The car battery diagram is a visual representation of the component s and connections within a car battery. It helps us understand how the battery functions and how it interacts with other parts of the vehicle's electrical system. The diagram typically includes the battery terminals, positive and negative cables, and various electrical connections. A conventional starter battery consists of 6 cells connected in series, each with a nominal voltage of 2 V, which results in a voltage of exactly 12.72 V when the battery is fully charged. The capacity and the cold start capability of the battery results from the number of plates per cell.
Batteries Part 2 Battery Types ilovefishing
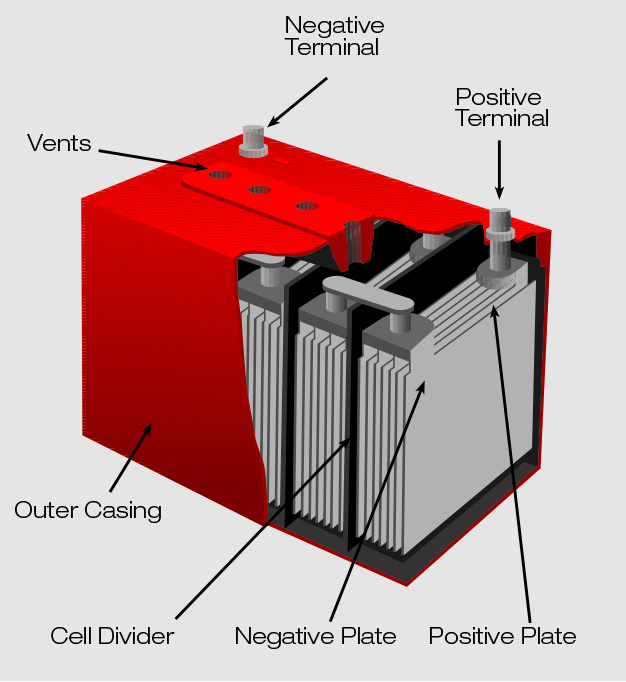
How Batteries Work Anatomy of Car Battery Battery Terminal/ Bushing: The terminals are connected to the positive strap and the negative strap of the end cells and are the interfacing point between the battery and the vehicle's electrical system. Battery Acid: The acid is a high-purity solution of sulfuric acid and water. SLI batteries constitute six galvanic cells - see the 'Anatomy of a car battery' diagram for details - laid out in series. Each cell delivers 2.1 volts of electromotive force that, when combined, produce a 12.6-volt SLI battery (commonly advertised as 12-volt). 2.1. Cold-Cranking Amperes (CCA) 2.2. Cranking Amperes (CA) 2.3. Ampere-Hour 2.4. Reserve Capacity 3. What Does a Battery Do in Your Car? 4. Is a Car Battery AC or DC? 5. What's the Difference Between AC and DC? 6. What are the Different Types of Car Batteries? 6.1. Lead-Acid (aka Flooded) 6.2. Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) An automotive battery, or car battery, is a rechargeable battery that is used to start a motor vehicle. Its main purpose is to provide an electric current to the electric-powered starting motor, which in turn starts the chemically-powered internal combustion engine that actually propels the vehicle.
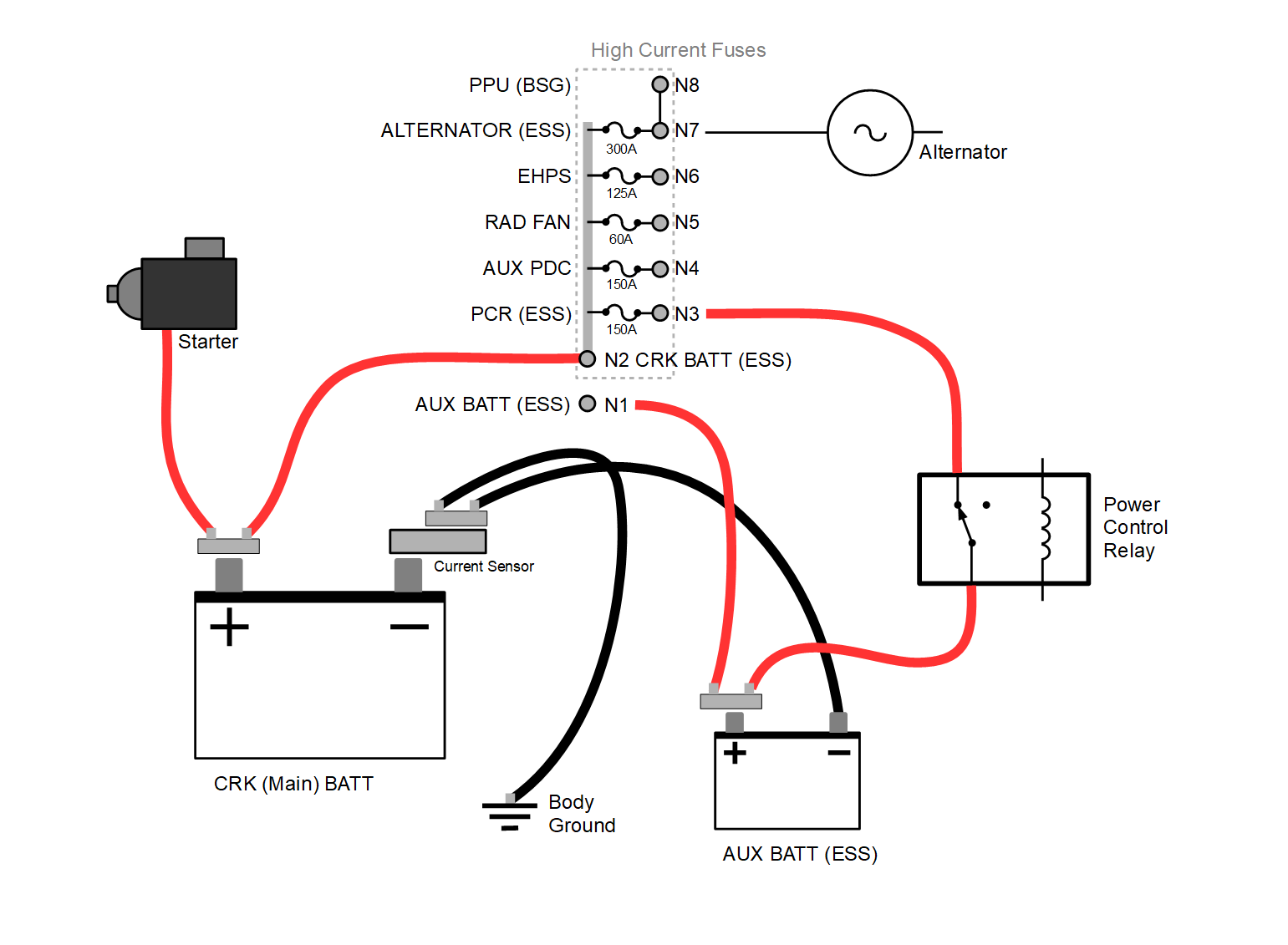
3.6L ESS Dual Battery Diagram 2018+ Jeep Wrangler (JL) News and Forum
Anatomy of a Battery Take a look at any battery, and you'll notice that it has two terminals. One terminal is marked (+), or positive, while the other is marked (-), or negative. In normal flashlight batteries, like AA, C or D cell, the terminals are located on the ends. Jan 24, 2023 0 In this article, we're going to take a look inside a car battery. We'll learn what's inside and how it works, and we'll also see some of the purpose's car batteries serve. Scroll to the bottom to watch the YouTube tutorial. Lets have a look at the main parts of a car battery and then we'll understand how it works. How does a car battery work, learn from the basics where we use and battery and how batteries work. With thanks to Squarespace for sponsoring this video. Go. Ah refers to the length of time the battery can deliver a continuous specified current - with the engine switched off a 70Ah battery would power your lights for longer than a 60Ah battery. CCA related to amount of amps the batteries can deliver at -17deg C for 30 seconds without dropping below 7.2v. This means that the more CCAs the better.

batteries Why grounding a battery to car chassis? Electrical
Sometimes also known as the "C20" rating, usually you'll see this on a deep-cycle battery sticker. It's a measurement of how much energy a battery can deliver continuously for 20 hours at 80. Measuring Battery Power Three traditional measures of battery power are listed right on the label. Cranking Amps (CA) - Indicates the number of amps a new, fully charged battery can deliver continuously at 32° F for 30 seconds while maintaining a voltage of at least 7.2 volts.
Battery Definition In general terms, a battery is a device that converts chemical energy into electricity. An automobile battery is a wet cell battery that contains actual energy that stores chemical energy and then transforms it into electrical energy for applications. Make sure not to accidentally touch either of the terminals with either of the connections to the car; the last thing you want is for sparks to appear. Use tape to block them off if you have to.

Car Battery Parts Diagram
3. Dry Cell Batteries. Dry cell batteries use a glass mesh to absorb the electrolyte, and operate much like wet cell batteries except the dry cell reduces spilling and allows the battery to be positioned in any orientation, which can be very useful when trying to fit a lot of power into a limited space. 4. Deep Cycle Batteries. Step 1: Find your vehicle's battery and locate the positive and negative terminals. Most cars have their battery under the hood. The positive terminal is marked with a "+," and the negative.




