By Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph.D. Updated on May 05, 2019 All matter consists of particles called atoms. Atoms bond to each other to form elements, which contain only one kind of atom. Atoms of different elements form compounds, molecules, and objects. Key Takeaways: Model of the Atom Bohr diagrams show electrons orbiting the nucleus of an atom somewhat like planets orbit around the sun. In the Bohr model, electrons are pictured as traveling in circles at different shells, depending on which element you have. Figure 2 2 contrast the Bohr diagrams for lithium, fluorine and aluminum atoms. The shell closest to the nucleus is.
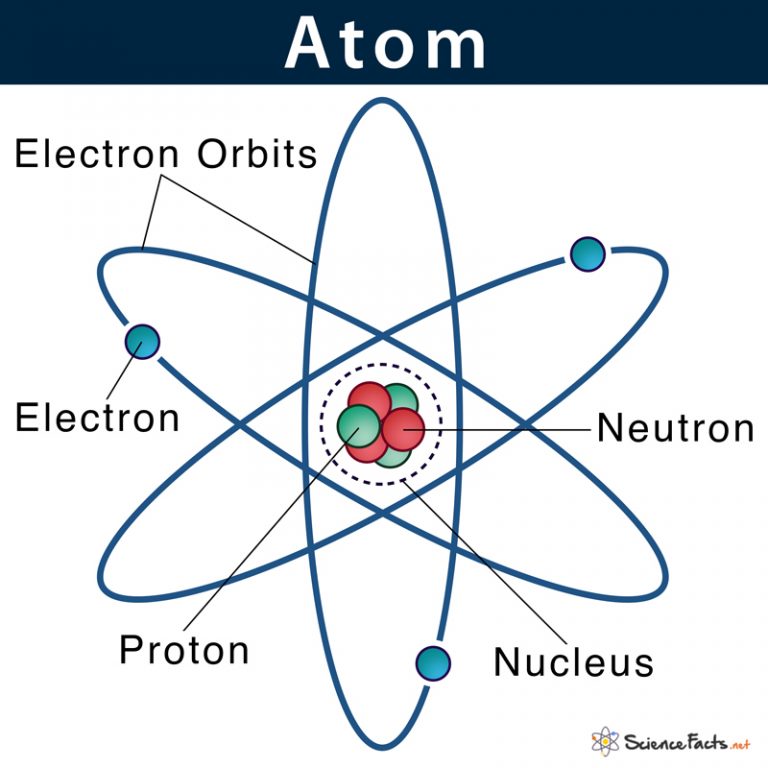
Atom Definition, Structure & Parts with Labeled Diagram
How does Niels Bohr's atomic model work? An overview of Niels Bohr's refinement of the Rutherford model. See all videos for this article Bohr model of the atom In the Bohr model of the atom, electrons travel in defined circular orbits around the nucleus. The orbits are labeled by an integer, the quantum number n. An early model of the atom was developed in 1913 by the Danish scientist Niels Bohr (1885-1962). The Bohr model shows the atom as a central nucleus containing protons and neutrons, with the electrons in circular electron shells at specific distances from the nucleus, similar to planets orbiting around the sun. What is an atom? Are all atoms the same size? What does the mass of an atom consist of? How is the atomic number of an atom defined? atoms How atoms can be seen. The simplest example of the Bohr Model is for the hydrogen atom (Z = 1) or for a hydrogen-like ion (Z > 1), in which a negatively charged electron orbits a small positively charged nucleus. Electromagnetic energy will be absorbed or emitted if an electron moves from one orbit to another. Only certain electron orbits are permitted.

Atom Free Stock Photo Public Domain Pictures
The model described the atom as a tiny, dense, positively charged core called a nucleus, in which nearly all the mass is concentrated, around which the light, negative constituents, called electrons, circulate at some distance, much like planets revolving around the Sun. Rutherford gold-foil experiment 5.10: Bohr Model of the Atom; 5.11: Energy Levels and Sublevels; 5.E: Models of the Atom (Exercises) 5: Models of the Atom is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Back to top; 4.11: Potential and Kinetic Energy; 5.1: Electron Configuration; The current theoretical model of the atom involves a dense nucleus surrounded by a probabilistic "cloud" of electrons. Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms.The concept that matter is composed of discrete particles is an ancient idea, but gained scientific credence in the 18th and 19th centuries when scientists found it could explain the. Bohr's model calculated the following energies for an electron in the shell, n. . : E ( n) = − 1 n 2 ⋅ 13.6 eV. Bohr explained the hydrogen spectrum in terms of electrons absorbing and emitting photons to change energy levels, where the photon energy is. h ν = Δ E = ( 1 n l o w 2 − 1 n h i g h 2) ⋅ 13.6 eV.

Modelos Atomicos De Thomson Rutherford Bohr Y Dalton Vários Modelos
Atom: Definition, Structure & Parts with Labeled Diagram Atom Atoms are tiny particles that form the basic building blocks of all matter in the universe, whether solid, liquid, or gas. All living organisms and nonliving objects found on Earth are made of trillions and trillions of atoms. The atomic model in the diagram below shows protons and neutrons concentrated at the atomic nucleus and electrons in the orbits surrounding it. Protons are positively charged, electrons are negatively charged, while the neutrons carry no charge. J.J. Thomson Plum Pudding Model
February 17, 2010 by Jerry Coffey Atom Diagram [/caption]The image on the left is a basic atom diagram. This one shows the protons, neutrons, and electrons of a carbon atom. Each is in a. 1 Answer Reyan Roberth · Stefan V. Jun 6, 2018 There are five basic atomic models which have contributed the structure of the atom itself. Explanation: They are: ⇒ John Dalton's atomic model: Dalton´s Billiard Ball (Solid Sphere) Model ⇒ J.J. Thomson's model: Plum Pudding model ⇒ Ernest Rutherford's model: Nuclear model
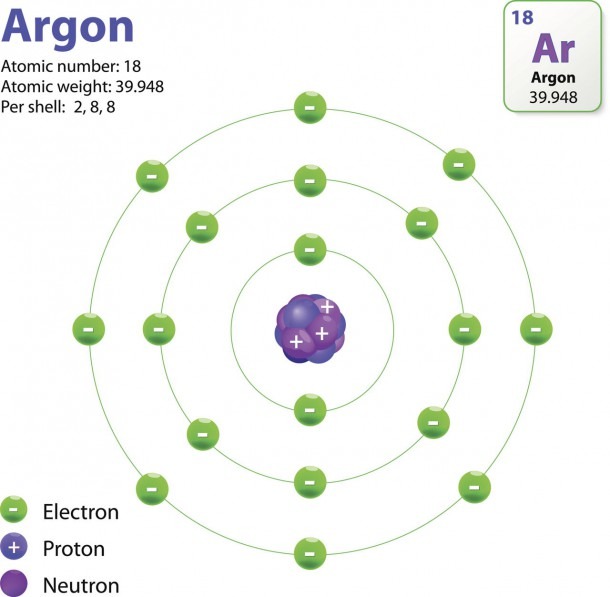
The Structure Of An Atom Explained With A Labeled Diagram Best
In 1915, the Danish physicist Niels Bohr proposed a new model of the atom that involved electrons orbiting the nucleus. Stationary states or energy levels would be fixed distances from the nucleus (see below). In this model, these energy levels or shells would be represented by the letter "n." Our current model of the atom can be broken down into three constituents parts - protons, neutron, and electrons. Each of these parts has an associated charge, with protons carrying a positive.




