The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. A mosque in Baku, Azerbaijan, near the shore of the Caspian Sea. The elongated sea sprawls for nearly 750 miles (1,200 km) from north to south, although its average width is only 200 miles (320 km). It covers an area of about 149,200 square miles (386,400 square km)—larger than the area of Japan—and its surface lies some 90 feet (27 metres.
Geopolitics in the Caspian Sea steel city scribblings
The Caspian Sea is an endorheic basin (drainage basin without an outflow). It covers a total surface area of about 386,400 km 2 and is about 1,200 km long and 320 km wide. The sea's surface is approximately 27 m below sea level and has a volume of 78,200 km 3. The Caspian Sea accounts for between 40-44% of the world's lacustrine waters. About the Caspian Sea Map with information about the Caspian Sea, showing adjoining countries with international borders and major cities. Measured by surface area, the Caspian Sea is Earth's largest inland water body, spanning about 371,000 square kilometers (143,200 square miles). Measured by economic, social, and biodiversity standards, it is priceless. Coordinates: 41°40′N 50°40′E The Caspian Sea is the largest lake on Earth by both area and volume. It has a surface area of 371,000 square kilometres (143,000 square miles). Its volume is 78,200 cubic kilometres (18,800 cubic miles). The Caspian has for 40 to 44% of the total lake waters of the world. [2]
The Caspian Sea is set to fall by 9 metres or more this century an
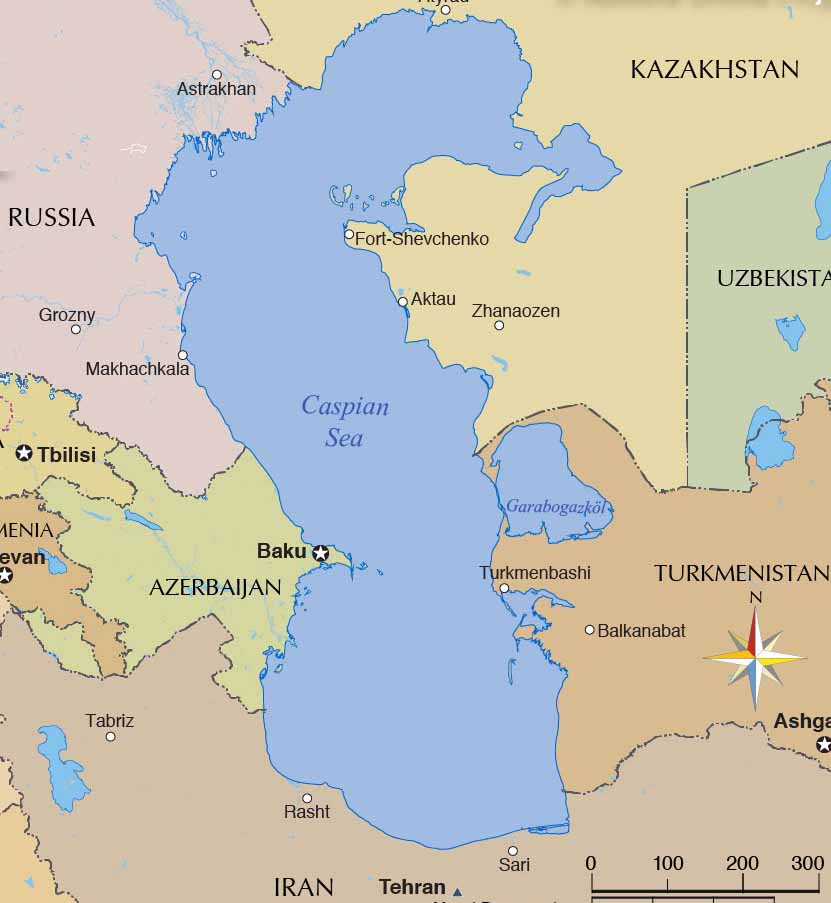
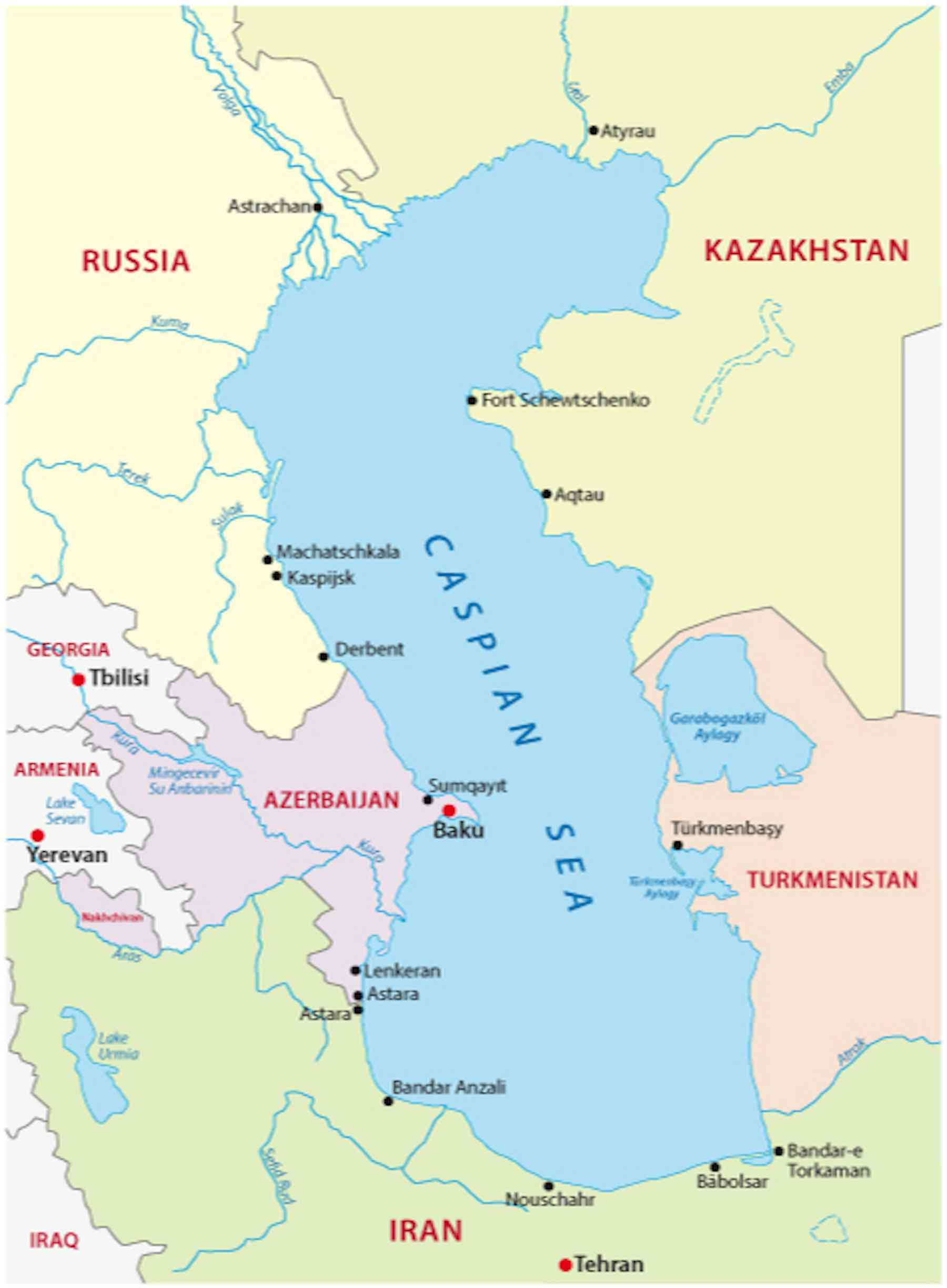
Caspian Sea, Inland salt lake between Europe and Asia, bordering Azerbaijan, Russia, Kazakhstan, and Iran. With a basin 750 mi (1,200 km) long and up to 200 mi (320 km) wide and an area of 149,200 sq mi (386,400 sq km), it is the largest inland body of water in the world. Though it receives many rivers, including the Volga, Ural, and Kura, the. Measured by surface area, the Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland water body. It covers roughly 371,000 square kilometers (143,200 square miles) and borders five countries. To the ancient Greeks and Persians, the lake's immense size suggested it was an ocean, hence its name. A large expanse of clear sky permitted an unobstructed view. The Caspian Sea lies to the east of the Caucasus Mountains and to the west of the vast steppe of Central Asia. World's largest lake. The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia, south of the fertile plains of Southern Russia in Eastern Europe, and north of the mountainous Iranian Plateau. It covers a surface area of 371,000 km2.
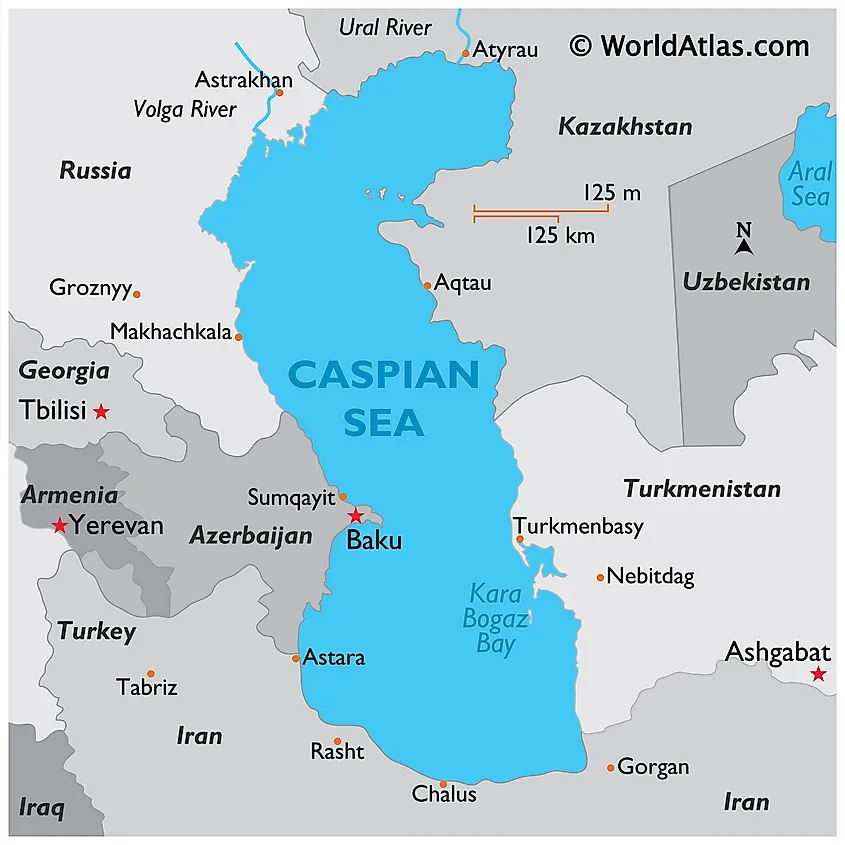
Caspian Sea WorldAtlas
Geography Caspian Sea's surface area is 378,000 km2 or 143,200 sq mi, and it boasts a volume of 78,200 km3. The lake is endorheic (meaning it has no outflows), and sits at the border between Europe and Asia. The countries on its shores are Kazakhstan to the NE, Russia to the NW, Azerbaijan to the West, Iran to the South and Turkmenistan to the SE. On a world map, the Caspian Sea would be located on the Eastern Europe and Central Asian border. Prior to the dissolution of the Soviet Union, only the Soviet Union and Iran bordered the.
Below, you'll find a Caspian Sea Region Map that shows the borders of the five countries that border the Caspian Sea as well as some major cities. Peter Hermes Furian/Shutterstock Caspian Sea region map Russia © Maykova Galina/Shutterstock Astrakhan, Russia Depth map of the Caspian Sea: the areas in red and yellow may disappear entirely. Allahdadi et al (2004) Yet people who lived beside the sea were able to overcome the swings. No human.
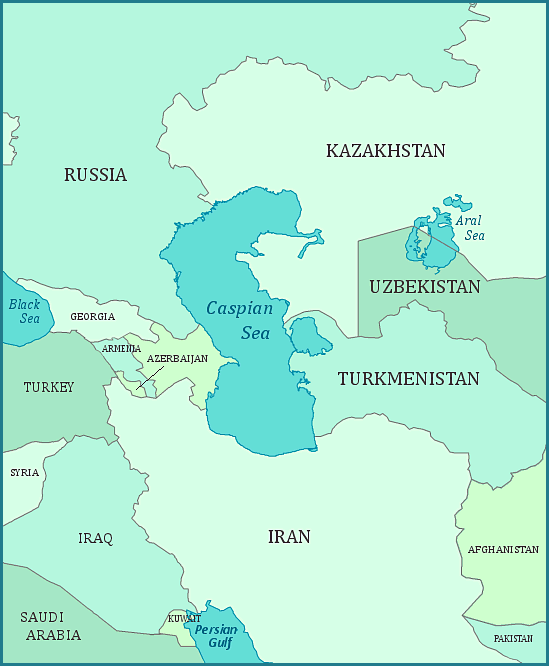
Map of the Caspian Sea
Caspian Sea. Sign in. Open full screen to view more. This map was created by a user. Learn how to create your own.. The Caspian Sea has a surface area of approximately 370,000-425,000 square kilometers, depending on estimates and changing sea levels from evaporation and inflow of water; its north to south length is approximately 1200 km, and its east-west width does not exceed 250 km. Its average depth is 184 m, with a maximum depth of 1025 m.




