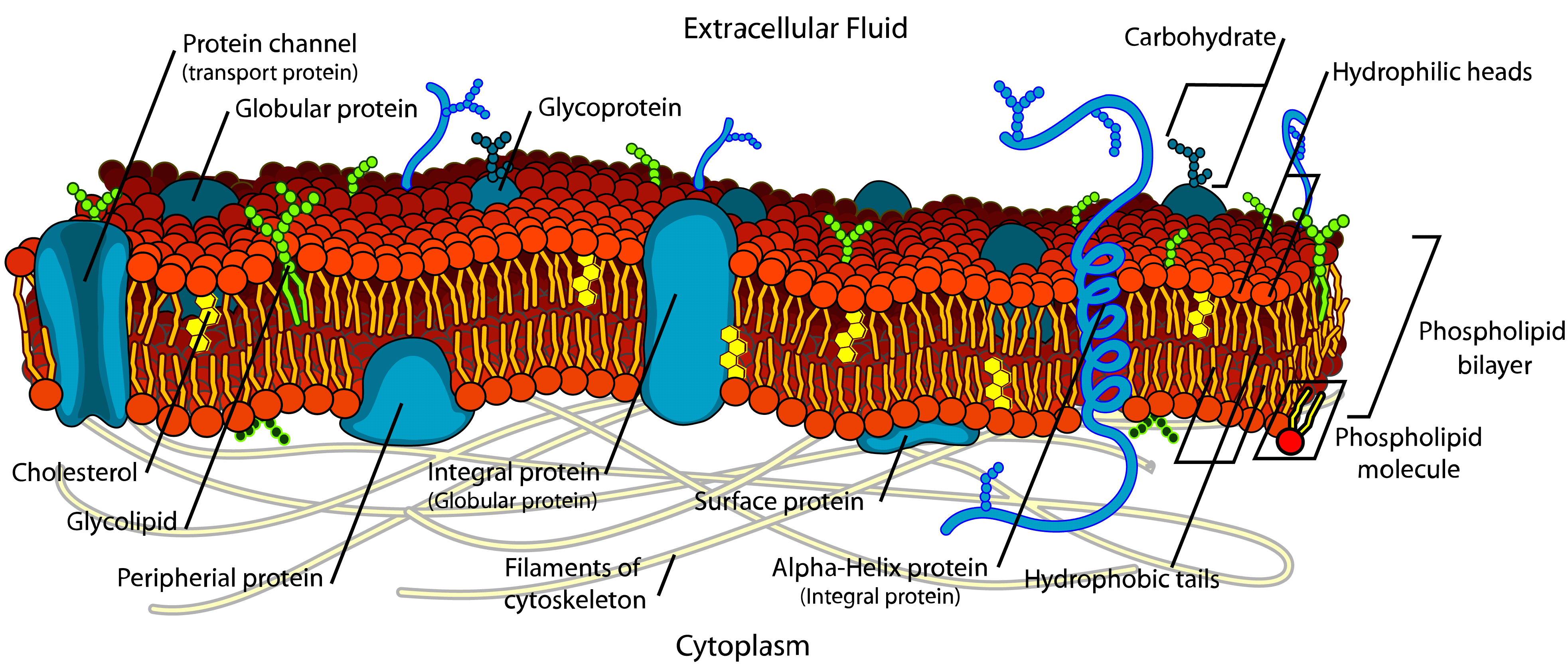
A diagram of a plasma membrane shows a phospholipid bilayer with 3 proteins embedded in the bilayer. One of the proteins is shown with a channel in it. The 3 proteins have lines with the label integral membrane proteins. On the inner side of the phospholipid bilayer is another protein that is positioned up against the inner portion of the bilayer. The plasma membrane is the border between the interior and exterior of a cell. As such, it controls passage of various molecules—including sugars, amino acids, ions, and water—into and out of the cell.. Diagram and micrograph of intestinal cells, showing the protruding "fingers" of plasma membrane—called microvilli—that contact the.
Function of the Plasma Membrane Biology Review (Video)
The fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane is how scientists describe what the cell membrane looks and functions like, because it is made up of a bunch of different molecules that are distributed across the membrane. If you were to zoom in on the cell membrane, you would see a pattern of different types of molecules put together, also known as. Like all other cellular membranes, the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins. The fundamental structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer, which forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments. In the case of the plasma membrane, these compartments are the inside and the outside of the cell. Proteins embedded within the phospholipid bilayer carry out the. For students doing IB Biology. Follow along and draw the plasma membrane.Music: Requiem for a fish by The Freak Fandango Orchestra http://www.jamendo.com/en. The addition of new membrane to the plasma membrane is usually coupled with endocytosis so that the cell is not constantly enlarging. Through these processes, the cell membrane is constantly renewing and changing as needed by the cell. Figure 3.1.9 - Exocytosis: Exocytosis is much like endocytosis in reverse. Material destined for export is.

AP Biology Blog
The plasma membrane of a cell is a network of lipids and proteins that forms the boundary between a cell's contents and the outside of the cell. It is also simply called the cell membrane. The main function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its surrounding environment. It is semi-permeable and regulates the materials that. Illustration of a eukaryotic cell membrane Comparison of a eukaryotic vs. a prokaryotic cell membrane. The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extracellular space).. Figure 3.5 Simple Diffusion across the Cell (Plasma) Membrane The structure of the lipid bilayer allows small, uncharged substances such as oxygen and carbon dioxide,. thus preventing them from drawing positive ions. The absence of ions in the secreted mucus results in the lack of a normal water concentration gradient. Thus, there is no. The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is a thin semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell. Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and the.
/plasma_membrane-58a617c53df78c345b5efb37.jpg)
Cell Membrane Function and Structure
Key Points. The principal components of the plasma membrane are lipids ( phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrates. The plasma membrane protects intracellular components from the extracellular environment. The plasma membrane mediates cellular processes by regulating the materials that enter and exit the cell. cell membrane, thin membrane that surrounds every living cell, delimiting the cell from the environment around it. Enclosed by this cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane) are the cell's constituents, often large, water-soluble, highly charged molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and substances involved in cellular metabolism.
University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee. In eukaryotic cells, the plasma membrane surrounds a cytoplasm filled with ribosomes and organelles. Organelles are structures that are themselves encased in membranes. Some organelles (nuclei, mitochondria, chloroplasts) are even surrounded by double membranes. Down. 1. negatively charged groups that form the outside of the phospholipid sandwich. 2. property of the plasma membrane that allows some substances into the cell and keeps others out. 4. main.
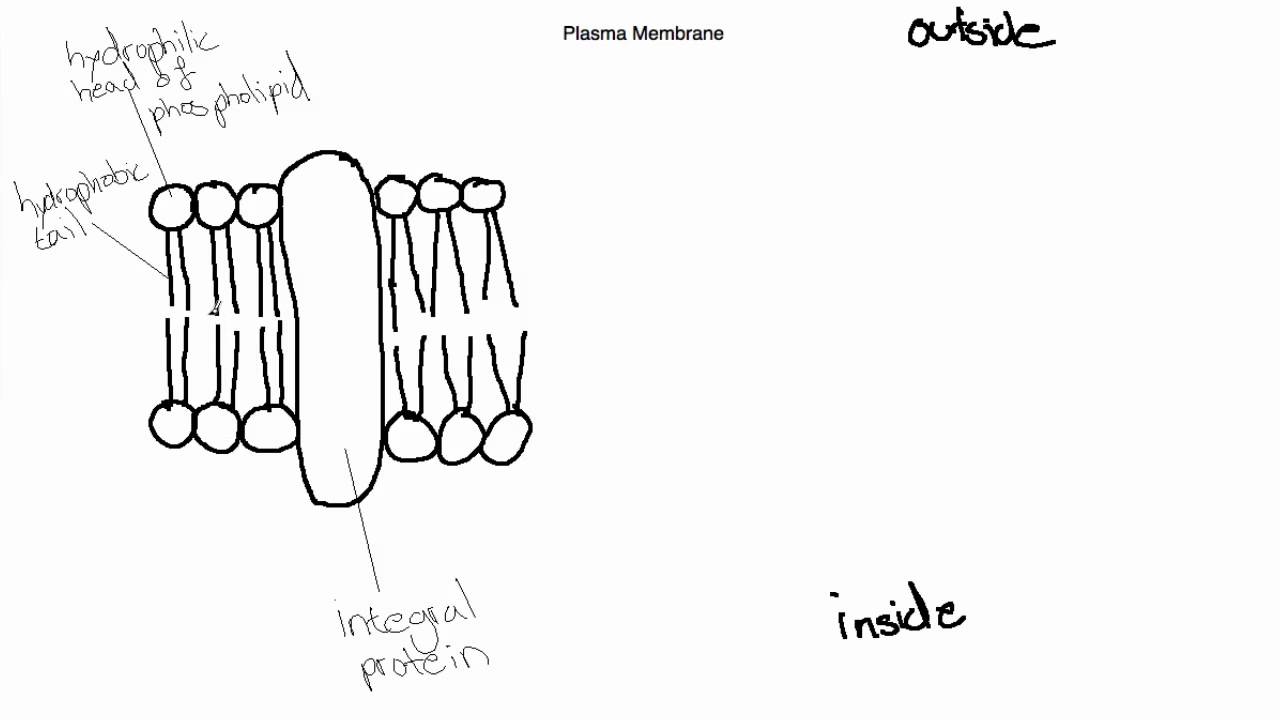
IB Biology Topic 2.4.1 Draw and Label the Plasma Membrane YouTube
Learn about the plasma membrane that surrounds all cells and keeps them alive!Transcript:All cells are completely surrounded by a membrane that separates the. The plasma membrane is a protective barrier that surrounds the interior of the cell. Also called the cell membrane, this structure is semi-porous and allows certain molecules in and out of the cell. It serves as a boundary by keeping the cell's contents inside and preventing them from spilling out. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have.


/plasma_membrane-58a617c53df78c345b5efb37.jpg)

