Sulfur Bohr Model — Diagram, Steps to Draw Sulfur has the atomic number 16 and is denoted by the chemical symbol S. Under normal conditions, sulfur occurs as a cyclic octatomic molecule represented by formula S 8. In this video we'll look at the atomic structure and Bohr model for the Sulfur atom (S). We'll use a Bohr diagram to visually represent where the electrons a.
Bohr Diagram The Element Sulfur
0:00 / 2:45 How to Draw the Bohr-Rutherford Diagram of Sulfur chemistNATE 247K subscribers Subscribe 415 32K views 4 years ago Sulfur / Sulphur has 2 electrons in its first shell, 8 in its. Physical & Theoretical Chemistry Supplemental Modules (Physical and Theoretical Chemistry) Electronic Structure of Atoms and Molecules The Bohr Rutherford diagram is a model that shows the arrangement of electrons within an atom. It was developed by Niels Bohr and Ernest Rutherford to explain the behavior of electrons in an atom. In the Bohr Rutherford diagram of sulfur, the nucleus is represented by a small dot in the center. Bohr diagram is very interesting and easy to draw. Here, we will draw the Bohr diagram of the Sulfur atom with some simple steps. Steps to draw the Bohr Model of Sulfur atom 1. Find the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in the Sulfur atom
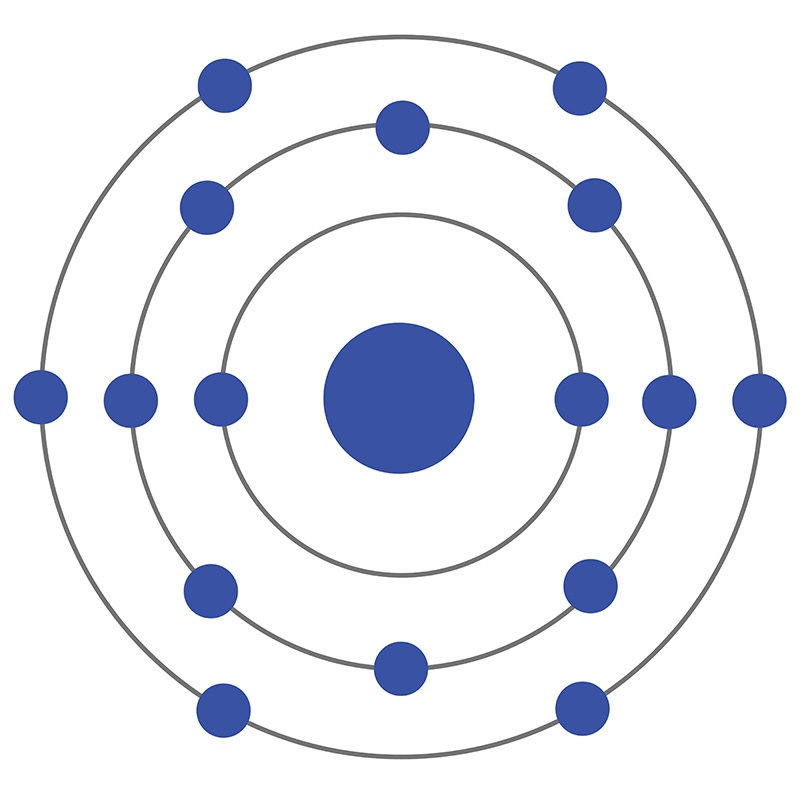
Sulfur (S) AMERICAN ELEMENTS
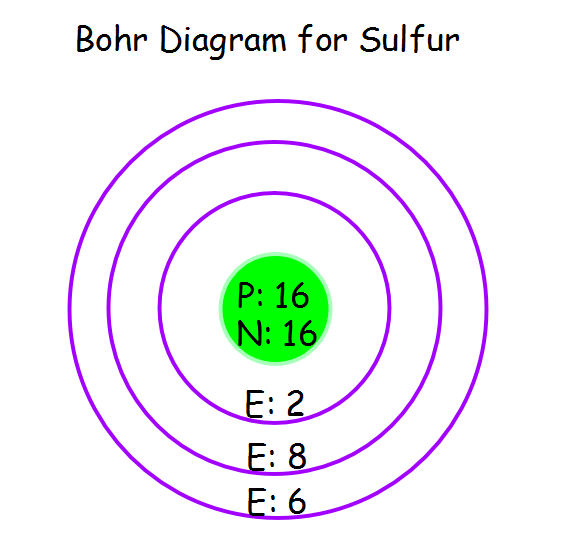
On the far left of Figure 3.6.1 3.6. 1 are the highest energy electromagnetic waves. These are called gamma rays and can be quite dangerous, in large numbers, to living systems. The next lower energy form of electromagnetic waves are called x-rays. Most of you are familiar with the penetration abilities of these waves. Bohr model of calcium: (CC BY-SA 2.0 uk;Greg Robson): Answer b. Bohr model of sulfur: (CC BY-SA 2.0 uk; Greg Robson). Valence electrons are located in the highest energy level of an atom. When drawing a Bohr diagram, the valence electrons would be present in the outermost electronic level/shell (furthest away from the nucleus). The electron configuration and the orbital diagram are: Following hydrogen is the noble gas helium, which has an atomic number of 2. The helium atom contains two protons and two electrons. The first electron has the same four quantum numbers as the hydrogen atom electron ( n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = +12 m s = + 1 2 ). The Bohr model of sulfur contains a nucleus having 16 protons and 16 neutrons in the center, and around this nucleus, there are three electron shells containing 16 electrons. Atomic Structure (Bohr Model) for Sulfur (S) Watch on Contents Steps #1 Write protons, neutrons, and electrons of sulfur atom #2 Draw nucleus of sulfur atom
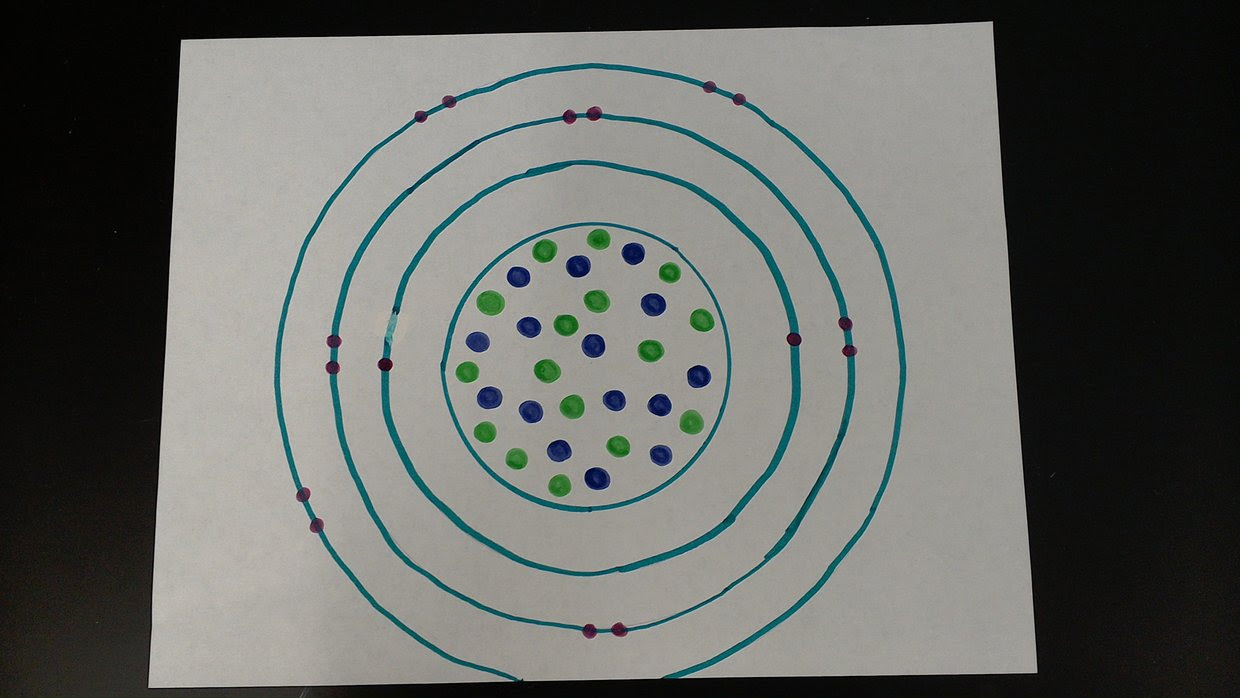
11+ Sulfur Bohr Diagram Robhosking Diagram
Bohr diagrams of various elements. Image credit: OpenStax Biology. Electron configurations and the periodic table. Elements are placed in order on the periodic table based on their atomic number, how many protons they have. In a neutral atom, the number of electrons will equal the number of protons, so we can easily determine electron number. The Bohr Model is a modification of an earlier atomic model, the Rutherford Model. The Bohr Model has an atom with a positively-charged nucleus surrounded by negatively-charged electrons that have circular, planetary-like orbits. Today, we know that the Bohr Model has some inaccuracies, but it's still used because of its simple approach to.
The sulfur atom has 16 protons, 16 neutrons and 16 electrons in three different energy levels, or orbits. Physics suggests that electrons do not physically exist as "points," but teachers use the Bohr atom model with fixed electrons as a way to simplify atomic structure. Creating the model requires the ability to cut with scissors and use glue. What is the Bohr diagram for sulfur? Bohr Model: In the Bohr model, electrons are confined to concentric spheres around the nucleus numbered as n =1, 2, 3,.. The sphere n = 1 can.
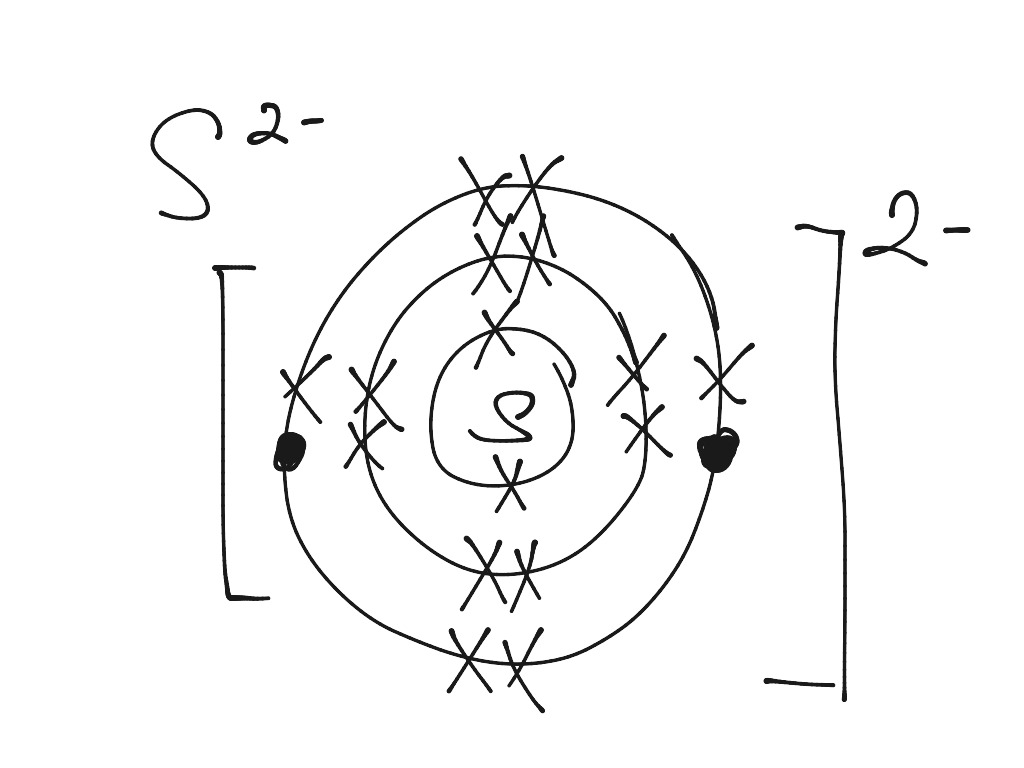
35 Bohr Diagram Of Sulfur Wiring Diagram List
The Bohr model of the hydrogen atom (Z = 1) or a hydrogen-like ion (Z > 1), where the negatively charged electron confined to an atomic shell encircles a small, positively charged atomic nucleus and where an electron jumps between orbits, is accompanied by an emitted or absorbed amount of electromagnetic energy (hν). The orbits in which the electron may travel are shown as grey circles; their. #1 Using aufbau principle #2 Using periodic table #3 From its Bohr model #4 From its orbital diagram Let's break down each method in detail. Using aufbau principle First, find electrons of sulfur atom Periodic table The atomic number of sulfur represents the total number of electrons of sulfur.



