Drawing the Bohr Model of Sulfur Sulfur is the 16 th element of the Periodic table. It belongs to Period 3 and group 16. The information that we can infer from the above-mentioned Sulfur box is as follows: • The atomic number of Sulfur is 16. • The electronic configuration of Sulfur is [Ne] 3s 2 3p 4. • The atomic symbol of Sulfur is S. In this video we'll look at the atomic structure and Bohr model for the Sulfur atom (S). We'll use a Bohr diagram to visually represent where the electrons a.

Sulfur Bohr Model — Diagram, Steps to Draw Techiescientist
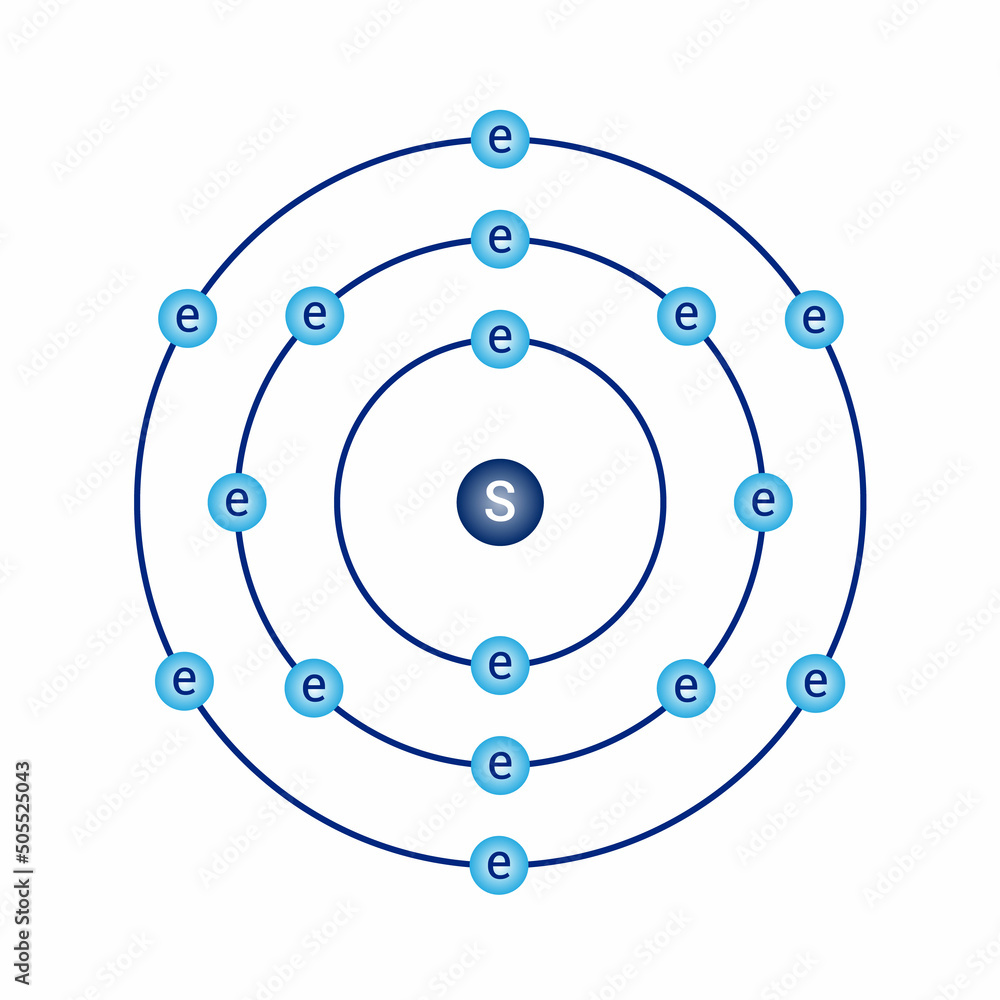
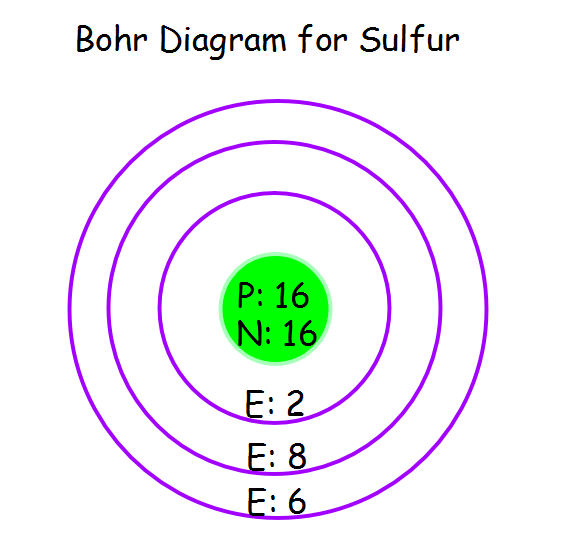
Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\) In Bohr's Model of the atom, electrons absorb energy to move to a higher level and release energy to move to lower levels. (CC BY-SA 3.0; Kurzon). The evidence used to support Bohr's model came from the atomic spectra. He suggested that an atomic spectrum is made by the electrons in an atom moving energy levels. The Bohr Model of Sulfur (S) has a nucleus that contains 16 neutrons and 16 protons. This nucleus is surrounded by three-electron shells named K-shell, L-shell, and M-shell. The outermost shell in the Bohr diagram of Sulfur contains 6 electrons that also called valence electrons. Page Contents show How to draw Bohr Model of Sulfur (S)? How to Draw the Bohr-Rutherford Diagram of Sulfur chemistNATE 247K subscribers Subscribe 415 32K views 4 years ago Sulfur / Sulphur has 2 electrons in its first shell, 8 in its second, 6 in. Bookshelves Physical & Theoretical Chemistry Supplemental Modules (Physical and Theoretical Chemistry) Electronic Structure of Atoms and Molecules
bohr model of the sulfur atom. electron structure of sulfur Stock
Bohr model of sulfur: (CC BY-SA 2.0 uk; Greg Robson). Valence electrons are located in the highest energy level of an atom. When drawing a Bohr diagram, the valence electrons would be present in the outermost electronic level/shell (furthest away from the nucleus). An atom can have from one to eight valence electrons. The Bohr model of the hydrogen atom (Z = 1) or a hydrogen-like ion (Z > 1), where the negatively charged electron confined to an atomic shell encircles a small, positively charged atomic nucleus and where an electron jumps between orbits, is accompanied by an emitted or absorbed amount of electromagnetic energy (hν). The orbits in which the electron may travel are shown as grey circles; their. Describe the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom Use the Rydberg equation to calculate energies of light emitted or absorbed by hydrogen atoms Sulfur Bohr model The Bohr model of sulfur contains a nucleus having 16 protons and 16 neutrons in the center, and around this nucleus, there are three electron shells containing 16 electrons. Contents Steps #1 Write protons, neutrons, and electrons of sulfur atom #2 Draw nucleus of sulfur atom #3 Draw 1st electron shell #4 Draw 2nd electron shell

Bohr Model Sulfur Atom Electron Structure Stock Vector (Royalty Free
The electron configuration and the orbital diagram are: Following hydrogen is the noble gas helium, which has an atomic number of 2. The helium atom contains two protons and two electrons. The first electron has the same four quantum numbers as the hydrogen atom electron ( n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = +12 m s = + 1 2 ). The Bohr Model is a modification of an earlier atomic model, the Rutherford Model. The Bohr Model has an atom with a positively-charged nucleus surrounded by negatively-charged electrons that have circular, planetary-like orbits. Today, we know that the Bohr Model has some inaccuracies, but it's still used because of its simple approach to.
Immediately before 1913, the Rutherford model conceived of an atom as consisting of a tiny positively charged heavy core, called a nucleus, surrounded by light, planetary negative electrons revolving in circular orbits of arbitrary radii. Britannica Quiz Matter and More Quiz How does Niels Bohr's atomic model work? Updated on January 27, 2020 The Bohr Model has an atom consisting of a small, positively charged nucleus orbited by negatively charged electrons. Here's a closer look at the Bohr Model, which is sometimes called the Rutherford-Bohr Model. Overview of the Bohr Model Niels Bohr proposed the Bohr Model of the Atom in 1915.
Bohr Diagram The Element Sulfur
In this state the radius of the orbit is also infinite. The atom has been ionized. Figure 5.4.2 5.4. 2 The Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom (a) The distance of the orbit from the nucleus increases with increasing n. (b) The energy of the orbit becomes increasingly less negative with increasing n. Physics suggests that electrons do not physically exist as "points," but teachers use the Bohr atom model with fixed electrons as a way to simplify atomic structure. Creating the model requires the ability to cut with scissors and use glue. Wear a pair of surgical gloves.




