Digestive System Bones and Organs Bones and Organs At the height of the cavity is the liver, the body's largest organ. It acts like a filtration system. It rids the body of toxins and. The major organs of the abdomen include the small intestine, large intestine, and stomach. Together, these three turn nutrients into usable energy, as well as help dispose of solid waste. Major.

Major Organs In The Abdominal Cavity Elegant Of Human Abdominal Cavity
Digestive system diagram Yaja' Mulcare The digestive organs in the abdomen do not work alone. They depend on organs in the mouth and chest, such as the esophagus and tongue, to help chew,. Overview The digestive system is made up of the gastrointestinal tract-mouth, esophagus, stomach, small & large intestine, and rectum. What is the stomach? The stomach is a J-shaped organ that digests food. It produces enzymes (substances that create chemical reactions) and acids (digestive juices). Reading time: 17 minutes Recommended video: Surface anatomy of the abdomen and the lower extremity [13:14] Overview of the surface anatomy landmarks found in the abdomen and lower limbs. Abdomen 1/2 Synonyms: Abdominal region, Regio abdominis , show more. Hello there fellow anatomist and welcome to abdomen and pelvis 101! Digestive system: general diagram showing all the major structures included in this system: mouth, tongue, oral cavity, teeth, buccal glands, throat, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine (duodenum, jejunum and ileum), large intestine (colon, rectum, anal canal and anus), liver, gall bladder and pancreas.
5 THE ABDOMEN Basicmedical Key
The abdominal muscles assist in the process of respiration, protect the inner organs, provide postural support, and serve to flex, extend, and rotate the trunk of the body. [4] The four main abdominal muscle groups, from innermost to outermost, can be remembered by the mnemonic TIRE: Transversus abdominis, internal oblique, rectus abdominis. Urinary Tract Learning Objectives Locate the thoracoabdominal diaphragm and identify the three major foramina within it. Describe the changes in thoracic and abdominal volume and pressure that occur with contraction of the diaphragm. Describe the relative positions and general functions of the organs within the abdomen. Thoracoabdominal Diaphragm The abdomen contains organs involved in the gastrointestinal tract, including the oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, cecum, appendix, colon, rectum and the anal canal. The gastrointestinal tract is an organ system that enables us to ingest food, digest it, absorb it, and then expel the remaining waste as faeces. The abdomen contains many vital organs: the stomach, the small intestine (jejunum and ileum), the large intestine (colon), the liver, the spleen, the gallbladder, the pancreas, the uterus, the fallopian tubes, the ovaries, the kidneys, the ureters, the bladder, and many blood vessels (arteries and veins).

organs in left quadrant Google Search Nursing Student Tips, Nursing
The abdomen is a body cavity—a hollow, fluid-filled space that holds organs and other bodily structures. Organs inside the abdomen include: Digestive system organs like the stomach, small. The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates.The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso.The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity.In arthropods, it is the posterior tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or.
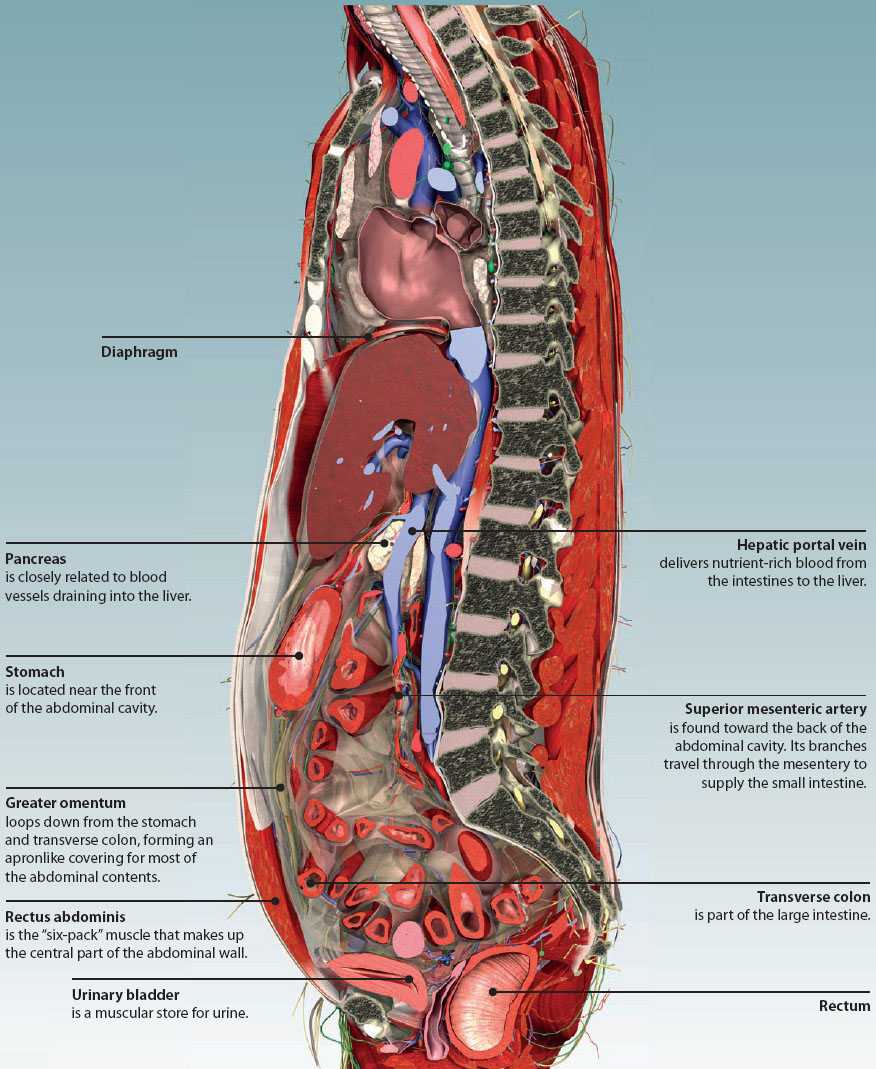
Picture of Abdomen The abdominal cavity is the part of the body that houses the stomach, liver, pancreas, kidneys, gallbladder, spleen, and the large and small intestines. The diaphragm marks the top of the abdomen and the horizontal line at the level of the top of the pelvis marks the bottom. abdominal cavity, largest hollow space of the body. Its upper boundary is the diaphragm, a sheet of muscle and connective tissue that separates it from the chest cavity; its lower boundary is the upper plane of the pelvic cavity. Vertically it is enclosed by the vertebral column and the abdominal and other muscles. The abdominal cavity contains the greater part of the digestive tract, the.

Abdomen Wikipedia, la enciclopedia libre
Stomach. Gaster. 1/4. Synonyms: Ventriculus. The stomach is an organ of the digestive system, specialized in the accumulation and digestion of food. Its anatomy is quite complex; it consists of four parts, two curvatures and receives its blood supply mainly from the celiac trunk. Innervation is provided via the vagus nerves and the celiac plexus . The abdominopelvic cavity is confined superiorly by the diaphragm and extends inferiorly into the pelvis. This cavity houses most of the organs of the digestive system and parts of the urogenital system. The vasculature of the abdomen and pelvis supplies the various organs and layers of tissue across many planes; it is among the most complex vascular systems in the body.




