But a baby x-ray is a quick and painless way to obtain important imaging of your infant's body. While radiation exposure is a part of x-ray technology, an occasional x-ray is deemed safe for babies. This helpful tool can quickly determine the cause of sickness, injury or pain, which can outweigh any risks related to the procedure. This article lists examples of normal imaging of the pediatric patients divided by region, modality, and age. Chest Plain radiograph chest radiograph premature (27 weeks): example 1 neonate: example 1 (lateral decubitus) 9-month-old: examp.

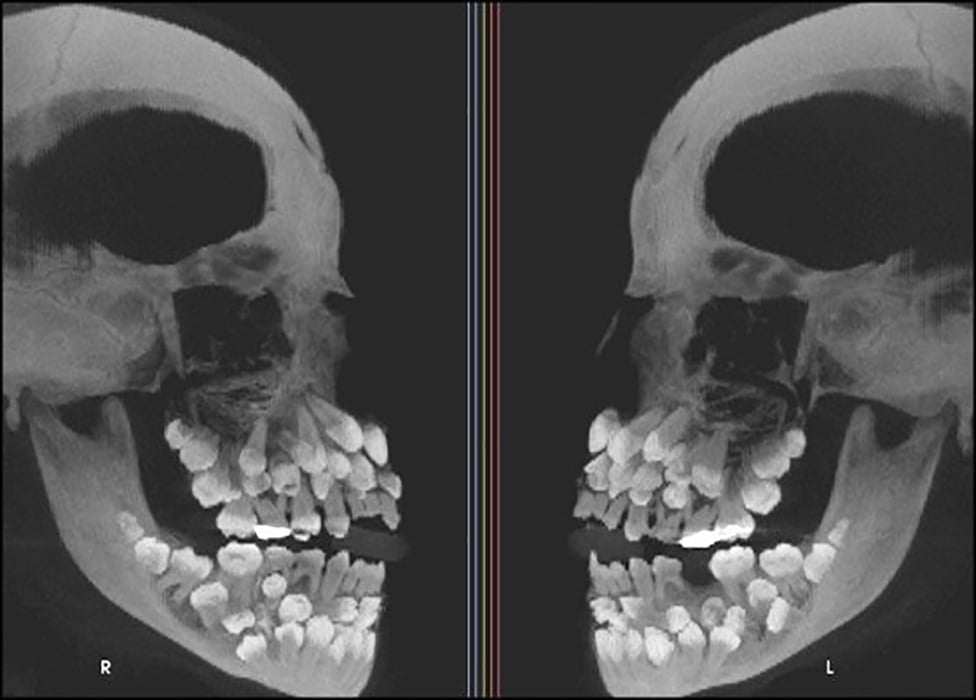
Onedayold male baby with CCMS. Skull xray, lateral view, shows
The online presentation reviews normal imaging findings at cranial US with an emphasis on a systematic approach and anatomic landmarks. Using a case-based approach, the online presentation also illustrates the gamut of imaging findings seen in routine pediatric radiology practice. Premature (<30-32 weeks gestation) and extremely low birth. Still in a minority of cases that are more complex, an X-ray may be helpful. "If the child's like less than a month old, has a high fever, a white (blood cell) count elevation, severe distress. An x-ray exam is a noninvasive medical test that helps doctors diagnose and treat medical conditions. X-ray exams use a small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the body. X-rays are the oldest and most frequently used form of medical imaging. An x-ray exam may be performed on newborns, infants and older children. Diagnosis of craniosynostosis may include: Physical exam. Your health care provider feels your baby's head for features such as suture ridges and looks for facial differences such as unbalanced features. Imaging studies. A computerized tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of your baby's skull can show whether any sutures.
15 Asombrosas fotos de raxos X que tendrás que mirar 2 veces
The art of interpreting skull radiographs is slowly being lost as trainees in radiology see fewer plain radiographs and depend more heavily on computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Nevertheless, skull radiographs still provide significant information that is helpful in finding pathologic conditions and appreciating their extents. Abnormalities in the skull may be reflected as. What will happen during the x-ray? Your baby will be placed on a table and positioned depending on which body area needs an x-ray. The rest of your baby's body will be covered to protect him or her from the x-ray beam. You may need to leave the room while the pictures are taken. The assessment of an infant or child with an abnormal head circumference commonly includes imaging of the head with neurosonography, computed tomography (CT), or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The choice of imaging modality depends on the patient's age, presentation, clinical condition, and suspected underlying abnormality.Macrocephaly, a head circumference more than 2 SD above the mean, or. Definition. A skull x-ray is a picture of the bones surrounding the brain, including the facial bones, the nose, and the sinuses.. Alternative Names. X-ray - head; X-ray - skull; Skull radiography; Head x-ray. How the Test is Performed. You lie on the x-ray table or sit in a chair.

Teeth Lozier Institute
X-rays are a kind of imaging test. They give your healthcare provider information about structures inside the body. These tests expose children to low doses of radiation. X-rays are forms of radiant energy, like light or radio waves. X-rays have more energy than rays of visible light or radio waves. They can penetrate your body. X-rays are the most common imaging test. They allow physicians to see bones and organs within your child's body. An X-ray is quick, painless and safe, especially when compared to other methods of examining bones and internal organs. No radiation remains in the body once the exam is complete. Radiation is a beam that is sent only when the.
Sometimes an asymmetrical baby head shape (flattening on one side of the head) is due to congenital torticollis, a normally mild condition characterized by limited neck mobility. Tight conditions in the womb, like if your baby is in the breech position, can affect the way the neck muscles develop. Babies with torticollis have a difficult time. Types of Head Shape Abnormalities. Positional plagiocephaly: Also known as flat head syndrome, this condition develops when babies spend too much time on their backs, whether in a crib, car seat or stroller.Noticeable flatness on the back or side of the head is a sign of this condition. Craniosynostosis: This is a condition in which the sutures (joints) between the skull bones close prematurely.
NORMAL FETAL SKULL (28 WEEKS)
Sinus infection ( sinusitis) Sometimes skull x-rays are used to screen for foreign bodies that may interfere with other tests, such as an MRI scan. A CT scan of the head is usually preferred to a skull x-ray to evaluate most head injuries or brain disorders. Skull x-rays are rarely used as the main test to diagnose such conditions. Often, a special baby xray tube is used to hold the child still and capture sharper images. This can be alarming for infants (as well as unprepared parents!), but carries no extra complications. This article provides information on how to prepare young kids for an entire baby xray, the risks involved, and what to expect in the radiology room.



