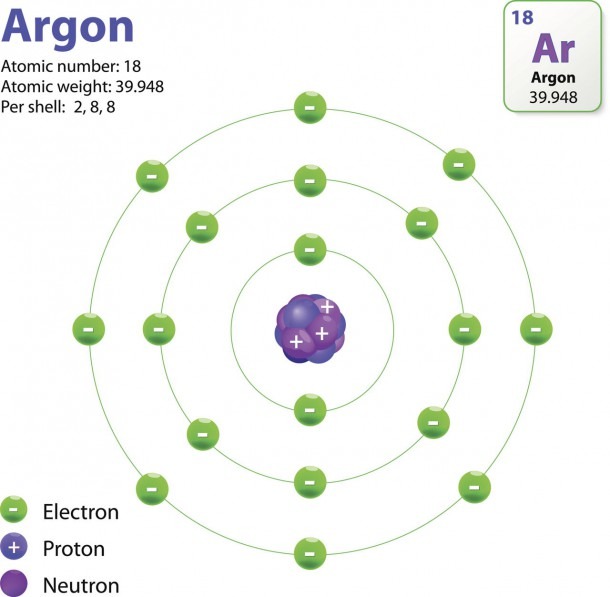
All atoms are roughly the same size, whether they have 3 or 90 electrons. Approximately 50 million atoms of solid matter lined up in a row would measure 1 cm (0.4 inch). A convenient unit of length for measuring atomic sizes is the angstrom (Å), defined as 10 −10 metre. The radius of an atom measures 1-2 Å. Here are electron shell atom diagrams for the elements, ordered by increasing atomic number . For each electron shell atom diagram, the element symbol is listed in the nucleus. The electron shells are shown, moving outward from the nucleus.
/GettyImages-141483984-56a133b65f9b58b7d0bcfdb1.jpg)
35 Label The Parts Of The Atom In The Diagram Below Labels For Your Ideas
The Structure of an Atom Explained With a Labeled Diagram - Science Struck The Structure of an Atom Explained With a Labeled Diagram An atom is the basic unit of matter. The following article provides you with diagrams that will help you understand the structure of an atom better. Atom: Definition, Structure & Parts with Labeled Diagram Atom Atoms are tiny particles that form the basic building blocks of all matter in the universe, whether solid, liquid, or gas. All living organisms and nonliving objects found on Earth are made of trillions and trillions of atoms. Because the sum of the numbers of protons and neutrons equals the mass number, 127, the number of neutrons is 74 (127 − 53 = 74). Since the iodine is added as a 1− anion, the number of electrons is 54 [53 - (1-) = 54]. Exercise 2.2.1 2.2. 1. An ion of platinum has a mass number of 195 and contains 74 electrons. By convention, elements are organized in the periodic table, a structure that captures important patterns in their behavior.Devised by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev (1834-1907) in 1869, the table places elements into columns—groups—and rows—periods—that share certain properties.These properties determine an element's physical state at room temperature—gas, solid, or liquid.

Atomic Structure Broad Learnings
February 17, 2010 by Jerry Coffey Atom Diagram [/caption]The image on the left is a basic atom diagram. This one shows the protons, neutrons, and electrons of a carbon atom. Each is in a. Bohr diagrams show electrons orbiting the nucleus of an atom somewhat like planets orbit around the sun. In the Bohr model, electrons are pictured as traveling in circles at different shells, depending on which element you have. Figure 2 2 contrast the Bohr diagrams for lithium, fluorine and aluminum atoms. The shell closest to the nucleus is. Relative charge. -1. The number of electrons in an atom is always the same as the number of protons, so atoms are electrically. neutral. overall. Atoms can lose or gain electrons. When they do. 5.8: Orbitals. Page ID. Ed Vitz, John W. Moore, Justin Shorb, Xavier Prat-Resina, Tim Wendorff, & Adam Hahn. Chemical Education Digital Library (ChemEd DL) A characteristic of the diagram Figure 1 in Electron Waves in the Hydrogen Atom is that it has been assigned an identifying label, namely, 1 s.

The Nucleus of the Atom and Radioactivity
Our current model of the atom can be broken down into three constituents parts - protons, neutron, and electrons. Each of these parts has an associated charge, with protons carrying a positive. Mass number. It is total number of proton and neutron present in the nucleus of each atom of an element. Mass number = No. of proton + no of neutrons. = atomic number - no of neutron. For example: the mass number of fluorine is 19 and atomic number is 9. Thus the number of neutron in an atom of fluorine is 19-9 =10.
In the article. We will learn the structure of an atom, subatomic particle, discovery, properties with some examples. What is an Atom? Atoms are the building blocks of matter. Therefore, the existence of different kinds of matter around us is due to atoms present. The idea of the relativity of matter was considered run back in India around 500 B C. This handy atomic basics worksheet with answers will help introduce your children to atoms, with a time-saving fact file. When you download this resource, you'll get a simple PDF with a brilliant fact file, worksheet, and answers! Show more Related Searches atomic structure periodic table atoms acids and bases electricity ions Ratings & Reviews
The Structure Of An Atom Explained With A Labeled Diagram Best
(Atom Definition) Atoms are defined as "the basic building blocks of matter". Atom is the basic of all matter. They are very small and consist of even tinier particles. Neutrons, Protons, and Electrons are the basic particles making up the atom. They join together with other atoms and create matter. It takes many atoms to create anything. How to Draw a Diagram of an Atom. Part of the series: Drawing Advice & Basics. You must draw a diagram of an atom in a very specific way for maximum authenti.
/GettyImages-141483984-56a133b65f9b58b7d0bcfdb1.jpg)



