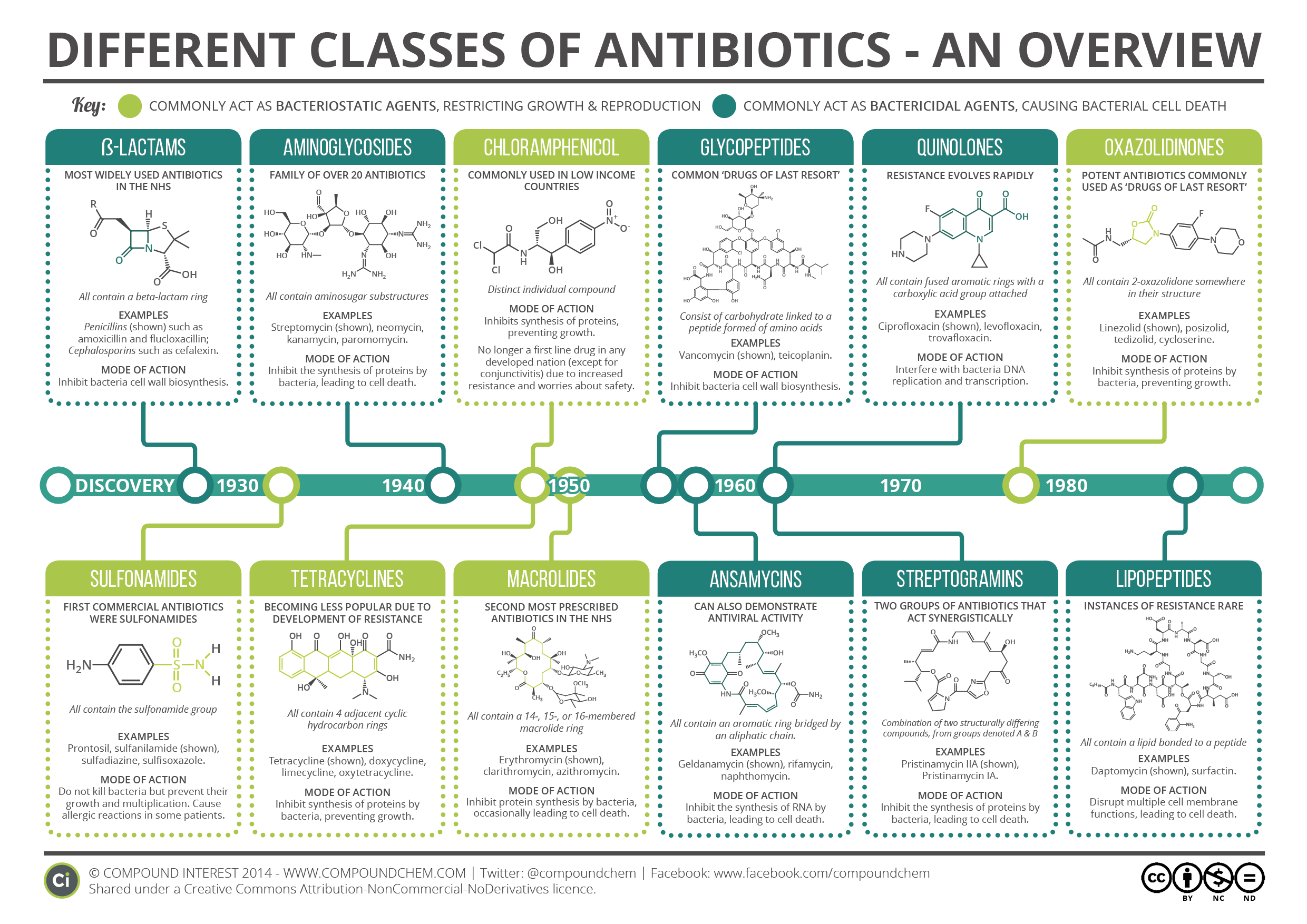
Antibacterial drugs are derived from bacteria or molds or are synthesized de novo. Technically, "antibiotic" refers only to antimicrobials derived from bacteria or molds but is often (including in THE MANUAL) used synonymously with "antibacterial drug.". (See also Antibiotics in Neonates .) Antibiotics have many mechanisms of action. 25-100mg/kg of sulphamethoxazole Q6 hrly (dose varies -> consult ID) SJS, blood dyscrasias, influenzae like symptoms, Doxycycline. tetracycline. gram +ve and gram -ve but widespread resistance. good cover for Chlamydophila, Mycoplasma, Rickettseiae, Spirocheataes, Brucella, Coxiella brunetii. 200mg LD -> 100mg Q24 hrly.
Guidelines for Antibiotic Use. Toolkit to Enhance Nursing and Antibiotic Stewardship. OPAT Patient Education Materials. Quarterly Newsletters. Intranet (restricted) Antimicrobial stewardship. Guidelines for Antibiotic Use. Share on Facebook; Share on Twitter; Share on Linkedin; Share on Pinterest; Antibiotic Adverse Reactions Drug Interactions Clinical Pearls Penicillins Penicillin G, oxacillin, ampicillin, amoxicillin GI upset (nausea, diarrhea) Hypersensitivity reactions Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia (rare) Neurologic (altered mental status, seizures) Interstitial nephritis
Teixobactin A New Antibiotic, and A New Way to Find More Compound
CONTENTS commonly used antibiotics Aminoglycosides Ampicillin & Ampicillin-Sulbactam Aztreonam Carbapenems (meropenem & ertapenem) Cephalosporins Cephalosporin G1: cefazolin Cephalosporin G3: ceftriaxone Cephalosporin G3: ceftazidime Cephalosporin G4: cefepime Cephalosporin G5: ceftaroline Clindamycin Daptomycin Doxycycline Fluoroquinolones Linezolid Macrolides (Azithromycin, Clarithromycin. Antibiotics — Vancomycin. Antifungals. Antiparasitic drugs. Antitubercular drugs. Antivirals (excluding drugs for HIV) UpToDate, electronic clinical resource tool for physicians and patients that provides information on Adult Primary Care and Internal Medicine, Allergy and Immunology, Cardiovascular Medicine, Emergency Medicine, Endocrinology.




